- Comprehensive Review of Tenecteplase for Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke - (https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/JAHA.123.031692)
- Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8903524/)
- Tenecteplase vs Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The ORIGINAL Randomized Clinical Trial - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39264623/)
- Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for treatment of acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9900099/)
- Comparative safety of tenecteplase vs alteplase for acute ischemic stroke - (https://www.strokejournal.org/article/S1052-3057(23)00490-1/abstract)
- Evidence that Tenecteplase Is Noninferior to Alteplase for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Meta-Analysis of 5 Randomized Trials - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31318627/)
- Intravenous Thrombolytics in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9807245/)
About
Acute ischemic stroke accounts for about 87% of all stroke cases worldwide, necessitating swift action to restore blood flow and minimize neurological damage.
Tenecteplase and Alteplase are key thrombolytics in this treatment. Evaluating their relative effectiveness and safety is vital for improving patient outcomes and informing clinical choices in acute stroke management(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Comprehensive Review of Tenecteplase for Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Go to source).
What is Acute Ischemic Stroke?
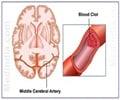
Acute Ischemic Stroke is when the blood supply to the brain is compromised due to a blood clot blocking an artery leading to the brain. As a result the tissues get damaged permanently and it should be treated as a medical emergency. High priority should be given to restoring circulation to the affected brain areas as soon as possible. Currently, thrombolytics and endovascular mechanical thrombectomy are the widely followed treatments(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review
Go to source).
Thrombolysis
The "golden hour" for acute ischemic stroke treatment emphasizes the critical 60-minute window in which timely interventions can significantly improve outcomes. During this crucial period, a thorough diagnostic assessment must be conducted to differentiate between stroke and conditions that may mimic it, as well as to identify any contraindications for administering thrombolytics(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Comprehensive Review of Tenecteplase for Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Go to source).
Thrombolysis, using the clot-busting drug rtPA (Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator), can enhance recovery chances by 30% when administered within 4.5 hours of ischemic stroke symptoms. Early treatment yields better results. tPA is listed among the WHO essential medicines, emphasizing the need for governments to ensure its availability through universal healthcare systems(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Intravenous Thrombolytics in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Go to source).

Alteplase vs Tenecteplase
The first FDA-approved thrombolytic agent for Acute Ischemic Stroke, alteplase is administered as a continuous intravenous infusion. It has a relatively short half-life, necessitating careful monitoring and dosing adjustments during administration(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review
Go to source).
Desmoteplase, Reteplase and Tenecteplase (TNK) are some of the thrombolytic agents currently studied in the management of arterial ischemic stroke. Developed through mutagenesis of alteplase, Tenecteplase features amino acid substitutions that enhance its thrombolytic potency, prolong its half-life, and improve resistance to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Intravenous Thrombolytics in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Go to source).
Pharmacokinetics
Alteplase: It has a half-life of approximately 5 minutes and requires careful infusion over 60 minutes. This rapid clearance can complicate its use, especially in acute settings where timing is crucial(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for treatment of acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials
Go to source).
Tenecteplase: With a longer half-life of about 20 to 24 minutes, it can be administered as a single bolus dose. This property reduces the burden on healthcare providers during critical moments, allowing for quicker and potentially more efficient treatment(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review
Go to source).
Efficacy
Alteplase is established as the standard treatment in multiple trials, showing significant improvements in patient outcomes. Tenecteplase has shown promising results in smaller studies, with higher reperfusion rates, but lacks direct comparison data against alteplase in large-scale trials(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The ORIGINAL Randomized Clinical Trial
Go to source).
Safety Profile
Alteplase carries a 6-7% risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), while tenecteplase appears to have lower rates of ICH based on early studies. However, further data is required to establish the long-term safety of Tenecteplase in diverse patient populations(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The ORIGINAL Randomized Clinical Trial
Go to source, 5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Comparative safety of tenecteplase vs alteplase for acute ischemic stroke
Go to source).
Administration and Logistics
Alteplase requires a 60-minute infusion, necessitating careful monitoring, while tenecteplase allows for rapid administration as a fixed dose. This difference simplifies logistics and may improve efficiency in emergency settings(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Evidence that Tenecteplase Is Noninferior to Alteplase for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Meta-Analysis of 5 Randomized Trials
Go to source).
Clinical Applications
Alteplase is the standard treatment for acute ischemic stroke (AIS), proven effective in restoring blood flow within a 3 to 4.5-hour window, significantly reducing long-term disability. Tenecteplase is emerging as a promising alternative, showing higher reperfusion rates in initial studies, particularly beneficial in busy emergency settings due to its single bolus administration(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Intravenous Thrombolytics in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Go to source).
In STEMI, alteplase is widely used, while tenecteplase was once favored for its safety profile. However, with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) becoming the norm, Tenecteplase is reserved for cases where PCI is unavailable(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Comparative safety of tenecteplase vs alteplase for acute ischemic stroke
Go to source).
There is ongoing research into tenecteplase’s potential for extended treatment windows beyond 4.5 hours and its use in large vessel occlusions. Additionally, studies are exploring combination therapies with antiplatelet agents to enhance treatment outcomes(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for treatment of acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials
Go to source).
In managing acute ischemic stroke, alteplase remains the gold standard due to its established efficacy. However, tenecteplase offers advantages like easier administration and potential benefits in specific cases. Ongoing research will clarify their optimal use, allowing clinicians to provide the best care for patients experiencing thrombotic events.