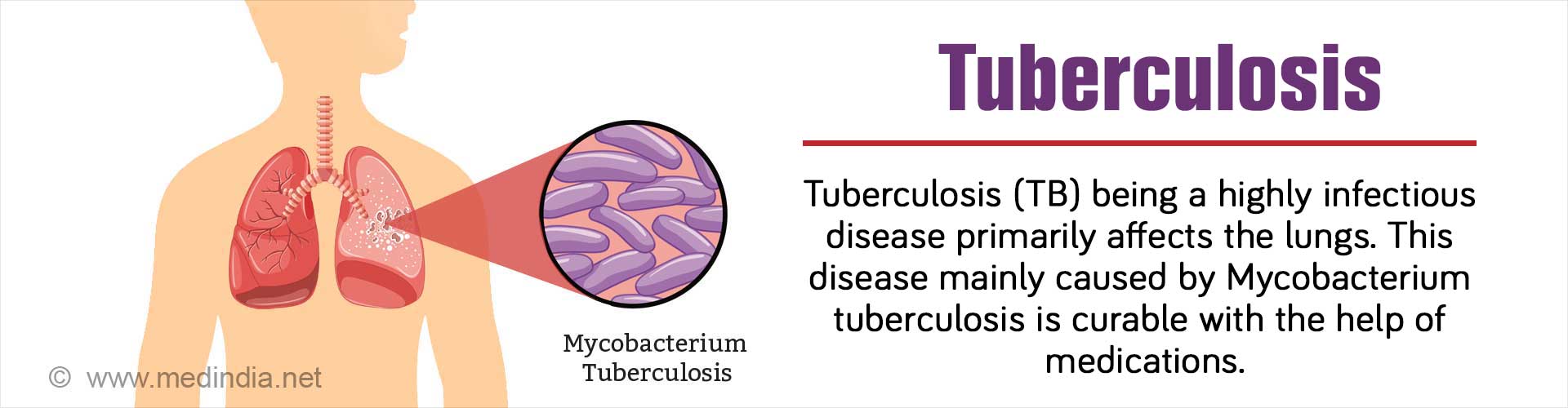
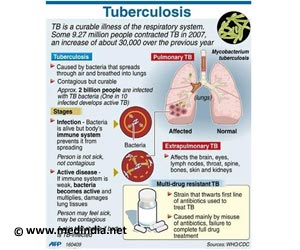
How can Tuberculosis be Treated?
Tuberculosis can be treated by taking a combination of antibiotics (usually 3-5 drugs) for a period of 6-8 months.
The treatment of tuberculosis depends on whether it is active or latent. Latent tuberculosis is treated with isoniazid (INH) for 6-12 months. Drugs that may be used to treat active Tuberculosis include-
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
- Amikacin
- Ethionamide
- Moxifloxacin
- Para-aminosalicylic acid
- Streptomycin
The treatment has to be taken regularly for the prescribed duration. A good nutritious diet is helpful. A kerchief or a bit of cloth or tissue should be used while coughing or sneezing; and sputum should not be spit anywhere. Instead the sputum should be collected in a container and buried or burnt.
The common side-effects of anti-Tuberculosis drugs are-
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Vision disturbance
- Orange or brown colored urine and/or tears
- Skin rash
- Dizziness
- Jaundice (rare)
Vaccination against Tuberculosis- BCG vaccination has to be taken under the Universal Immunization Program. BCG vaccine is given soon after birth and protects against developing the severe forms of TB in childhood but does not protect adults from developing the adult forms of pulmonary TB.
A new tuberculosis vaccine, called H56(January 23,2011), has been more effective in preventing TB in infected mice than the current vaccine. The vaccine is still undergoing clinical trials.