Signs and symptoms
Changes in the mucus pattern and small rise in basal body temperature are the most common symptoms that occur during ovulation.
Ovulation time can be predicted by various signs, which may vary from woman to woman. Some woman can distinctly feel the changes during ovulation while others may not able to discern the changes. Changes in the cervix, cervical mucus pattern and slight rise in basal body temperature are the common signs experienced by most women. Some women may also experience secondary symptoms like ovulation pain, increased sex drive and heightened sense of smell.

Common signs of ovulation which helps to predict the time of ovulation are as follows:
- Changes in the cervical mucus: For a few days after menstruation, the woman does not feel any vaginal discharge. Around the time of ovulation, the mucus discharge becomes clear, slippery and stretches without breaking. This mucus resembles the white of the egg and is present for a day or more. During the later parts of the cycle, the cervical mucus becomes sticky and cloudy.
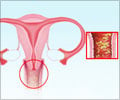
- Change in cervical position and firmness: A woman can be taught to appreciate changes in the cervix associated with ovulation. The cervix is the tubular part of the uterus that projects into the vagina. Around the period of ovulation, the cervix becomes soft, wet, open and is positioned slightly high. After ovulation, the cervix will be hard, closed and low.
- Change in basal body temperature: The basal body temperature is the temperature measured just before the woman gets out of bed in the morning. For most women, due to hormonal changes, a slight rise in basal body temperature is observed during ovulation.
Less common symptoms associated with ovulation are:
- Light spotting
- Abdominal cramps
- Ovulation pain or mittelschmerz
- Abdominal bloating
- Increased sex drive
- Heightened sense of taste, vision and smell
- Night sweats and hot flashes
- Water retention
- Increased energy levels