- National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine -Pharmacological causes of hyperprolactinemia- Daria La Torre and Alberto Falorni - - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2376090/)
- Hyperprolactinemia - Hormone Health Network - - ( https://www.hormone.org/diseases-and-conditions/hyperprolactinemia)
- Dopamine, PIF, and other regulators of prolactin secretion - - ( https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6105975/)
- John Hopkins Medicine- Neurology and Neurosurgery-The Pituitary Center - - (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/centers_clinics/pituitary_center/conditions/hyperprolactinemi a.html)
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine Diagnosis and management of hyperprolactinemia- Omar Serri, Constance L. Chik, Ehud Ur, and Shereen Ezzat
- Prolactin - (http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/hypopit/prolactin.html)
- Hyperprolactinemia - - (https://www.hormone.org/diseases-and-conditions/pituitary/hyperprolactinemia)
What is Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
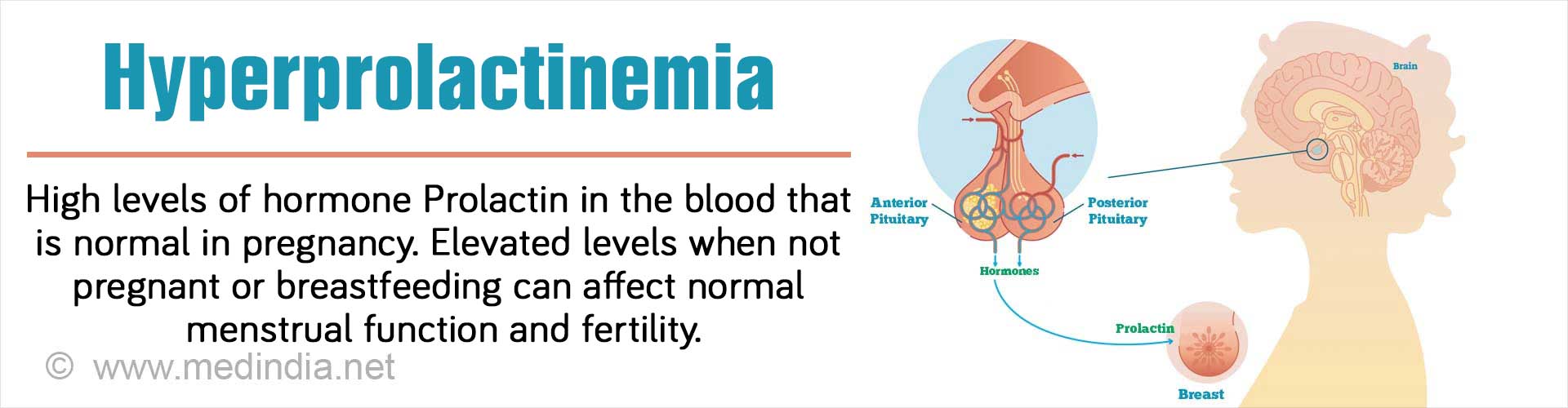
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition of abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. Prolactin is one of the peptide hormones produced by the pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the breast. The main, normal function of prolactin is during and after pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the prolactin secretion increases and stimulates growth of the breast, but high levels of Estrogen and Progesterone hormones prevent breast milk production (lactation). After delivery, the Estrogen and Progesterone levels drop and Prolactin stimulates lactation by the alveolar cells in the breast.
This peptide hormone - prolactin is also responsible for absence of menses during pregnancy and for a few months after delivery. It also affects the levels of sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone in both women and men.
What are the Causes of Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
Hyperprolactinemia occurs due to both natural and unnatural causes such as:
- Pregnancy: This is a natural cause for hyperprolactinemia responsible for the production of breast milk for the fetus.
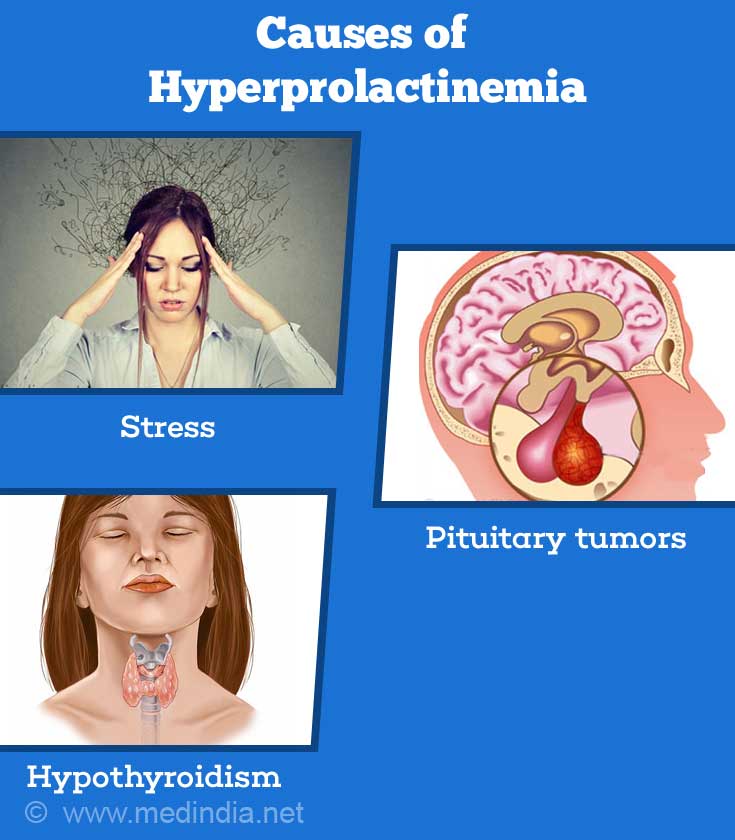
- Stress: High-stress levels are known to cause high blood levels of prolactin.
- Chest Wall Injury: Pain in the chest wall, shingles involving the chest wall, breast stimulation and bronchogenic carcinoma. can cause an increase in the amount of Prolactin in the blood.
- Pituitary Tumors: Abnormal elevations in prolactin can occur when prolactin-producing cells inside the pituitary gland, grow abnormally to form tumors known as prolactinoma and produces hormone imbalance by more than the normal secretion of the prolactin hormone.
- Hypothyroidism: Low levels of thyroid hormones can also cause hormonal imbalance by raising the levels of prolactin and is a common cause of hyperprolactinemia. This condition is treatable with thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Side Effect of Psychiatric Medications: Many anti-depressants and anti psychotic drugs such as risperidone, phenothiazines, haloperidol, paliperidone, are known to raise Prolactin levels in your body.
- Side Effects of Drugs: Narcotics, oral contraceptives and drugs to control hypertension are known causes to raise blood Prolactin levels.
- Liver disease such as cirrhosis
- Chronic kidney disease
- During orgasm or sexual stimulation
- Spinal cord lesion
- Pituitary and Hypothalamic diseases: Acromegaly, Cushing's disease
- Metastases, tuberculosis, hemochromatosis (iron overload)
- Radiation to skull
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
The symptoms and signs in both men and women as applicable to the gender, include:
- Irregular menstrual periods or absence of menstrual periods
- Excessive breast milk secretion (galactorrhea) when not breast feeding or pregnant
- Breast pain/tenderness
- Infertility
- Painful intercourse due to vaginal dryness
- Mood swings and decreased libido
- Acne and excessive body and facial hair growth (hirsutism)
- Menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, breast pain/soreness, and painful sex due to vaginal dryness) due to hormone imbalance
- Osteoporosis (thinning and weakening of the bones) and osteopenia
- Additional symptoms such as headaches and visual disturbances may occur if hyperprolactinemia is due to a pituitary tumor.

Men may have symptoms such as:
- Erectile dysfunction or Impotency
- Low sperm count
- Breast enlargement and breast pain
- Loss of libido
- Hypogonadism, due to hormone imbalance such as, excess prolactin interferes with secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone which results in decreased testosterone hormones in men.
How do you Diagnose Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
Hyperprolactinemia diagnosis is based on a patient’s symptoms, medical history, medication use, and ruling out pregnancy in a woman.
- Thyroid Tests: These tests are done to rule out hypothyroidism as a cause of hyperprolactinemia.
- MRI of the Brain and Pituitary: MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and this procedure uses a special machine that creates images of body tissues that help to diagnose a pituitary tumor. An MRI can reveal the size of a Prolactinoma (benign tumor of the pituitary gland that produces the hormone Prolactin).
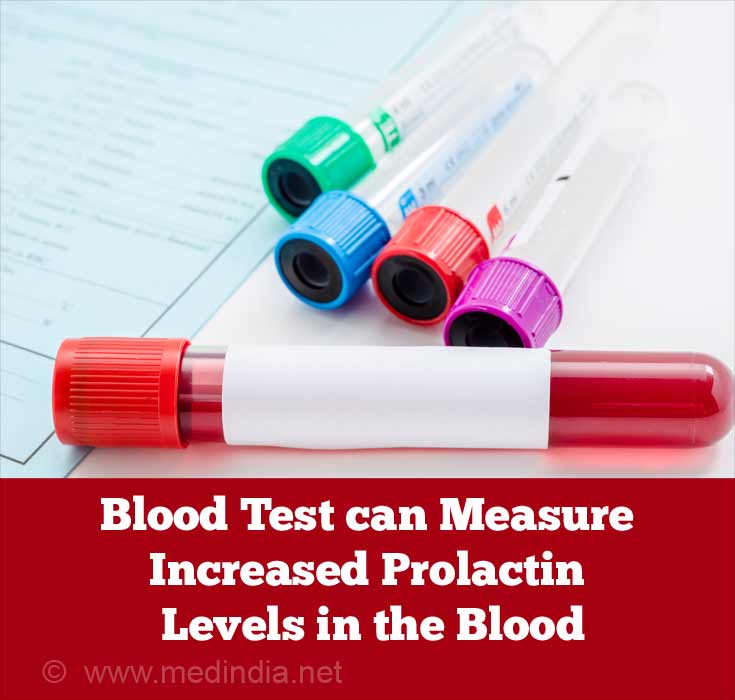
- Blood Tests: A blood test is done to measure the amount of Prolactin in the blood. Prolactin levels above 25 nanogram/milliliter, in women who are not pregnant, are considered elevated.
How do you Treat Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
The treatment options include:
- Medications: Dopamine agonists Bromocriptine (Parlodel and Cycloset) and Cabergoline (dopamine receptor antagonist - Dostinex) are mostly used to treat hyperprolactinemia.
- These medications limit the production of prolactin from the pituitary via prolactin-inhibiting factors (PIFs), and Prolactin levels drop in about two to three weeks. These medicines mimic dopamine (a brain chemical) and are used for a majority of patients suffering from elevated Prolactin.
- Thus, dopamine acts as a prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF) and helps treat hyperprolactinemia by inhibiting the synthesis and secretion of prolactin.
- Thyroid hormone: Hyperprolactinemia is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone if hypothyroidism is the causative factor.
- Surgical treatment: This is the treatment of choice for high prolactin level due to a large pituitary tumor (macroadenoma). This surgical procedure is known as Transsphenoidal Adenoma Resection.
- Radiation therapy: This therapy usually follows the surgical treatment.
How do you Prevent Hyperprolactinemia / High Prolactin Levels?
There are no proven methods to prevent unnatural hyperprolactinemia. However, detecting the causative factor early and treating the same effectively, is the best option. Some of the measures include:
- Diet modification with reduction of stress levels may aid in keeping the prolactin levels down
- Quit high-intensity workouts or activities that add to strain and chest discomfort
- Avoid tight clothing that may overstimulate your nipples and cause breast pain/galactorrhea
- It is found that vitamin B6 is involved in the process of dopamine production that in turn helps in managing higher levels of prolactin levels
- Also, vitamin E prevents the rise in prolactin levels naturally
- Thus, intake of vitamin B6 and vitamin E supplements might assist in controlling/preventing hyperprolactinemia