- About - Mastoiditis - (https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/mastoiditis)
- Acute Mastoiditis - (https://radiopaedia.org/articles/acute-mastoiditis)
- All You Need To Know About Mastoiditis - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001034.htm)
- What is Mastoiditis? - (http://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/m/mastoiditis)
- More Information on Mastoiditis - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/mastoiditis/)
What is Mastoiditis?
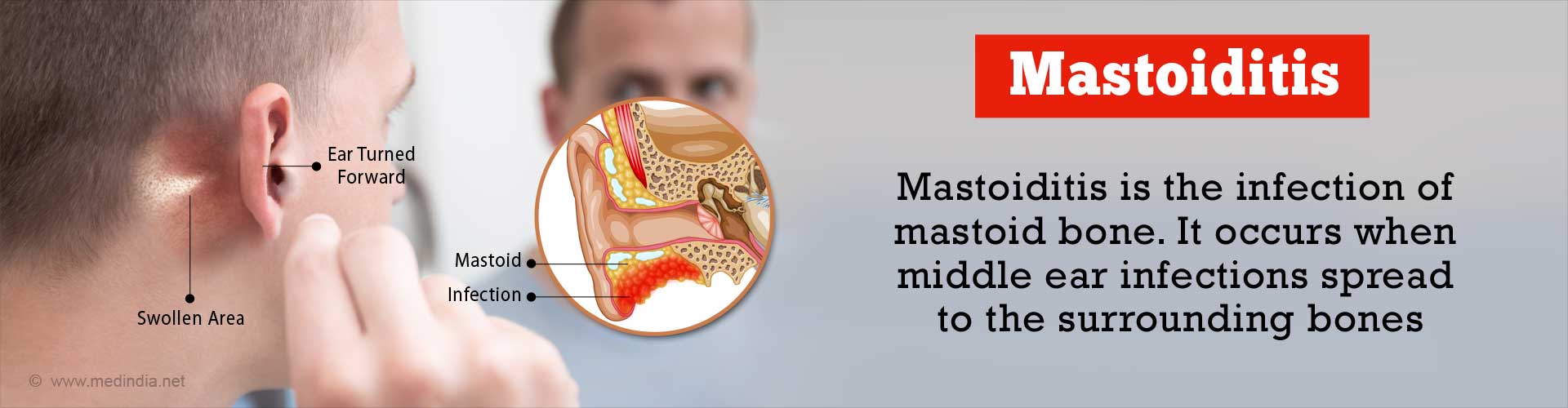
Mastoiditis, the infection of mastoid bone just behind the ear, is often the result of middle ear infections (acute otitis media) spreading to the surrounding bones.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Mastoiditis?
Go to source) Infection or inflammation of mastoid cells can be classified as acute mastoiditis or chronic mastoiditis. When mastoiditis occurs together with middle ear infection, it is termed as acute otomastoiditis.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Acute Mastoiditis
Go to source)
Mastoid process is the conical prominence that extends from the temporal bone, just behind where the ear is located. The neck muscles are attached to the mastoid process. It is filled with cavities similar to the sinuses. The spread of infection from the mucosa of the middle ear to the sinuses of the mastoid process results in the infection of the mastoid bone. Untreated mastoiditis can spread to the surrounding tissues and cells and even to the brain.
What are the Causes of Mastoiditis?
Mastoiditis is usually the result of an untreated middle ear infection. Sometimes cholesteatoma (an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear) can erode into the mastoid process, resulting in mastoiditis and other complications.
The causal organisms include:
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Haemophilus influenza
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Mycobacterium species
What are the Symptoms of Mastoiditis?
Symptoms of mastoiditis are similar to those of the middle ear infections. The honey-comb like structure of the mastoid bone fills up with the infected material leading to redness and pain behind the ear.
Other symptoms include:
- Ear discomfort. Fever, which can be sudden and high.
- Toothache just below the infected mastoid.
- Swelling behind the ear, making the ear stick out. Draining of fluid from the ear.
- Hearing loss in the affected ear.
- Some symptoms may be non-specific to mastoiditis but occur as a part of the infection.
- Diarrhea
- Irritability
- Malaise (feeling of general discomfort)
- Loss of appetite
- Headache, more concentrated behind the ear and radiating towards the sides of the head.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
All You Need To Know About Mastoiditis
Go to source)

How to Diagnose Mastoiditis?
Clinical diagnosis of mastoiditis includes:
- Medical history of ear infections.
- Patient symptom presentations like headaches and ear discharge.
- Physical examination to look for redness, tenderness and swelling behind the ear.
Blood tests show:
- Excessive leukocytes.
- Elevation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
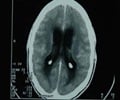
Computerized tomography (CT scan) reveals:
- Opacity of the mastoid air cells - air cells appear clear with there is no infection.
- Erosion of the mastoid bone.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful in confirming:
- Opacity of the mastoid air cells.
- Presence of fluid in mastoid air cells.
Culture tests:
- Culture testing of the ear discharge reveals the type of bacteria present.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
About - Mastoiditis
Go to source)

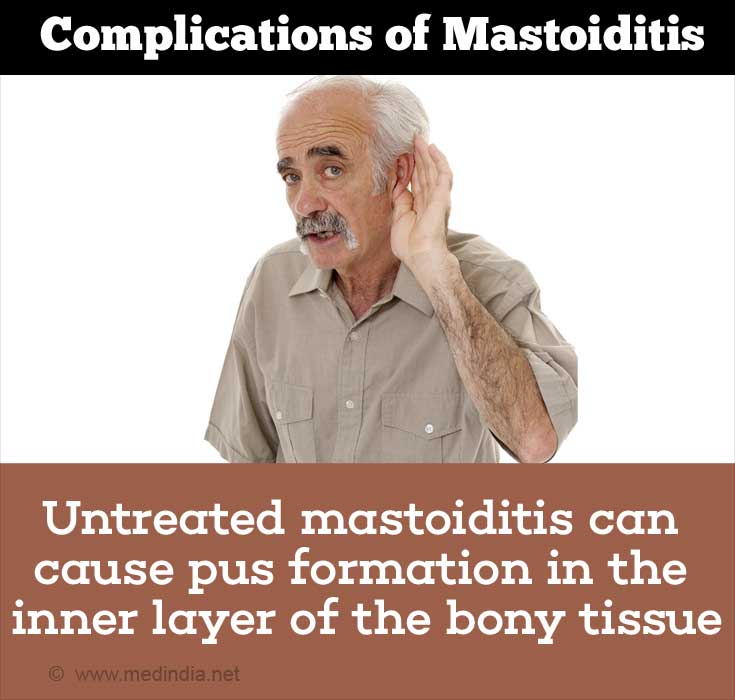
What are the Complications of Mastoiditis?
Untreated mastoiditis can cause many complications.
- Dizziness or vertigo as it affects the vestibular system which maintains body balance.
- Destruction or erosion of the mastoid bone.
- Subperiosteal abscess (pus formation in the inner layer of the bony tissue).
- Cranial nerve involvement. Gradenigo’s syndrome – Facial nerve paralysis, deep facial pain and otitis media.
- Meningitis (inflammation of membranes of the brain).
- Brain abscess.
- Bezold abscess (collection of pus behind the muscle of the neck)
- Moderate to severe hearing loss.
How to Treat Mastoiditis?
Various options may be considered for the treatment of mastoiditis depending on the severity of the condition.
Medicines:
- High dose of broad spectrum antibiotics is given orally or intravenous. Vancomycin and ceftriaxone are included in the treatment.
- Painkillers like paracetamol and ibuprofen are given.
Surgery:
- Insertion of tube via the eardrum to drain out the excess mucus and pus.
- Mastoidectomy:
- Simple mastoidectomy – surgical removal of the infected mastoid air cells.
- Radical mastoidectomy – surgical removal of the tympanic membrane and other middle ear structures and closure of the Eustachian tube.
- Modified mastoidectomy – all other parts except a part of the tympanic membrane and the tiny middle ear bones are removed.
The spread of the infection to brain and surrounding areas may require drainage of the abscess in those areas or neurosurgical intervention.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
More Information on Mastoiditis
Go to source)

Health tips
- Do not leave any infections of the head and neck untreated.
- Avoid swimming pools that are not cleaned regularly.
- Avoid water retention in the ear canal.
Keep yourself away from allergies as they can cause inflammation of the mucus lining that in turn get infected.