Q: Which doctor should I consult for liver cancer?
A: The family doctor should be consulted first. If the doctor suspects liver cancer, then you will need to see either a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist (who specializes in diseases of the liver) or an oncologist (who specializes in treating cancer).
Q: Is it important to get a second opinion for a diagnosis of liver cancer?
A: There may be some reasons that might make you want a second opinion.
Being diagnosed with a rare type of cancer, not being able to choose from several treatment options and insurance are some of them.
Q: Who is an interventional radiologist?
A: An interventional radiologist is a person who uses minimally-invasive image-guided procedures to diagnose and treat diseases.
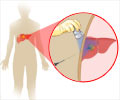
Q: Is cirrhosis of the liver a form of cancer?
A: No, it is not although it can lead to liver cancer. Cirrhosis occurs when liver cells die and are replaced by scar tissue.
Q: What is the size of the liver?
A: The liver size is influenced by a person’s age, sex and body build.
The mean length of the liver in a woman is 9 cm and it weighs between 1200 to 1400 grams. The liver of a man is 10.5 cm long on an average, and weighs between 1400 to 1500 grams.
Q: Does smoking cause liver cancer?
A: Smoking increases the risk of getting liver cancer.
Q: What are benign liver tumors?
A: Benign liver tumors are non-cancerous or non-malignant tumors that can sometimes grow large enough to cause problems. They however do not metastasize to nearby tissues or distant parts of the body. Surgery is the cure for benign tumors.
Examples are liver hemangioma (mass of blood vessels), hepatic adenoma (hormone-induced), focal nodular hyperplasia and lipoma (mass of adipose tissue).
Q: Are there other types of liver cancers apart from primary and secondary kinds?
A: Angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma are rare cancers that begin in the cells of the blood vessels supplying blood to the liver. They advance quickly and diagnosis is usually late eliminating surgery as an option. Chemotherapy and radiation therapies may slow down the disease but not cure it.
Hepatoblastoma is a rare cancer that occurs in children less than 4 years old.