Glossary
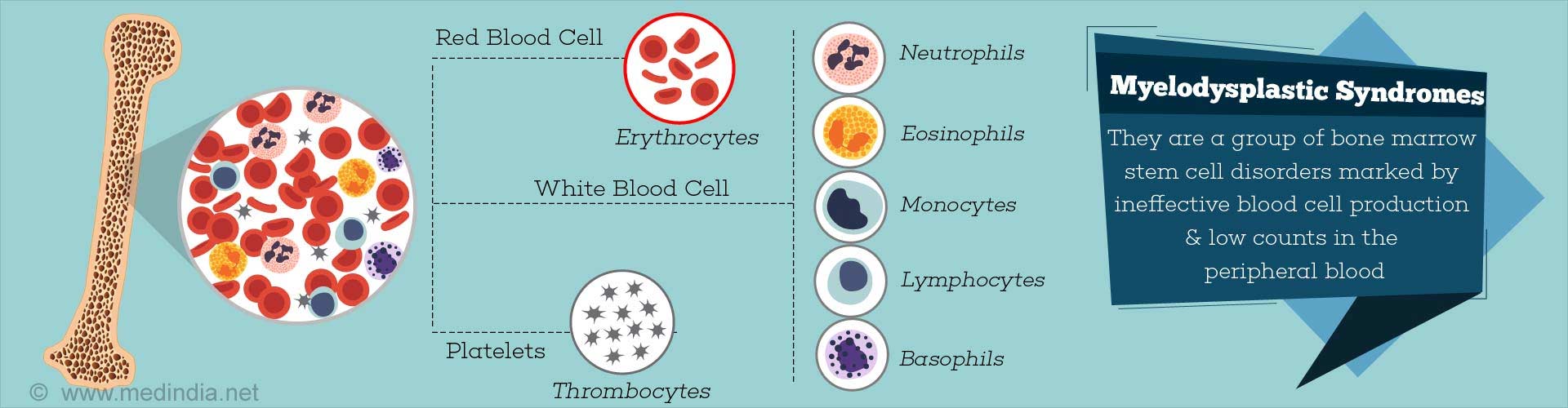
Platelets: A type of blood cell that helps prevent bleeding by causing blood clots to form. Also called thrombocytes.White blood cells: A type of cell in the immune system that helps the body fight infection and disease. White blood cells include lymphocytes, granulocytes, macrophages, and others.
Red blood cells: Cell specialised for oxygen transport, having a high concentration of haemoglobin in the cytoplasm.
Allogeneic: Taken from different individuals of the same species.
Dysplasia: Cells that look abnormal under a microscope but are not cancer.
Bone marrow: The inner, spongy tissue of large bones where red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets and made.
Aplastic anemia: A condition in which the bone marrow is unable to produce blood cells.
Bone marrow transplant: A procedure in which a patient''s bone marrow is destroyed by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy and replaced either with donated bone marrow or the patient''s own marrow which has been collected and stored prior to chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
Bone marrow aspiration: The removal of a small sample of bone marrow (usually from the hip) through a needle for examination under a microscope.
Bone marrow biopsy: The removal of a sample of tissue from the bone marrow with a needle for examination under a microscope.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): A quickly progressing disease in which too many immature blood-forming cells are found in the blood and bone marrow. Also called acute myeloid leukemia or acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.
Cytogenetics: Related to chromosomes.
Karyotype: A chromosomal analysis which is carried out by arranging the chromosomes according to their size and location of the centromere.
Blasts: Immature blood cell precursors found in the bone marrow.