Glossary
Audiologist: Health care professional who is trained to evaluate hearing loss and related disorders, including balance (vestibular) disorders and tinnitus, and to rehabilitate individuals with hearing loss and related disorders.Auditory Nerve: Eighth cranial nerve that connects the inner ear to the brainstem and is responsible for hearing and balance. Auditory Perception - Ability to identify, interpret, and attach meaning to sound.
Auditory Prosthesis: Device that substitutes or enhances the ability to hear.
Augmentative Devices: Tools that help individuals with limited or absent speech to communicate, such as communication boards, pictographs.
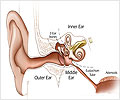
Cochlea: Snail - shaped structure in the inner ear that contains the organ of hearing.
Cochlear Implant: Medical device that bypasses damaged structures in the inner ear and directly stimulates the auditory nerve, allowing some deaf individuals to learn to hear and interpret sounds and speech.
Ear Wax: Yellow secretion from glands in the outer ear (cerumen) that keeps the skin of the ear dry and protected from infection.
Hearing: Series of events in which sound waves in the air are converted to electrical signals, which are sent as nerve impulses to the brain, where they are interpreted.
Hearing Aid: Electronic device that brings amplified sound to the ear. A hearing aid usually consists of a microphone, amplifier, and receiver.
Hearing Disorder: Disruption in the normal hearing process that may occur in outer, middle, or inner ear, whereby sound waves are not converted to electrical signals and nerve impulses are not transmitted to the brain to be interpreted.
Inner Ear: Part of the ear that contains both the organ of hearing (the cochlea) and the organ of balance (the labyrinth).
Labyrinth: Organ of balance located in the inner ear. The labyrinth consists of three semicircular canals and the vestibule.