Diagnosis of Cystitis
Primary diagnosis of cystitis is based on the signs and symptoms followed by urine tests and culture to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of cystitis is made through:
- History- Most often, cystitis can be diagnosed with the help of a detailed history given by the patient.
- Urinalysis- A urine specimen is tested with the help of a testing dip-stick, or by a laboratory, using a microscope. Urine culture and sensitivity test allows the doctor to find out which antibiotic will best eradicate the infection.
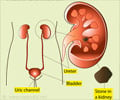
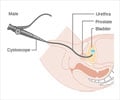
- Ultrasound or X-ray of the kidney and bladder- These tests can be performed to rule out any possible underlying cause for repeated urinary infection (after one attack in a male or multiple attacks in a female). They include ultrasound scans and X-ray of the kidneys and bladder using a dye injected into the blood vessels (intravenous urography), or looking into the bladder using an endoscope (cystoscopy).