Serious Complications of Pregnancy
Anemia:
Anemia is due to deficiency of iron and is found commonly in pregnant women. This is due to the increased demands caused by the growing fetus. Your doctor may encourage you to take iron supplements to overcome this problem. A nutrient rich healthy diet is essential for an expecting mother and can be a key factor to prevent further complications during and after pregnancy.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus:
The World Health Organization has reported an estimate of 180 million people worldwide suffering from diabetes. It is believed that these figures are likely to double by 2030. Pregnant mother also fall into this category and can face serious health problems. The development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus is quite common and requires prompt recognition and early treatment to avoid complications to the baby, as well as the mother during delivery. Regular check ups with your practitioner is therefore always recommended for early diagnosis and corrective treatment.
Chorio-amnionitis:
Infection of the membranes covering the baby is called chorio-amnionitis and can lead to an abortion or premature delivery. It can happen after a viral infection in the mother. Avoid self-medication and contact the doctor in the event of a fever. Urinary tract infections are common and appropriate antibiotics are required.
Cervical incompetence:
Opening up of the cervix or passage to uterus before term is called cervical incompetence and can lead to premature labor and delivery. It may be heralded by sudden leakage of amniotic fluid or discomfort in the back. Some people are also prone for this unfortunate event in which case the doctor might put a stitch in the cervix to keep it from opening. It can be picked up early in a susceptible person by regular surveillance.
Polyhydramnios:
The baby is usually surrounded by a bag of fluid in which it floats freely. This water may sometimes become excessive in quantity, more so in the case of twins. This condition called polyhydramnios is also an indicator of problems in the baby’s food pipe, though at times it may occur without any problems in the baby. Ultrasound scans will help ascertain the cause. When the doctor diagnoses polyhydramnios, he or she will frequently follow the baby’s growth by scans and blood tests in the mother if called for.
Placenta Previa:
The placenta occasionally occupies a lower than normal position, covering the opening to the cervix and obstructing the baby’s journey during delivery. This is ‘Placenta Previa’ and very often requires delivery by Cesarean section. It can sometimes cause heavy bleeding too.
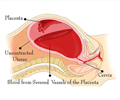
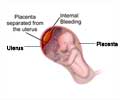
Abruptio Placenta:
The placenta may on occasion get separated from the uterine bed with bleeding occurring in the space between the uterus and placenta. This is referred to as “Abruption Placenta” and if the bleeding is of sizeable amount can give rise to an emergency situation for mother and baby. This dreaded complication can happen in a mother with pregnancy induced hypertension, placenta previa to name a few. It can seriously endanger the well being of the baby and often requires a cesarean section.
Pregnancy induced hypertension:
PIH or Toxemia of pregnancy” as it was known before is sudden rise of blood pressure during the last few months of pregnancy in a previously non-hypertensive mother along with swelling of the mother’s feet and legs or even entire body. There is also increased protein being sent out in the mother’s urine. This condition can be controlled by means of medications for the blood pressure and necessitates close monitoring of the baby as well as the mother. There may be restricted growth of the baby along with an increased tendency in the mother to bleed, to develop other complications like fits, kidney failure and so on.
Preterm labor:
Premature onset of labor leading to preterm delivery of the baby between 28 weeks to 35 weeks is not ideal for the baby. The baby may require a period of intensive care in the newborn intensive care unit. Having more than one baby, viz. twins or triplets predisposes to preterm labor. It may also occur due to illnesses in the mother like PIH and so on. Though preterm labor cannot be prevented always, those women at high risk of developing it must report to the doctor at the earliest hint of something suspicious like bleeding, passing of waters or low back pain or abdominal pain.
Intra-uterine growth restriction:
The baby may be very small and suffer from growth restriction within the mother’s womb. The baby will require a lot of special care after birth until it gains weight appropriate to its age. During such situations the waters surrounding the baby may be greatly reduced in quantity. This condition called oligohydramnios also heralds problems with the baby’s kidneys. Severe malnutrition, Anemia and illnesses such as PIH can result in IUGR.
Post-Dated pregnancy:
Delayed onset of labor pains at the end of term i.e after 40 weeks and non-responsiveness to induction of labor by drugs is one of the common causes leading to cesarean section. This is thought to be due to the sedentary life style of today’s world. The doctor will then try to induce a normal delivery or perform a cesarean section.
Obstructed labor:
After the onset of labor, there may be obstruction to the baby’s passage into this world due to the birth passage being too narrow. This may also necessitate a cesarean section. If the obstruction is not recognized and the labor continues it can lead to bursting or rupture of the uterus. This drastic scene has to be managed as an emergency.
Fetal distress:
During the course of labor or even prior to that the baby may show signs of distress in the form of lessened or absent movements or by a slowing if its heart beat. This means that the environment within the uterus is no longer friendly for the baby and it has to be delivered immediately, perhaps by a C-section.
Post-partum bleeding:
Excess bleeding during or immediately after the baby’s birth can lead to shock and is one the commonest causes of mothers dying following delivery, especially in developing countries. Ascertaining the mother’s blood group during the ante-natal visit is thus helpful in acquiring and transfusing blood in cases of heavy bleeding.
Rh incompatibility:
A mother having an Rh-negative blood group may carry an Rh positive baby. If the baby’s blood mixes with the mothers system at the time of delivery it can lead to a problem called Rh incompatibility, which has serious implications. Here is another scenario when blood grouping of the mother helps in the management of her baby. This can be avoided by giving the mother a dose of “Anti-D immunoglobulin” after delivery.
Post- Partum Psychoses:
Some women suffer from severe depression or even psychoses after the birth of the baby. This requires counseling and appropriate care by a psychiatrist. The cause for this problem is once more believed to be due to the changing hormonal milieu in the mother.
If this condition is not rectified it can even lead to suicide by the mother.
Intra-uterine Death of the baby:
Intra-uterine death of the baby is the most tragic complication and can occur due to various reasons. Careful monitoring of the baby and the mother can prevent this complication. It is a not infrequent occurrence in gestational diabetes, pregnancy induced hypertension. Rigorous adherence to treatment regime is a must to avoid this regrettable event.