- The Liver - (https://www.cag-acg.org/images/publications/EN_GAST_13B.pdf)
- Hepatomegaly: causes and consequences - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7717896)
- Techniques: Liver & Ascites - (https://depts.washington.edu/physdx/liver/tech.html)
- Sometimes Drugs and the Liver Don't Mix - (https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/sometimes-drugs-and-liver-dont-mix)
- Drug-induced liver injury. - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000226.htm)
- Liver Cirrhosis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2271178/)
- Hepatomegaly - (https://healthtools.aarp.org/articles/#/health/hepatomegaly)
- Liver - Fatty Liver Disease - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/liver-fatty-liver-disease)
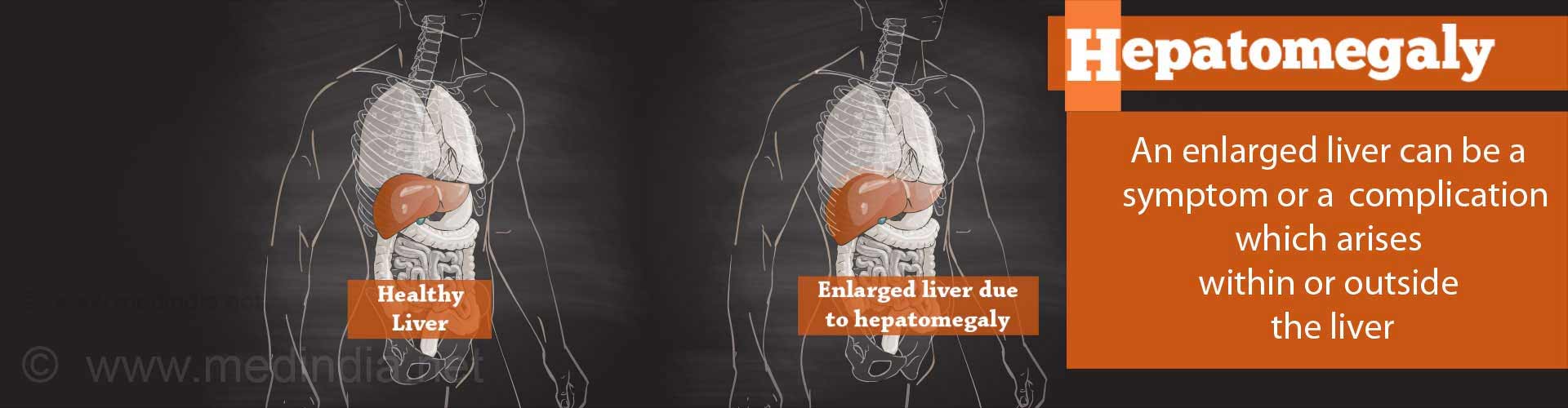
Enlarged Liver or Hepatomegaly
An enlarged liver in medical terms is called hepatomegaly and means an increase in the size of the liver. "Hepatic" refers to the liver and "megaly" refers to an increase in size.
The liver is largest organ of the human body and situated in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. It weighs a little less in women than men. The weight is 1200 to 1400 g in the adult woman and 1400 to 1500 g in the adult man. It is vital organ in the human body. It is responsible for the digestion of fats (broken down by bile secreted by liver cells), storage of glucose in the form of glycogen and metabolism of the pharmaceutical drugs that we consume.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
The Liver
Go to source)
The factors that affect the size of the liver are age, gender, body weight and body shape. A liver that is 3 centimeters larger or smaller is still considered normal. The normal liver can sometimes be felt under the right rib cage and is normally soft and smooth with no irregularities.
Diseases that cause the liver to get enlarged have to be treated immediately since they interfere with the liver’s functionality.
What are the Causes of Hepatomegaly?
Some of the known causes of hepatomegaly are(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Drug-induced Liver Injury.
Go to source, 3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hepatomegaly: Causes and Consequences
Go to source)
- Hepatitis or inflammation of liver due to hepatitis A, B, C, D & E viruses.
- Excessive intake of alcohol - Women are twice as likely as men to develop alcoholic hepatitis. Also intake of alcohol other than meal times triples this risk.
- Malaria and Kala Azar are illnesses caused by protozoa and are a common cause of liver enlargement in India.
- Liver Cancer can originate primarily in the liver as:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma which affects the liver cells [hepatocytes]; this is the commonest form of liver cancer.
- Cholangiocarcinoma or bile duct cancer accounts for 10-15 % of all liver cancers.
- Hepatoblastoma, a rare type of liver cancer that is mostly found in children less than 3 years of age.
- Or it can be cancer metastasized from other parts of the body as in leukemia [blood cancer], lymphoma [a type of white blood cell] and multiple myeloma [cancer of plasma cells].
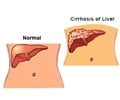
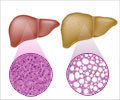
- Cirrhosis of liver is caused by long-term exposure to toxins such as alcohol or viral infections.
- Fatty liver disease can be alcohol related or non alcohol related [NAFLD].
- Blood circulatory problems like congestive cardiac failure [CCF] or obstruction in the veins that drain the liver.
- Liver abscess due to amebiasis [caused by protozoa Entamoeba histolytica] or other infections.
- Viral infections such as infectious mononucleosis and yellow fever.
- Drug-induced causes such as consuming acetaminophen [tylenol], pain relievers such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen, and cholesterol lowering drugs like statins. Natural products which are toxic to the liver include black cohosh, comfrey tea, kava, skullcap, and yohimbe. Even vitamin supplements and dietary supplements in excess can be harmful. Too much iron or vitamin A [>5000 units/day] can result in significant liver damage.
- Exposure to toxic agents such as carbon tetra chloride [a dry cleaning solvent agent], chloroform, vinyl chloride (used to make plastics), and polychlorinated biphenyls.
- Genetic diseases such as hemochromatosis [iron storage disease], Wilson's disease [copper storage disease], glycogen storage diseases, and Gaucher’s disease [fat storage disease].
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hepatomegaly?
Symptoms of hepatomegaly are serious and have to be evaluated as soon as possible.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Sometimes Drugs and the Liver Don't Mix
Go to source)
- Jaundice [yellowing of the skin and eyes]
- Fever, if infection is the causative factor
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in abdomen and feeling of distension
- Reflux of bile
- Heartburn
- Itching
- Loose pale colored stools.

How do you Diagnose Hepatomegaly?
The doctor will first ask for the medical history and conduct a physical examination to check the liver. Palpation and percussion in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen give a rough estimate of the size and texture of liver. Further tests might be suggested if an enlarged liver is suspected.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Techniques: Liver & Ascites
Go to source)
- Raised levels of liver enzymes. Also known as liver function tests (LFT), they monitor levels of ALT [alanine aminotransferase], AST [aspartate aminotransferase], alkaline phosphatase, albumin and bilirubin. Raised levels of ALT and AST suggest liver disease, whereas high levels of alkaline phosphatase indicate an obstruction in the bile flow. Raised levels of bilirubin [a yellow substance formed by breakage of red blood cells in liver] and albumin [a protein made in liver] indicate that the liver is not functioning properly.
- Blood tests will measure any raised levels of antibodies in hepatitis A, B, C infections and also prothrombin time [PT] which is a blood clotting factor made by liver.
- Abdominal ultrasound helps to determine size of liver, dilatation or narrowing of bile duct or blood vessels, tumors and abscesses.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan gives detailed images of the internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body.
What are the Complications of Hepatomegaly?
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent any complications that could be fatal. An enlarged liver may lead to inflammation and cirrhosis if there is regular alcohol intake, poor control of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and chronic viral infections.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Liver Cirrhosis
Go to source)
- Liver failure.
- Cirrhosis or replacement of normal liver tissue by scar tissue.
- Encephalopathy, which includes mental confusion, slurry speech, seizures, sleepiness, and coma.
- Bleeding problems due to insufficient amounts of clotting factors being produced by liver.
How do you Treat Hepatomegaly?
Treatment will vary according to the underlying cause of hepatomegaly.(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hepatomegaly
Go to source)
- Hepatitis B is treated with drugs such as adefovir dipivoxil, entecavir, lamivudine, and interferon.
- Hepatitis C is treated with drugs such as boceprevir, daclatasvir, interferon, ribavirin, and sufosbuvir.
- Hepatitis A & E are self limiting diseases. Adequate rest, healthy nutrition and abstaining from alcohol are usually advised.
- If the liver enlargement is alcohol related then complete abstinence from alcohol, adequate rest, healthy and low fat diet are recommended.
- Liver transplant is an option in cases of liver failure.
- Surgical resection of the diseased liver part is an option in liver disease.
- Chemotherapy and radiation are treatment options for liver cancer.
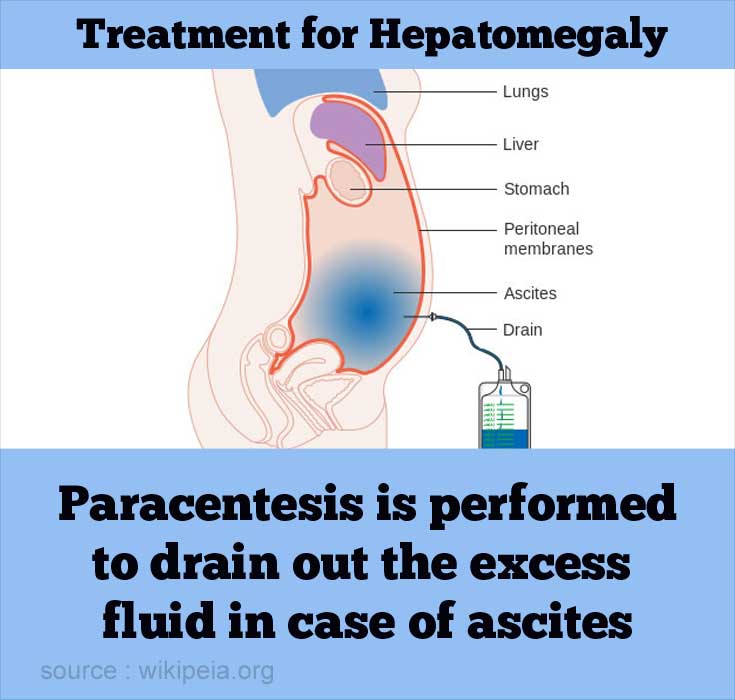
- In cases of ascites [accumulation of fluid in abdomen], paracentesis is performed to drain the excess fluid.
- Homeopathic medicines such as Chelidonium majus, Cardus marianus, Lycopodium clavatum have proven beneficial in treating liver inflammation.
- Lifestyle changes like maintaining healthy weight in obese people and keeping normal sugar levels have to be followed.
How do you Prevent Hepatomegaly?
Hepatomegaly can be prevented by:(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Liver - Fatty Liver Disease
Go to source)
- Stopping intake of alcohol.
- Keeping blood sugar under control.
- Preventing viral infections hepatitis A and B by vaccination.
- Practicing safe sex.
- Eating healthy. Avoid white flour, sugar, and white rice. Include whole wheat flour, brown rice, and multigrain flour in the diet. Also include plenty of vegetables [cooked and raw], and proteins from eggs, lean meat, fish, nuts, legumes, seeds, greek yogurt in the daily diet.
- Including healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil for cooking and salad dressings. Also eat a low fat diet. Avoid saturated fats /trans fats.
- Keeping weight under check. Avoid drastic weight fluctuations.
- Exercising regularly.
- Avoiding contact with toxic chemicals.
- Choosing herbal medicines and dietary supplements carefully.