Glossary
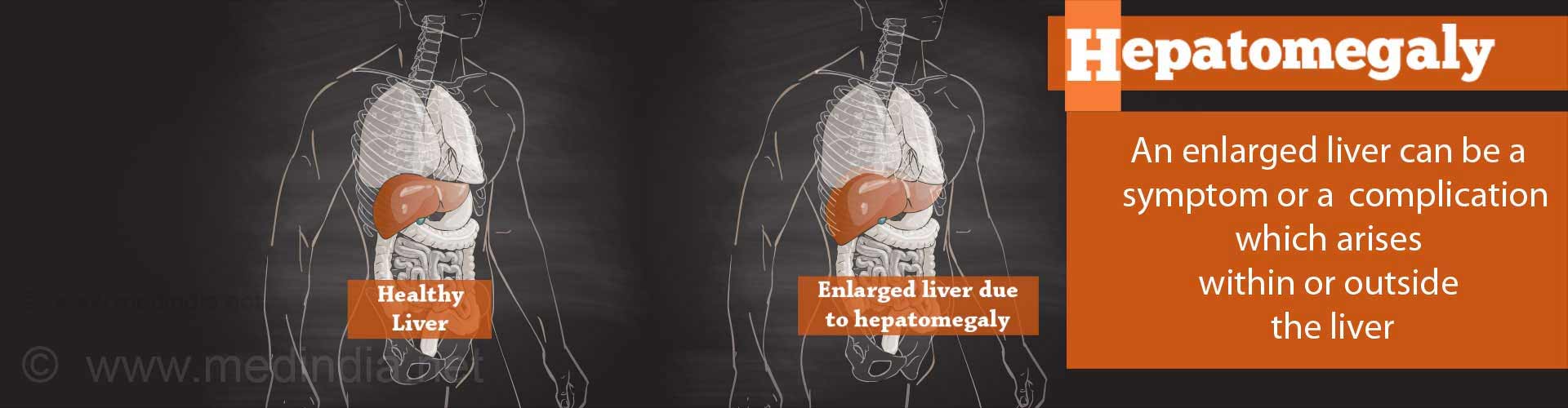
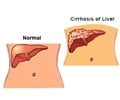
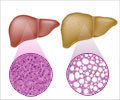
Cirrhosis: A type of chronic, progressive liver disease.Hepatomegaly: Enlargement of the liver.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A type of adenocarcinoma, the most common type of liver tumor.
Hepatoma: A liver tumor.
Liver: A large, glandular organ, located in the upper abdomen, that cleanses the blood and aids in digestion by secreting bile.
Liver Cancer: A disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the tissues of the liver.
Liver Failure: The final stage of liver disease, in which liver function becomes so impaired that other areas of the body are affected, most commonly the brain.
Liver Metastases: Cancer that has spread from the original (primary) tumor to the liver.
Liver Scan: An image of the liver created on a computer screen or on film. A radioactive substance is injected into a blood vessel and travels through the bloodstream. It collects in the liver, especially in abnormal areas, and can be detected by the scanner.
Liver transplantation: Surgery to replace a disease liver with a healthy one from a donor.