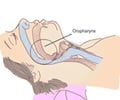
Classification of Sleep Disorders - Narcolepsy
A single sleep attack may last about 15 minutes or may even extend to an hour, after which the victim feels recharged, fresh and energized. The victim can have a recurrent attack in the hours following the first attack. The sleep attacks occur in cycles of wake up and sleep times.
For some narcolepsy victims, it may be a constant battle to overcome a general feeling of drowsiness throughout the day, though they may not necessarily fall asleep. Narcolepsy in spite of adequate therapy can sometimes be difficult to eliminate.
It usually begins in the teens or early twenties and affects an estimated 25 in every 100,000 people.
Symptoms of narcolepsy include-
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Cataplexy- A sudden temporary loss of muscle tone in the body, which occurs during times of intense emotional states like laughter or anger.
- Hallucination- Some patients hallucinate before they drift into sleep. This is medically called hypnogogic, while some experience hallucinations after waking up, medically termed as hypnopompic. The victims come out of the hallucination within minutes.
- Sleep paralysis- Some victims are unable to move as soon as they wake up or just before they drift into sleep.
Treatment of narcolepsy includes-
- REM sleep suppressants
- Anticataleptic agents
- Stimulant medications