- Muscle Atrophy - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22310-muscle-atrophy)
- Muscle atrophy - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003188.htm)
- Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Skeletal Muscle Atrophy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9854691/)
- Electrical Stimulation of Muscle: Electrophysiology and Rehabilitation - (https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/physiol.00015.2019)
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA) - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/multiple-system-atrophy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20356157)
- Exercise and Muscle Atrophy - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32342463/)
What is Muscle Atrophy?
Muscle atrophy, as the name suggests, is a weakening or reduction of muscle due to lack of use or due to a disease. It is a result of a mismatch between the rates of protein synthesis and protein breakdown.
Protein is required for muscle mass, therefore muscle wasting occurs when the amount of protein broken down is more than that synthesized.
What are the Causes of Muscle Atrophy?
Muscle atrophy is caused due to several reasons. Some of them are listed below
Neurogenic muscle atrophy is caused when the nerve supplying a particular muscle is affected by a disease or is injured.
The onset of atrophy is sudden and this form of atrophy is severe. Causes of neurogenic muscle atrophy include:
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Polio
- Lou Gehrig disease
- Injury to the spinal cord
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
Disuse atrophy results when muscles are not used for a prolonged period. This type of atrophy can be rectified with appropriate diet and exercise. Causes of disuse atrophy include:
- Prolonged bed rest
- Sedentary form of work
- Spaceflight (due to loss of gravity)
- Reduced levels of activity
- Joint disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
Other causes of muscle atrophy include:
- Diseases that increase catabolic rates like hyperthyroidism, cancer, AIDS, burns, congestive cardiac failure, kidney failure, and chronic obstructive lung disease
- Starvation/malnutrition/fasting
- Older age
- Prolonged corticosteroid treatment
- Muscular dystrophy
- Metabolic acidosis
- Genetic conditions like spinal muscular atrophy(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Muscle Atrophy
Go to source)
Did You Know? (Muscle Atrophy)
An intriguing and an interesting fact about muscular atrophy is its connection of Muscle Atrophy with space travel. Astronauts in space who live in a microgravity environment often experience a form of muscular atrophy. Their muscles weaken and lose mass as there is no requirement to support their body weight or move against gravity.This phenomenon has been a significant area of study for space agencies like NASA, as understanding and combating muscular atrophy is crucial for the health and safety of astronauts on long-duration space missions. These studies also have important implications and learnings for medical science on Earth, particularly in the treatment and management of muscle-wasting conditions.What are the Symptoms and Signs of Muscle Atrophy?
Muscle atrophy is characterized by shrunken muscles with less strength. Some of the symptoms of muscle atrophy include:
- Thinning out of the muscle
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Disability

In the case of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) I, children are unable to sit, roll, or stand. They usually do not survive beyond the age of 2 years. Children with SMA II cannot walk without support although they live well into their adolescence. Children with SMA III can walk at a certain point in their lives and have a normal lifespan(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Muscle atrophy
Go to source).
Read more about Spinal Muscle Atrophy (SMA)
Those with neuralgic amyotrophy have extreme pain followed by atrophy in the upper limbs.
Click here to learn more about Muscle Atrophy in legs
How do you Diagnose Muscle Atrophy?
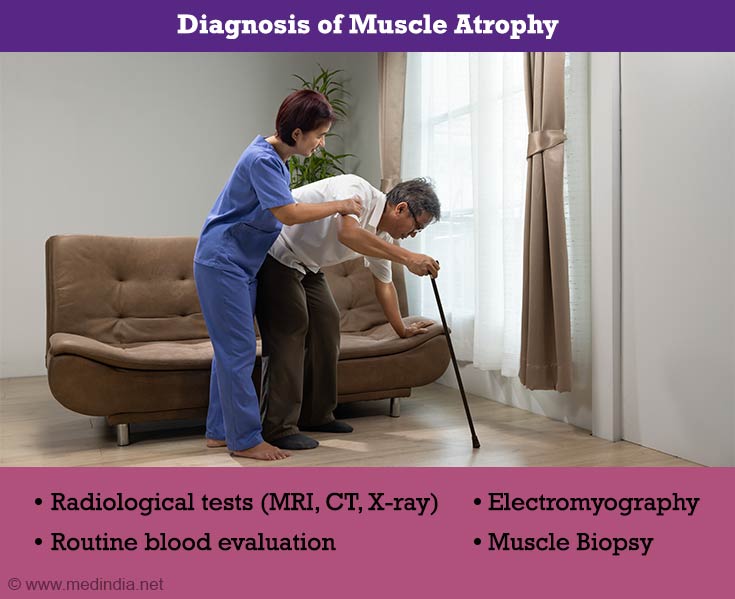
The diagnosis of muscle atrophy is based on the clinical examination of the patient. Tests are conducted to confirm the diagnosis and to identify the underlying cause. These include:
- Radiological Tests: Radiological tests like MRI, CT scan, and x-ray can confirm the presence of muscle atrophy. Radiological imaging of the spine may help to detect spinal abnormalities contributing to the atrophy. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan provides information on the functioning capacity of the muscle. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) gives a measure of bone mineral density, which may also be reduced in a patient with skeletal muscle atrophy(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Skeletal Muscle Atrophy
Go to source). - Blood Tests: Routine blood tests as well as specific blood tests to confirm the suspected cause will be necessary.
- Electromyography and Nerve Conduction Studies: Electromyography (which studies the electrical activity of muscles) and nerve conduction studies can help to diagnose the location of the problem.
- Biopsy of Nerves or Muscles: Biopsy of the muscle and sometimes the nerve supplying the muscle can diagnose the exact reason for the muscle atrophy(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Electrical Stimulation of Muscle: Electrophysiology and Rehabilitation
Go to source).
Can Muscle Atrophy be reversed? To know read
(https://www.medindia.net/health/conditions/can-muscle-atrophy-be-reversed.htm)
How do you Treat Muscle Atrophy?
There is no effective drug to treat muscle atrophy including spinal muscle atrophy. In general, the goal of treatment is to reduce the symptoms of the condition and make life more comfortable for the patient. Ultrasound therapy, physical therapy, and the use of wheelchairs, braces, and surgery are some of the ways used to treat muscle atrophy. Oral prednisone is also used in some patients(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Multiple system atrophy (MSA)
Go to source).
To know more details about Muscle Atrophy tablets: Click here
Disuse muscle atrophy can be reversed with the following treatments:
Testosterone Supplementation
It has been observed that testosterone supplementation is very useful in treating muscle atrophy due to old age. It is particularly effective when combined with load-bearing exercise. There is an improvement in the size of muscle fibers, muscle strength, and muscle-regenerating satellite cells in older people.
Exercise
Two types of exercises can be performed to prevent or treat certain forms of muscle atrophy.
Endurance Exercise -This form of exercise is very effective in decreasing muscle atrophy, increasing the production of proteins, and improving muscle mass and strength. This type of exercise is very effective in improving muscle mass in the elderly although other health conditions should be taken into consideration before such exercises are prescribed. Resistance exercise is when the muscle is made to exert a force against resistance, such as an immovable object, weight, or water.
Endurance Exercise -This form of exercise is great for cardiovascular health. However, since there is no weight or load placed on muscles, the atrophy of skeletal muscles continues. This exercise is helpful when it is combined with resistance exercise. Aerobic exercise improves the use of oxygen by the body and also improves the heart rate(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Exercise and Muscle Atrophy
Go to source).
Follow these muscle atrophy exercises to prevent and alleviate symptoms of atrophy
https://www.medindia.net/health/conditions/muscle-atrophy-exercises-to-build-atrophied-muscles.htm
Nutrition
Creatine: This nutritional supplement helps in improved recovery following a period of immobilization. Creatine improves muscle mass and the production of energy. Despite varied reports on the usefulness of creatine in preventing muscle atrophy, this inexpensive supplement remains a relevant supplement in alleviating muscle atrophy. The dosage and the time of day when the supplement is given, may play a role in relieving muscle atrophy.
Amino Acid Supplementation: Exercise may not always be feasible as in the case of bed rest. Hence, supplementation with essential amino acids helps to increase the synthesis of protein, though the increase in muscle mass with amino acid supplementation is not to the same extent as exercise. It is most effective when combined with exercise.
Health Tips
Those with a genetic predisposition to muscle diseases should see a genetic counselor to identify their risk of having the condition.