- What is hydrops fetalis - (https://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions/hydrops-fetalis)
- Hydrops Fetalis - (https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=hydrops-fetalis-90-P02374)
About
Hydrops fetalis, often referred to as hydrops, is a serious condition characterized by the accumulation of excessive fluid in a baby's tissues and organs, leading to significant swelling (edema). This condition can manifest as a result of various underlying issues, including homozygous alpha thalassemia, a severe fetal disease that impairs the production of red blood cells.
Did You Know?
Nearly 50% of babies born with hydrops fetalis do not survive. #medindia #healthcare #hydropsfetalis
Although less common in the United States due to advancements in preventing hemolytic diseases, hydrops fetalis remains a life-threatening condition. Nearly 50% of affected infants do not survive(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is hydrops fetalis
Go to source).
Types of Hydrops Fetalis
There are two primary types of hydrops fetalis:
Immune Hydrops Fetalis:This type occurs when the mother's immune system attacks the baby's red blood cells, leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn. It represents the most severe complication associated with this condition.
Non-Immune Hydrops Fetalis: This more common type arises when various diseases or complications interfere with the baby's fluid regulation. Conditions such as alpha thalassemia major, where the fetus cannot produce adequate red blood cells, can lead to this type of hydrops.
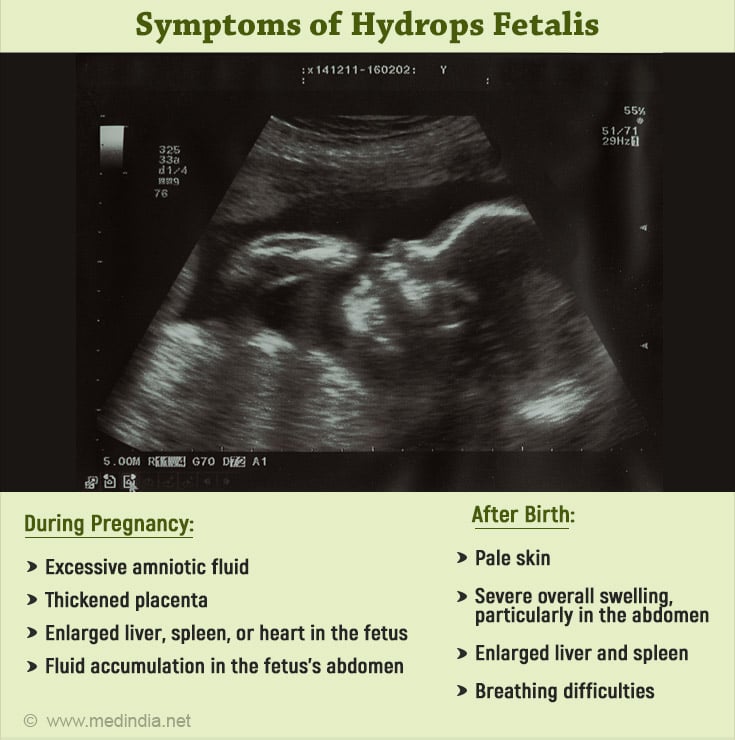
Symptoms of Hydrops Fetalis
Hydrops fetalis can be detected both during pregnancy and after birth. Key symptoms include:
During Pregnancy:
- Excessive amniotic fluid
- Thickened placenta
- Enlarged liver, spleen, or heart in the fetus
- Fluid accumulation in the fetus's abdomen
After Birth:
- Pale skin
- Severe overall swelling, particularly in the abdomen
- Enlarged liver and spleen
- Breathing difficulties
Causes of Hydrops Fetalis
A range of conditions can lead to hydrops fetalis, including:
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn
- Severe anemia
- Infections present at birth
- Congenital heart or lung defects
- Chromosomal abnormalities and birth defects
- Liver disease
Diagnosis of Hydrops Fetalis
Diagnosing hydrops fetalis involves several key tests to confirm the presence of the condition and identify its cause:
Ultrasound: This imaging technique provides detailed pictures of the baby’s organs and tissues, helping to identify fluid accumulation and other abnormalities.
Fetal Blood Sampling: A procedure that involves taking a small sample of the baby’s blood from the umbilical cord to test for anemia, infections, or other blood disorders.
Amniocentesis: A diagnostic test where a sample of amniotic fluid is extracted from the uterus to analyze for genetic abnormalities, infections, or other factors contributing to hydrops.
Additional diagnostic methods may include fetal echocardiography to assess heart function and genetic testing to determine any chromosomal abnormalities.
Treatment of Hydrops Fetalis
Treatment for hydrops fetalis is tailored to address the underlying cause of the condition. Approaches vary depending on whether the diagnosis is made before or after birth(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hydrops Fetalis
Go to source).
Prenatal Treatment
Medications: Certain medications may be administered to manage conditions such as maternal infections or severe anemia.
Intrauterine Procedures: In cases where the cause is treatable in utero, procedures such as intrauterine transfusions can be performed to address blood cell deficiencies or other issues.
Postnatal Treatment
Oxygen Therapy and Mechanical Ventilation: These interventions are used to support breathing if the baby has difficulty breathing due to fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Fluid Drainage: Excess fluid around the lungs and abdomen can be removed using a needle, which helps relieve pressure and improve respiratory function.
Diuretics: Medications may be used to help the kidneys eliminate excess fluid from the body.
Supportive Care: Comprehensive care in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) may include monitoring vital signs, providing nutritional support, and addressing any complications that arise.
The effectiveness of these treatments often depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for optimizing outcomes and managing any long-term effects.
Prognosis of Hydrops Fetalis
The prognosis for hydrops fetalis varies. The condition can severely impact organ systems, with survival rates for affected babies often dependent on the cause and the effectiveness of treatment.