- You and your hormones- An education resource from the society for endocrinology - (http://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/testosterone.aspx)
- Testosterone and Its Benefits to Women- by Brock Smith, RPh - (http://www.project-aware.org/Resource/articlearchives/testosterone.shtml)
- Hormone Health Network from the Endocrine Society- Testosterone and Androgens - (https://www.hormone.org/hormones-and-health/hormones/testosterone)
- Signs of High Testosterone in Women- Medically Reviewed by Barb Depree, MD - (https://www.healthywomen.org/content/article/signs-high-testosterone-women)
- The Reality behind Testosterone Therapy-Sheryl Kraft - (https://forevher.healthywomen.org/treatment/the-reality-behind-testosterone-therapy/)
- Testosterone side effects - (https://www.recallreport.org/side-effects/testosterone/)
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a male sex hormone or androgen that stimulates development of secondary sexual characteristics. This anabolic steroid hormone is produced mainly in the testes, but also in the ovaries, fat cells and adrenal cortex. Although considered a male hormone, androgens play an important role in a woman's reproductive cycle and general health. Both men and women have similar sex hormones but in varying amounts.
Low levels of testosterone can cause symptoms of male menopause such as a low sex drive, decrease in energy levels and erectile dysfunction at around fifty years of age.
What are the Causes of High Testosterone Level In Women?
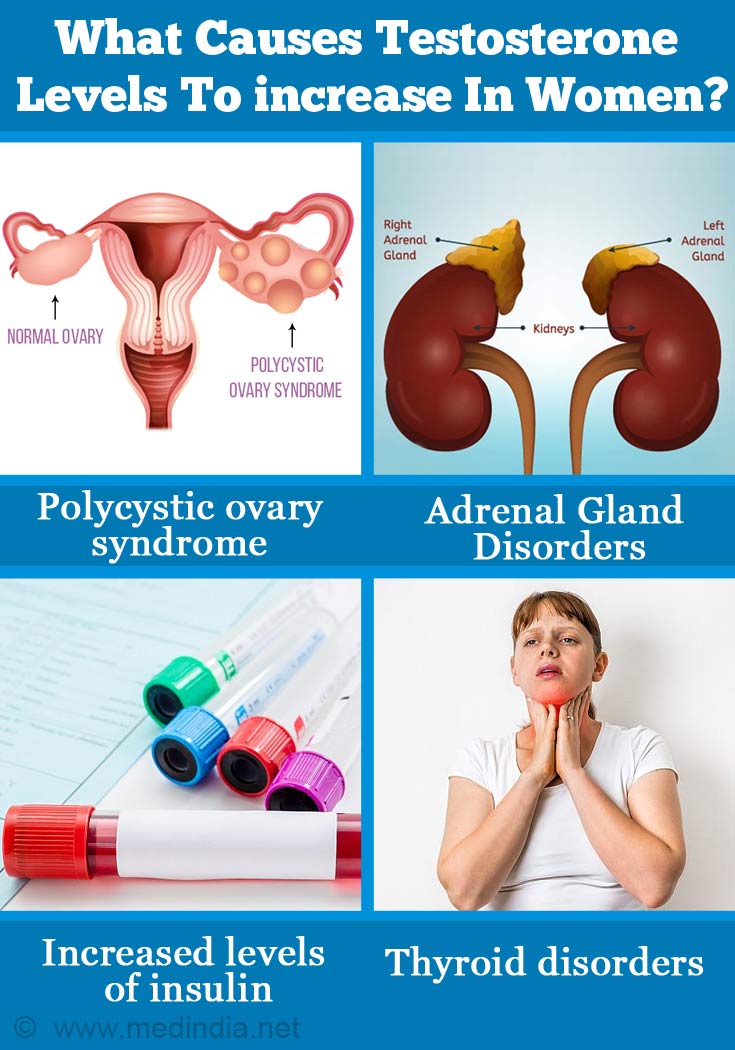
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) - This is one of the commonest causes of high testosterone levels. It is associated with irregular periods, unwanted body hair growth, and enlarged ovaries that may not function properly.
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) - This is a disorder of the adrenal glands which results in an excessive production of androgen.
- Hyperinsulinemia (increased levels of insulin) - Insulin encourages the ovaries to produce more testosterone and can lead to a significant increase in testosterone in the bloodstream.
- Thyroid disorders - When thyroid function slows down, the sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) levels fall and result in higher levels of testosterone.
- Stress.
- Lack of exercise. Exercise helps keep insulin levels in check by sensitizing your cells to insulin, thus lowering testosterone levels in the body.
- Obesity.
- Tumors of ovaries or adrenal glands secreting testosterone
- Medications - Danazol (used to treat endometriosis), corticosteroids, fluoxetine
What are Symptoms and Signs of High Testosterone Level In Women?
Excess testosterone can cause several undesirable side effects such as
- Menstrual abnormalities or absence of periods
- Excess body hair (hirsutism), specifically hair growth on chin or upper lip.
- Acne especially around jaw or chin around ovulation cycles
- Male pattern baldness
- Enlarged clitoris
- Increase in muscle mass
- Changes in body shape
- Decrease in breast size
- Deepening of the voice
- Low sex drive (possibly due to low self-esteem and issues with body image)
- Changes in mood
- Infertility

What are the Complications of High Testosterone Level in Women?
Some of the complications associated with elevated testosterone levels in women include
- Emotional distress, anxiety or depression
- Low self esteem
- Infertility
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypercholesterolemia
How do you Diagnose High Testosterone Level In Women?
High testosterone levels are mostly diagnosed by taking a clinical history, family history and performing a physical examination. Details about the onset of menses, menstrual history, reproductive history and onset of high testosterone symptoms are noted.
A laboratory test can also be done to evaluate levels of sex hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin, and sex hormone binding globulins (SHBG).

Treatment for high testosterone depends on the cause and includes both medication and lifestyle changes.
- During menopause due to reduced estrogen levels the testosterone levels may rise. These are best treated with a combination of lifestyle changes, natural treatment and
hormone replacement therapy (HRT) . - In case of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), the treatment is primarily based on the treatment of symptoms such as acne, hair growth or irregular periods. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians low dose birth control pills are the best choice. You can use androgen deprivation therapy to block the effect of testosterone with antiandrogens such as spironolactone or medications that decrease insulin production such as metformin.
- If the high testosterone is due to congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), glucocortcoids are used to treat the low cortisol production and the corresponding increase in production of androgens by the adrenal glands.
- Making certain lifestyle changes such as a regular exercise or weight loss program is also beneficial.
- Cosmetic procedures such as bleaching the facial hair, shaving, using products such as benzoyl peroxide to manage oily skin or advanced procedures such as electrolysis and laser therapy are preferred by some women.
- Herbal remedies made from spearmint, peony, licorice, saw palmetto, chaste berries and black cohosh have proven anti androgenic properties.






