- Types, Causes and Risk Factors of Pulmonary Fibrosis - (http://www.lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pulmonary-fibrosis/symptoms-causes-and-risk.html)
- Pulmonary fibrosis - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-fibrosis/basics/causes/con-20029091)
- Davidson's Principles of Medicine
What is Pulmonary Fibrosis?
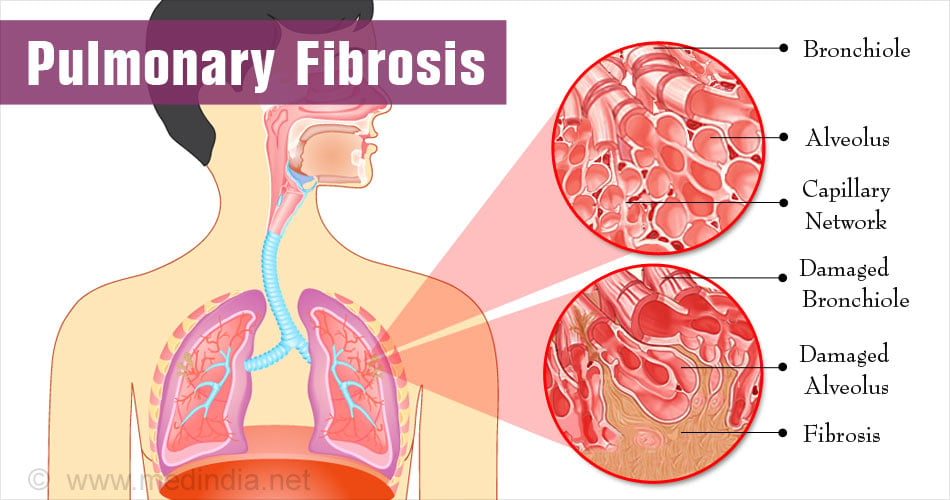
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition of the lung wherein the lung tissue gets scarred making it difficult to breathe. It is an autoimmune disease wherein the body’s immunity fights against lung tissue and damages it. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) where no cause is known for the disease, is the most common form of the disease. It is estimated that there are between 80,000 and 135,000 patients who suffer from this form of IPF in Europe.
It is an autoimmune disease wherein the body’s immunity fights against lung tissue and damages it.
IPF has no cure yet. Many people live only for about 3 to 5 years after diagnosis. The most common cause of death related to IPF is respiratory failure. Other causes of death include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
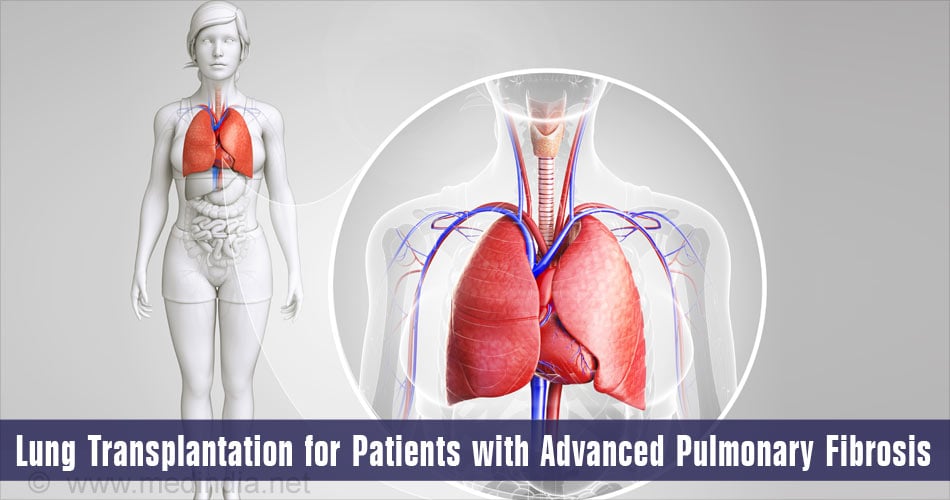
IPF is known to run in families and may have a genetic predisposition. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is not a curable disease and has a poor prognosis and the only treatment that benefits is lung transplantation and currently IPF is the most common indication for such transplantation in the United States. Recent studies show that both the lungs should be replaced rather than doing a single lung transplant for the condition.
The lungs consist of elastic air sacs through which exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Scarring of the lung tissue reduces the elasticity of the sacs and makes gas exchange difficult.
What are the Causes of Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis can be caused by various reasons.
- Idiopathic – Idiopathic means that the exact cause of the condition is unknown. Most cases of pulmonary fibrosis fall under this category.
- Exposure to certain promoting factors including viruses.
- Exposure to occupational dusts and airborne toxins, resulting in:
- Silicosis is common amongst quarry workers who inhale silica dust in the form of quartz.
- Coal worker’s Pneumoconiosis which occurs after a prolonged inhalation of coal dust.
- Asbestosis which occurs due to exposure to chrysotile (white asbestos) or amosite (brown asbestos).
- Berylliosis which occurs following inhalation of beryllium vapors and fumes.
- Intake of certain drugs like amiodarone or methotrexate, or exposure of the chest to radiation.
- Genetic causes.
- As a part of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cigarette smoking.

What are the Symptoms of Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is associated with various symptoms and signs like:
- Gradual onset of breathlessness/dyspnea – Breathlessness is caused due to increased scarring of lung tissue leaving less space for gas exchange at the level of the air sacs.
- A cough without a sputum or dry cough
- Generalized fatigue.
- Fast shallow breathing.
- Weight loss.
- Aching muscles and aching joints if the patient has rheumatoid arthritis.
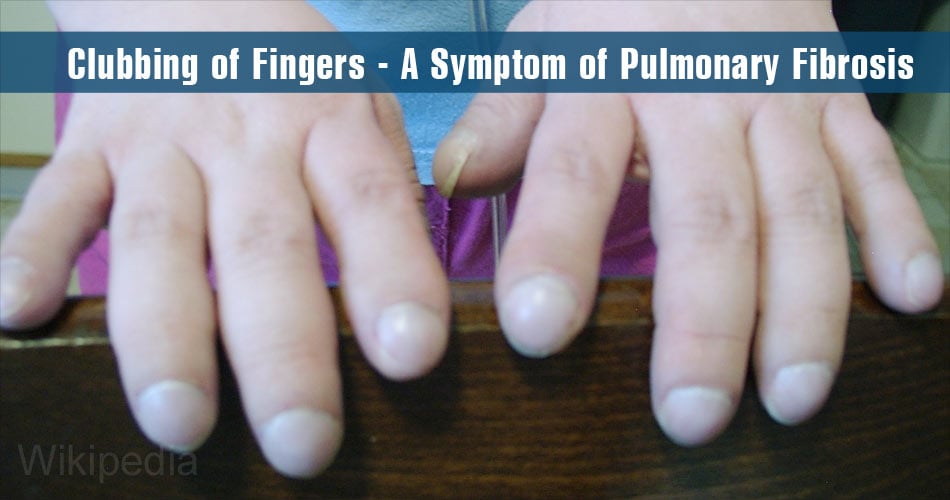
- Clubbing of fingers – Clubbing refers to round finger tips appearing as the shape of a club.
How Do You Diagnose Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is diagnosed based on history given by the patient and physical examination done by the clinician. There are also various tests and investigations to be done to support and confirm the diagnosis. Investigations include:
- Blood test – This is done to check for the presence of anti-rheumatoid factor, which indicates the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pulse oximetry - Estimation of oxygen levels in the blood through oximetry, to assess the extent of the pulmonary fibrosis. A simple sensor is clipped on to your ear or finger, which estimates the oxygen in the blood. A blood test can also be used to check the oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary function test – During a pulmonary function test, the patient breathes into a small instrument according to instructions given. In pulmonary fibrosis, the test may reveal reduced lung volumes.
- Chest X-ray – A chest x-ray may not show changes specific to pulmonary fibrosis. In some cases of pulmonary fibrosis, it shows honeycomb appearance of the lung. googlemiddleads
- HRCT (High Resolution CT scan). This test is more specific for the diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis.
- Lung biopsy – A lung biopsy is diagnostic for the condition. It is obtained through an endoscope.
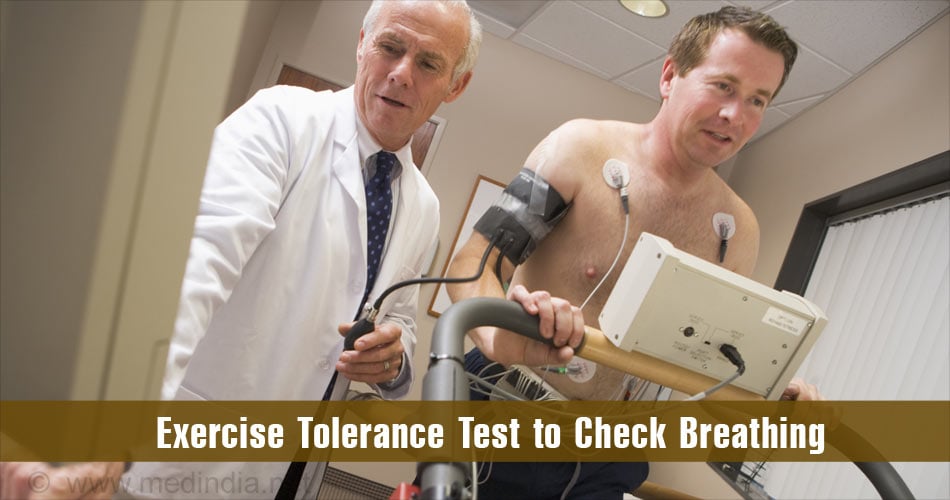
- Exercise tolerance test – This test is used to check breathing during exercise like running on a treadmill or using a stationary bike. A 6 minute walk test is also often used to understand the extent of the disease in the patient.
How Do You Treat Pulmonary Fibrosis?
No definitive treatment for pulmonary fibrosis has been found till date. Management includes:
- Medical management – Prednisolone, which is a corticosteroid and reduces inflammation, can be given to decrease tissue changes of pulmonary fibrosis. Other drugs to suppress the immune system like azathioprine and cyclophosphamide may be given. The drugs nintedanib and pirfenidone are specifically approved by the FDA for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- Oxygen therapy – It is a palliative method of treatment to replace the reduced levels of oxygen in the body.
- Vaccination against flu is advised.
- Lung transplantation – It must be considered in young patients with advanced disease.
Pulmonary Fibrosis Prognosis
Life expectancy is approximately 3 years on an average, but it varies from few months to many years based on disease progression. The prognosis or likely outcome for the patient may be obtained by serial lung function testing.
Health Tips
Cigarette smoking may be linked to pulmonary fibrosis and thus abstinence from smoking is an important factor in decreasing the incidence of pulmonary fibrosis. Smoking addiction can be dealt with by nicotine patch, early intervention, counseling, group discussions, etc.