How can Pre-eclampsia be Treated?
The goal of the treatment of pre-eclampsia is to manage the condition until 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Delivery is the most preferred treatment if the fetus has grown enough to survive outside the womb. A
Emergency delivery of the baby may be necessary if any of the following conditions occur-
- Destruction of red blood cells, known as hemolysis.
- Elevated levels in liver function tests.
- Falling platelet count.
- Pain in the right upper abdomen.
- Persistent and severe headache.
- Signs of kidney failure.
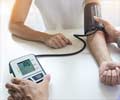
- Very high blood pressure for more than 24 hours
If delivery is not possible because it is early pregnancy, steps should be taken to manage pre-eclampsia until the baby can be delivered. These steps include-
- Bed rest

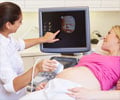
- Careful monitoring of blood pressure, weight checks, and regular urine tests for protein will help timely treatment.
- Reducing the blood pressure with medicines (anti-hypertensives)
- In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
- Dietary changes- Reducing daily salt intake helps in long term to reduce the blood pressure. Drink plenty of fluids.
- Other medicines- Corticosteroids can be prescribed after 24 weeks of pregnancy to improve the liver and platelet function to help prolong the pregnancy. Corticosteroids also help the baby’s lungs to become mature. An anticonvulsant like magnesium sulfate can be given to prevent seizures in severe pre-eclampsia.