- Pleural Disorders - (http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pleurisy)
- Pleurisy - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21172-pleurisy)
- Pleurisy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558958/)
What is Pleurisy?
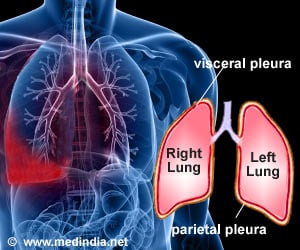
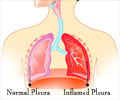
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is a condition where the pleura is inflamed. The pleura is a double layer of tissue that surround the lungs. The layer in close contact with the chest wall is called parietal pleura, while the layer in contact with the lungs is called visceral pleura. Between the two layers is a thin fluid film in a space called the pleural space. The fluid ensures that the two layers glide smoothly over each other when referred to as the pleural rub, and diagnostic tests includes imaging studies, blood tests, and examination of the pleural fluid. Pleurisy often subsides once the underlying cause is treated.
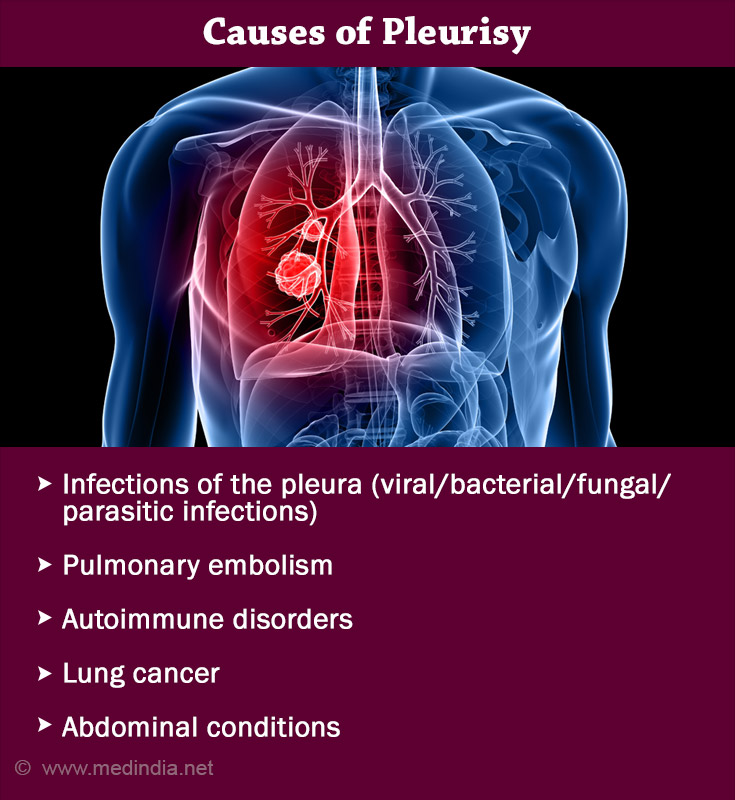
Causes of Pleurisy
Pleurisy is often considered as a symptom of an underlying disease, rather than a disease itself. In some cases, the exact cause of pleurisy cannot be identified. Conditions that are commonly associated with pleurisy include:
- Respiratory Tract Infections of the pleura, which may spread from the lungs include:
- Viral infections
- Bacterial infections like pneumonia and tuberculosis
- Fungal infections
- Parasitic infections
- Infections just below the diaphragm like abscess
- Pulmonary embolism, a condition where a clot is present in the blood vessels of the lungs
- Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and
rheumatoid arthritis - Lung cancer
- Chest trauma during accidents or surgery like coronary bypass or cardiac valve replacement surgery
- Lung diseases like asbestosis
- Other abdominal conditions like pancreatitis, inflammatory bowel disease.
- Intake of medications like procainamide, nitrofurantoin, methotrexate, procarbazine, hydralazine and isoniazid.
Symptoms of Pleurisy
- Sharp and stabbing pain in a particular area of the chest, often in the lower part. The pain worsens during deep inspiration, sneezing, or coughing when the two layers of the pleura rub against each other. It may be relieved to some extent when the patient lies down on the affected side. In some cases like cancer, the pain may be dull.
- Shallow breathing to reduce expansion of the lungs and pleura, and therefore pain.

- Other symptoms depending on the presence of the underlying condition. These include fever and chills in cases of infections, productive cough in case of bacterial lung infections, and rashes and pain in joints in conditions like connective tissue disorders(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pleural Disorders
Go to source).
Diagnosis of Pleurisy
Diagnosis of pleurisy is based on history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Medical history of the patient, where the patient complains of distinct chest pain. The patient may also give a history of an associated condition like lupus or tuberculosis
- Physical examination, which includes a detailed chest examination. A scratching sound called pleural rub will be heard by the doctor with a stethoscope. The sound is most prominent at the end of inspiration
- Blood tests that may indicate the presence of infection or other conditions
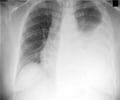
- Radiological test, which includes x-ray, CT scan and MRI. These may help to diagnose conditions like pneumonia and abscess
- Testing of pleural fluid by thoracentesis to determine the cause of inflammation
- Pleural biopsy if necessary
Differential Diagnosis of Pleurisy
The essential medical conditions to assess when dealing with pleuritic pain include acute coronary syndromes, aortic dissection, pneumothorax, pericardial effusion/tamponade, and pulmonary embolism.
Once these have been examined using imaging and serum chemistry, additional considerations may include pleural effusions, pericarditis, pulmonary infectious processes, or intrathoracic malignancies.
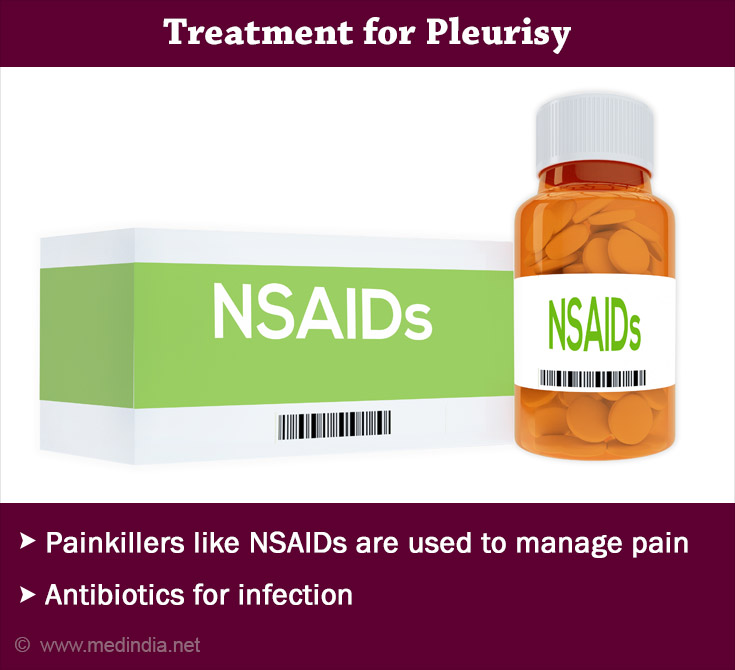
Treatment for Pleurisy
Pleurisy management involves a comprehensive approach aimed at addressing the diverse aspects of this inflammatory condition.
Pleurisy is treated once the underlying illness is managed. Treatment includes rest, painkillers, and treatment of the underlying condition. Symptomatic treatment for pleurisy includes:
- Painkillers (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation
- Cough suppressants, to suppress dry cough
- Adequate rest; the patient is advised to lie down on the affected side
Pleural effusion if present should be drained if necessary.
Complications of Pleurisy
Empyema (pus-filled pleural effusion) refers to the accumulation of pus within the pleural cavity. Complications of parapneumonic effusions and empyemas may include pleural thickening, leading to trapped lung, recurrent pneumonia, and bloodstream infections if not adequately evacuated. Malignant effusions can also result in pleural thickening and fibrosis, potentially causing restrictive lung disease.
Pulmonary emboli may lead to pulmonary hypertension, resulting in chronic dyspnea, exertional intolerance, or hypoxemia. If not promptly treated, pulmonary emboli may also lead to death or prolonged hospitalization.
When a person has pleurisy, the associated pain with breathing deeply may lead to shallow breathing, which can contribute to atelectasis. Additionally, if atelectasis causes a partial lung collapse, it can lead to pleurisy-like symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
Pleurisy Prognosis
The outlook for pleurisy and pleuritic chest pain relies on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment. Pleurisy prognosis can vary depending on the individual's overall health. In general, most cases of pleurisy resolve with proper treatment and do not lead to long-term complications.
However, the prognosis can be influenced by factors such as the presence of underlying conditions, the promptness of diagnosis and treatment, and the individual's response to therapy.
Malignant pleural disease carries a grim prognosis, with one study reporting a median survival of 13 months post-diagnosis(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pleurisy
Go to source).
Pleurisy Prevention
Swift detection and effective management of the primary health issue can potentially thwart the onset of pleurisy. For instance, promptly diagnosing and treating infections early may hinder the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity or mitigate inflammation levels.
Due to the general nature of chest pain, which is a predominant symptom of pleurisy, diagnosis can be challenging.
Ensuring an ample amount of rest and adhering to a wholesome diet are also beneficial practices in preventing conditions like pleurisy from arising as a consequence of an illness(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pleurisy
Go to source).