- Abdominal Tuberculosis-Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Management - (http://www.apiindia.org/pdf/medicine_update_2007/102.pdf)
- Clinical Aspects of Adult Tuberculosis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4691808/)
- Active Tuberculosis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513246/ )
- Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis: the importance of laparoscopy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC539656/ )
- Treatment of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in adults and children. American Thoracic Society - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8000420)
About
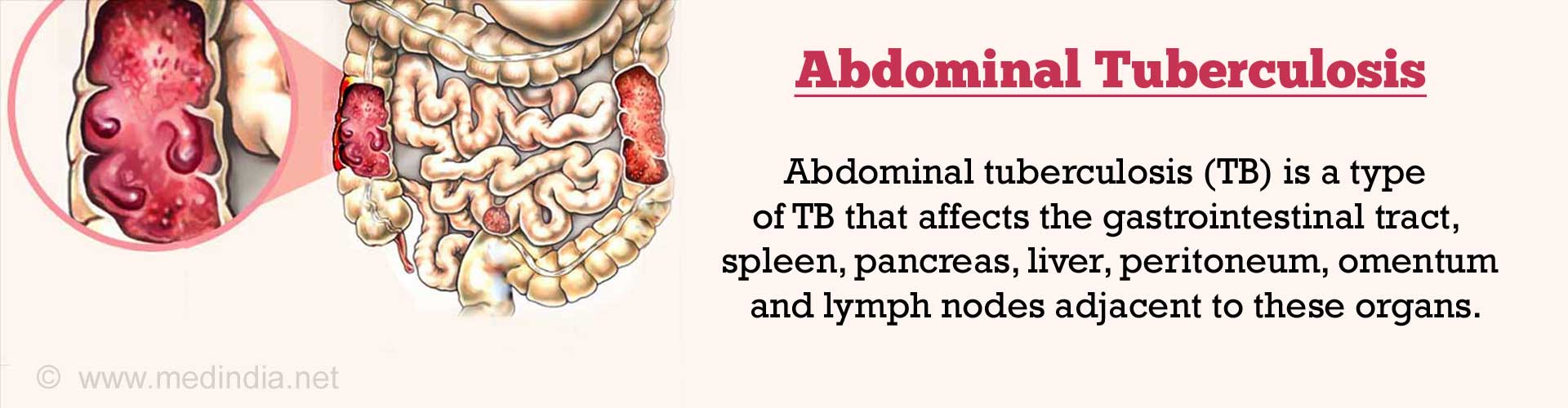
Abdominal tuberculosis, which is one of the forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, affects the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, pancreas, liver, peritoneum, omentum and lymph nodes adjacent to these organs.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Abdominal Tuberculosis-Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Management
Go to source)
Abdominal tuberculosis could be the result of a primary infection or the reactivation of a dormant focus (post primary tuberculosis). The latter can happen due to decreased immunity levels like in the case of severe infections, HIV, malnutrition etc.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Clinical Aspects of Adult Tuberculosis
Go to source)
With the increasing incidence of HIV, there is a rise in extra-pulmonary tuberculosis, that is, tuberculosis that occurs outside the lungs. Abdominal tuberculosis is one of the common forms of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. Common pathogens involved are Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis.
Spread of abdominal tuberculosis is through blood, direct contact with primary focus or ingestion of sputum containing bacilli from the active pulmonary focus.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Active Tuberculosis
Go to source)
There are three types of abdominal tuberculosis depending upon the kind of presentation. They are:
- Ascitic: This type of abdominal tuberculosis presents with accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, swollen abdomen and with nodules of 1-2mm in size over the peritoneum (the inner lining of the abdomen) which are slightly raised. It is also commonly referred to as wet type of abdominal tuberculosis.
- Obstructive: This type is also called dry type and manifests with adhesions over the omentum and loops of intestines causing them to become thick and rubbery and leading to intestinal obstruction.
- Glandular: This type affects mesenteric lymph nodes which enlarge in size and become firm, hard and are less mobile. They can at times be felt through the abdominal wall. Some amount of ascites and intestinal obstruction can be present but are not that characteristic.
Common symptoms of abdominal tuberculosis are:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Colicky pain in the abdomen
- Abdominal Swelling and tenderness
- Night sweats

Diagnosis & Treatment of Abdominal Tuberculosis
Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis is often clinical, but is confirmed with tests (blood test and other investigations). Treatment is with antitubercular drugs and surgery in combination or alone depending upon individual patient requirement.
Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis is made with the help of Mantoux test, liver function tests, ESR, serum albumin levels, x-rays/ ultrasound / CT scan abdomen, endoscopy, colonoscopy and laparoscopy. Fine needle aspiration cytology, peritoneal biopsy, ascitic fluid assessment with PCR assay and QuantiFeron - TB test are all effective in reaching a conclusion with the diagnosis.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis: the importance of laparoscopy
Go to source)
Treatment is with antitubercular drugs and/or surgery. Antitubercular drugs are given for at least six months initially; depending upon the results of response to therapy, treatment is continued further (12- 18 months). Common drugs employed are ethambutol, pyrazinamide, isoniazid and rifampicin.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Treatment of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in adults and children. American Thoracic Society
Go to source)
Surgical treatment is usually conservative. Correction for strictures with stricturoplasty and perforations in the intestines with resection and anastomosis is recommended. Intestinal obstruction is initially treated with drug therapy before proceeding to corrective surgeries.