Causes and Diagnosis
Meniere’s disease occurs due to endolymphatic hydrops, the exact reason why this occurs is not known. The patient is diagnosed through clinical examination and audiometric testing.
Causes
An increase in fluid pressure in the inner ear, a condition called endolymphatic hydrops, has been found to be the main abnormality in Meniere’s disease. The reason why this occurs is not known. Some patients have relatives suffering from the same disease hence it is suggested that Meniere’s disease could be hereditary. It has also been suggested that it may occur due an immune reaction or an allergy. Stress is known to precipitate attacks of Meniere’s disease. Beside Meniere’s disease, endolymphatic hydrops could also occur in other conditions such as trauma, viral infection, migraine, electrolyte changes in the internal ear or a structural abnormality of the inner ear or the bone in which the inner ear is placed.
Diagnosis
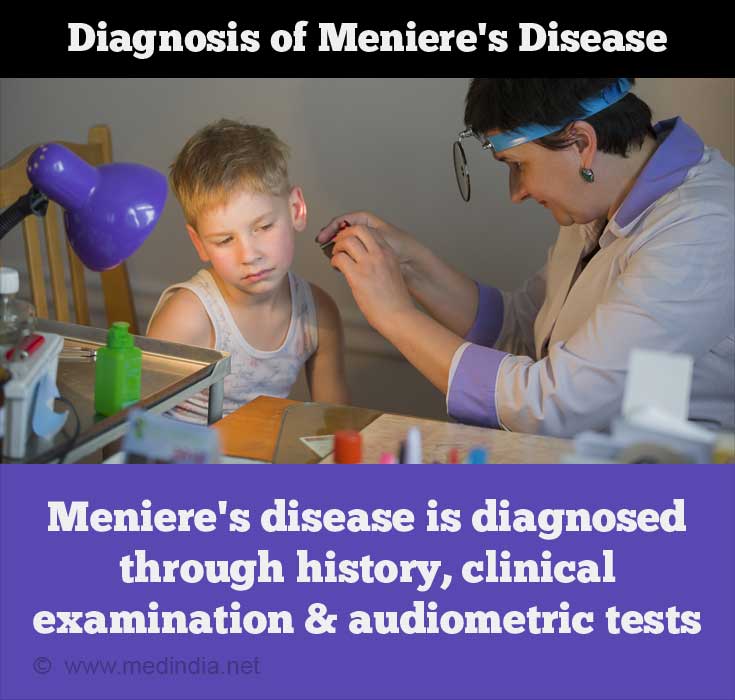
Meniere’s disease is diagnosed through history, clinical examination and audiometric tests. The patient should fulfil the following criteria to confirm the diagnosis –
- He should experience at least 2 definitive episodes of vertigo of minimum 20 minutes each.
- Tinnitus and/or fullness of the ear should be present on the affected side
- The hearing loss should be confirmed at least once with audiometric tests.
Two additional tests, glycerol dehydration test and electrocochleography are used in cases that are difficult to diagnose. CT scan and MRI are helpful to rule out other conditions that cause vertigo.