- Hypothyroidism in pregnancy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3354841/)
- Pregnancy and Thyroid Disease - (https://www.thyroid.org/thyroid-disease-pregnancy/)
- Thyroid Disease & Pregnancy - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/pregnancy-thyroid-disease)
What is Hypothyroidism?
The thyroid gland is an endocrine organ present in front of the neck. It produces thyroid hormone which is regulated by pituitary and hypothalamus through TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). Hormones that are produced by the thyroid gland are important for metabolism growth and maturation.
Hypothyroidism is a health condition where the thyroid gland produces less thyroid hormone than essential for the body. Uncorrected hypothyroidism in pregnancy shows adverse effects on both the mother and the child in the womb. However, since it can be treated easily, a prompt diagnosis and treatment can reduce the adverse effects in mother and fetus significantly.
Facts and Statistics of Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy
- The prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy is 2-3%.
- The prevalence of overt hypothyroidism in pregnancy is 0.3-0.5%.
Thyroid Function during Pregnancy
Physiological changes are normal during pregnancy. Thyroid physiology too alters in pregnancy to meet the new needs of pregnancy.
The demand for thyroid hormones increases during pregnancy because of an increase in the thyroid binding globulins, increase in the placental type 3 deiodinase and transfer of hormones to the fetus.
The demand for high thyroid hormones is met through the human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) released by the placenta, which acts on the TSH receptor of the thyroid and increases the synthesis of thyroid hormone.
What Causes Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
The causes of hypothyroidism in pregnancy are -
- Endemic deficiency of iodine is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in pregnancy worldwide.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis is the most common cause in an area with no iodine deficiency.
- Other less common causes are radioiodine ablation or surgery when treating thyroid cancer. Central hypothyroidism, ectopic thyroid, drugs like rifampicin and phenytoin can cause hypothyroidism.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
The clinical features due to hypothyroidism in pregnancy are -
- Subclinical hypothyroidism: It is usually asymptomatic (showing no symptoms).
- Hypothyroidism: Cold intolerance, inappropriate weight gain, muscle cramps, deep tendon reflexes are delayed, dry skin, poor concentration and memory.

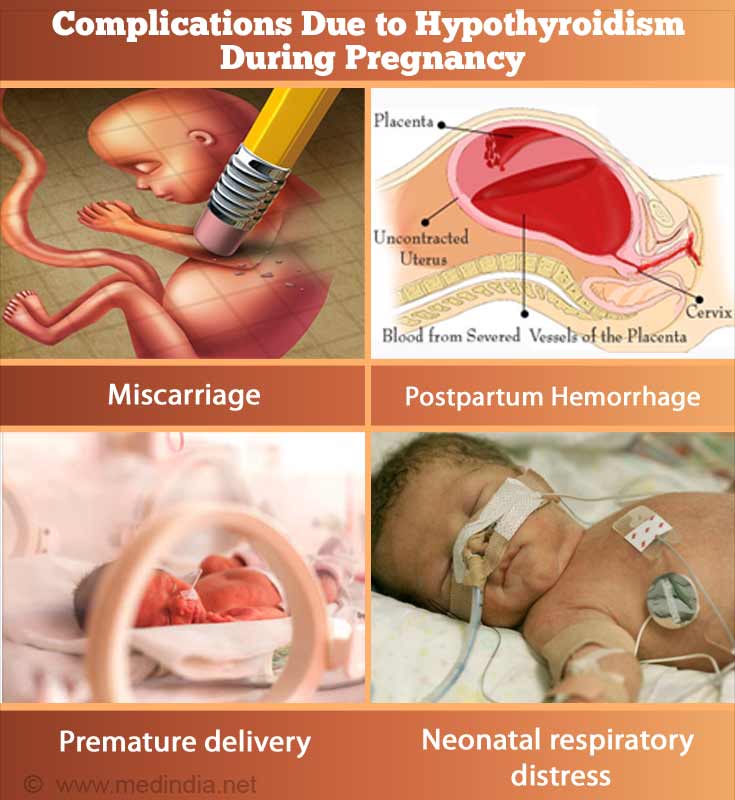
What are the Complications due to Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
The complications due to hypothyroidism in pregnancy are -
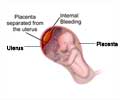
Maternal complications: Hypothyroidism in pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, pre-eclampsia, placental abruption, anemia in pregnancy and postpartum hemorrhage.
Fetal complications: It may increase the risk of premature delivery, low birth weight and neonatal respiratory distress in the baby. The milestones are delayed in children and low IQ is seen.
How do you Diagnose Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
From the patient history and clinical examination, it is possible to identify some cases of hypothyroidism. Thyroid function tests help in the diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
- TSH: A high serum level of TSH is found in primary hypothyroidism.
- Free T4 level: It is decreased. Free T4 levels rather than total T4 levels are used in pregnancy because of the elevated levels of thyroid binding globulin (TBG).
- In autoimmune thyroiditis, antibodies against thyroid peroxidase or thyroglobulin will be present.

How do You Treat Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
Levothyroxine is used for treating hypothyroidism in pregnancy.
A larger dose of levothyroxine is required in pregnancy because of high levels thyroid binding globulins (TBG). Measure the levels of TSH and T4 after one month of initiation of treatment. The dose should be enough to maintain TSH level less than 2.5mIU/l in the first trimester and also it should maintain good T4 level. Monitor the levels of TSH and free T4 to know if any alteration in the dose is required.
In a patient with hypothyroidism onset before pregnancy needs 30-50% more levothyroxine dose that pre-pregnancy dose.
How Can You Prevent Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy?
The following are a few recommendations to prevent hypothyroidism effects during pregnancy -
- Screening and treatment of thyroid disease before planning a pregnancy.
- If a woman is diagnosed with hypothyroidism during pregnancy, immediate treatment with levothyroxine is required. The levels of TSH and T4 should be regularly monitored to adjust the dose if required.
- If a woman is hypothyroid before pregnancy, treatment should be continued; dose should be adjusted and closely monitor the TSH and free T4 levels.