Glossary
Hyperopia:Long-sightedness. Objects in the distance are relatively clearer than objects close up which are relatively more blurred (opposite of short sight).Contact lenses:Lenses which fit directly on the eyeball under the eyelids.
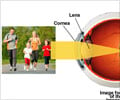
Cornea: The clear tissue in front of the eye resembling a crystal of a watch.
Diplopia: The seeing of one object as two.
Nystagmus: An involuntary, rhythmical movement of the eyeballs.
Opthalmoscope:Device for viewing the interior of the eye or the retina.
Optic nerve: The nerve which carries visual impulses from the retina to the brain.
Optician: A technician who designs, verifies and dispenses lenses, frames and other fabricated optical devices upon the prescription of an ophthalmologist or an optometrist.
Opthalmologist: A physician who is qualified and especially trained to diagnose and treat all eye and visual system problems, as well as diagnose general diseases of the body.
Photophobia: Abnormal sensitivity to light.
Refractive error: A defect in the eye that prevents light from being brought to a single focus exact on the retina.
Pupil: Apature allowing light to enter into the eye regulated by the iris and ciliary muscles.
Retina: Light sensitive membrane at the back of the eye. Light is focused onto this membrane and the retina then transmits this information to the brain as impulses which the brain interprets as sight.
Sclera: The firm white fibrous membrane that forms the white part of the eye.
Visual Acuity: Clarity of vision, with corrective glasses.