Symptoms and Complications of Ascites
Abdominal swelling, swelling of hands and feet, shortness of breath, fatigue and weakness are the usual clinical features of a patient with ascites. Infection, causing Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis is the main complication.
A patient with Ascites may have the following symptoms-
- Increase in abdominal girth and swelling of the abdomen.
- Swelling of hands and feet
- Shortness of breath

- Severe fatigue and weakness

- Frequent heartburn and fullness after eating
- Change in bowel function
- Back pain

- Fever and abdominal pain in case of infection.
On examination, the following features may be observed-
- A full bulging abdomen is seen
- Shifting dullness: The dull sound that the physician elicits on tapping the abdomen shifts as the patient shifts his position, indicating the presence of fluid in the abdomen.
- Abdominal wall hernias may be present
- Patient is undernourished and shows muscle wasting
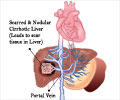
- The patient may show some features of portal hypertension, which include dilated veins in the palms and around the umbilicus, and enlargement of the spleen.
Complications
Complications of Ascites include:
1. Infection
Infection of the ascitic fluid can be spontaneous or secondary to an intra-abdominal surgical procedure.
- Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis is a spontaneous, severe bacterial infection of the ascitic fluid without an intraabdominal cause. The bacteria spread to the ascitic fluid from the gut.
Over 90% of the ascitic fluid infections are spontaneous
- Surgery or procedures used to drain ascitic fluid can also cause infection.
2. Hepatorenal Syndrome
Some patients with advanced cirrhosis and Ascites may suffer from kidney failure.
3. Hepatic Encephalopathy
This is a serious complication and is defined as an alteration in mental status and cognitive function which occurs in the presence of liver failure.
Certain toxins from the gut reach the brain because they cannot be removed by the sick liver. An increase in the ammonia levels play a role in causing the symptoms associated with hepatic encephalopathy.
4. Tense Ascites
Sometimes patients with ascites do not report to the physician until the pressure caused by the accumulated fluid causes difficulty in breathing. This then requires to be drained urgently.
5. Abdominal wall hernias
Umbilical or incisional hernias are common in patients with ascites. In general, these patients should avoid surgery and wear an abdominal binder.
6. Pleural Effusions
Accumulation of fluid just outside the lungs is called pleural effusion. It is common in patients with cirrhosis and ascites, especially on the right side. When it is large enough to obscure the right lung, it is called hepatic hydrothorax. Tuberculosis and pancreatitis should be considered when the effusion is left sided.