- Pinworm Infection FAQs - (https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/pinworm/gen_info/faqs.html)
- Pinworm Infection - (https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/pinworm/fact_sheet.htm)
- Prevalence and symptoms of Enterobius vermicularis infections in a Peruvian shanty town. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1801349)
- Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis Infection among Preschool Children in Kindergartens of Taipei City, Taiwan in 2008 - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2688803/)
- Ascaris Lumbricoides - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8261/)
- Pinworms - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2306321/pdf/canfamphys00240-0140.pdf)
- Complications of Pinworm infections - (http://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/hw50226)
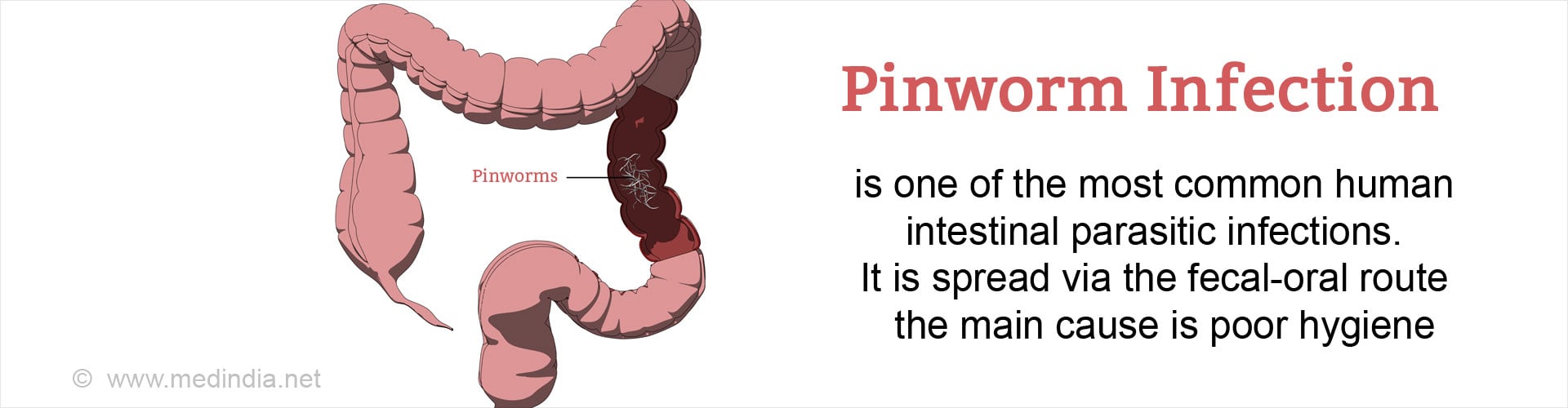
What is Pinworm Infection?
Pinworm (also known as Enterobius vermicularis or threadworm) infection is one of the most common human intestinal parasitic infections. It is usually not dangerous but is highly contagious. In this infection, tiny worms infest the intestines and lay eggs around the anus, a condition specifically known as enterobiasis or oxyuriasis. It causes itching around the anus that leads to difficulty in sleeping and restlessness.
What are the Causes of Pinworm Infection?
Pinworm infection spreads via the fecal-oral route, and its main cause is poor hygiene. It mainly spreads through the transfer of infective pinworm eggs from the anus to someone’s mouth, either directly by hand or indirectly through contaminated articles. From the hands, the eggs may be transferred to any article that is touched, such as:
- Bed sheets
- Carpets
- Towels
- Clothes
- Fingernails
- Furniture
- Kitchen utensils and countertops
- Toilet seat
- Swimming pools
- Toys
Pinworm eggs become infective within a few hours after being deposited on the anal area and can survive for 2 to 3 weeks on contaminated surfaces. Although pinworm infections occur worldwide and affect persons of all ages it is most common in:
- school-aged and preschool-aged children
- institutionalized settings
- household members and caregivers of infected persons
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Pinworm Infection?
A person infected with pinworm is often asymptomatic, but itching around the anal area is a common symptom. Symptoms often attributed to pinworm infection are as follows:
- Perianal itching, enuresis (bed wetting), and teeth grinding in infected children.
Enuresis , is found to be more common in primary school-age children with high pinworm egg counts - Difficulty in sleeping and irritability
- Abdominal pain and nausea
- In the case of girls, pinworms can also travel from the anus into the vagina, affecting the uterus, fallopian tubes, and other pelvic organs. Vaginitis (vaginal itching and irritation) and endometritis (inflammation of the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus) or other infections may result
- Severe infections can lead to symptoms like nervousness, restlessness, loss of appetite and weight loss

How do you Diagnose Pinworm Infection?
Diagnosis of pinworm can be confirmed through standard pinworm tape test. The best time to collect perianal specimens is in the morning before bathing or defecation. Three specimens should be taken on consecutive days before pinworm infections are diagnosed. Cellophane tape is placed against the anal area that picks up the ova.
The tape is then placed with its sticky side down on a microscope slide and a drop of toluene is used to identify the eggs. The pinworm eggs can only be seen in clumps of thousands and hence can easily be seen under the microscope.
A second option for diagnosis is analyzing samples taken from under fingernails under a microscope. Since anal itching is very common in an infected person, eggs picked up under the nails while scratching could be used for diagnosis.
Pinworm eggs are not found in stool, so stool examination is not recommended. Serologic tests are not helpful in making the diagnosis.
What are the Complications Associated with Pinworm Infection?
Complications of pinworm infections are rare; but may include:
- Extra intestinal infections that may cause intestinal lesions.
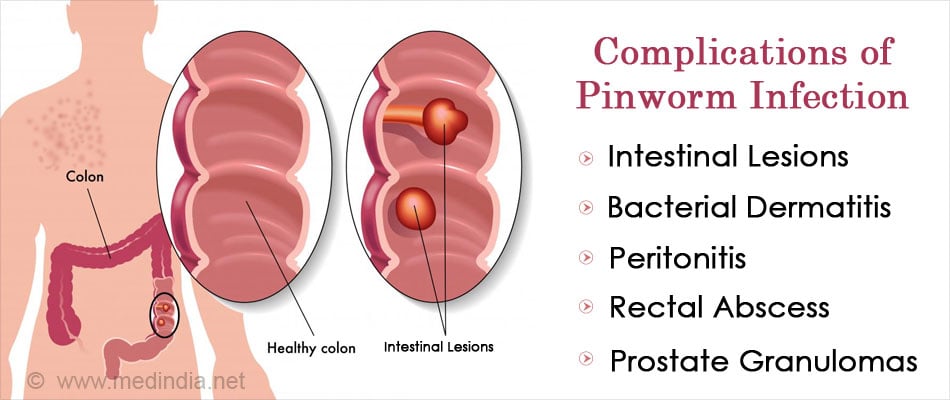
- The itching leads to continuous scratching of the area around the anus, which can further worsen skin symptoms such as secondary bacterial infections, including bacterial dermatitis (skin inflammation) and folliculitis (hair follicle inflammation).
- Inflammation inside the abdomen (peritonitis).
- Rectal abscess (a painful condition in which a collection of pus develops near the anus).
- Prostate granulomas may occur when pinworms travel up the urethra and deposit in the prostate gland.
How do you Treat Pinworm Infection?
Adult Enterobius vermicularis lives for only three to six weeks; it is therefore possible to break the cycle of infection by maintaining proper hygiene. Though hygiene plays an important role, drug therapy is the treatment of choice. The most common and effective medications to treat pinworm infection are:
- Mebendazole- It is a broad spectrum antihelmintic. A single 100 mg tablet with one repetition after a week is the suggested treatment for both adults and children aged 2 to 12.

- Albendazole (Albenza)- It is given as a 400 mg single oral single dose that is repeated in 2 weeks. When multiple or repeated symptomatic infections occur, re-treatment after 14 to 21 days may be needed.
- Pyrantel pamoate - This drug is a second-line medication that kills adult worms by neuromuscular blockade. It is administered as a single dose of 11 mg/kg and is supplied as a suspension or tablet.
- Piperazine (Antepar and others)- This drug produces flaccid paralysis of the adult worms, which are then evacuated from the bowel by normal peristalsis. Daily doses of 65 mg/kg each day for eight days results in 95-100% cure.
Usually one course of medication is sufficient that involves an initial dose, which is followed by a second dose 2-3 weeks later. More than one course may be necessary to completely eliminate the pinworm eggs. Physicians may also prescribe creams & ointments to help relief inflamed and itchy skin.
How do you Prevent Pinworm Infection?
When an infection is recognized, efforts should be made to improve personal hygiene which includes:
- Perianal region should be washed well.
- Fingernails of children should be trimmed.
- Night clothes must be changed and bed linen should be laundered properly.
- Dogs and cats should be washed and the house cleaned, particularly bedrooms.
- Other members of a patient's family should be checked for any possibility of infection.
- Hands and fingernails should be washed thoroughly, after using the bathroom, before eating and after changing diapers.
- Nail biting and scratching bare anal areas should be discouraged to avoid re-infection.