Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis is made with the help of physical examination, family history, laboratory investigations and radiological tests.
The diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis is made with the help of the following:
Physical examination -
A thorough physical examination is done to check for tenderness and pain sensitive areas along the back and pelvic region. During the examination, the mobility of the individual is also assessed.
Family History -
A past history of iritis and intestinal disorders like Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis are checked for as these are commonly found in association with ankylosing spondylitis.
Laboratory investigations -
- Blood test- Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and presence of anemia are associated with ankylosing spondylitis. A blood test to detect human antigen of type HLA-B27 is also advised.
Radiological Tests -
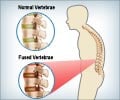
- X-Ray examination reveals hazy joint margins with widened joint spaces. In advanced stages, the spinal bones are fused together and the X-ray of the spine has a bamboo like appearance.
- MRI of the spine is also used to diagnose the condition.