Treatment
Testicular tumor treatment is an example of our improved understanding of the disease and the success with adjuvant therapy, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, along with radical surgery.
Patients who present with symptoms other than a palpable lump, are administered antibiotics to rule out epididymis or orchitis. If the symptoms do not subside in 2 weeks time an ultrasound of the testicles is recommended.
Once a person is diagnosed with testicular cancer, a surgery known as the radical inguinal orchiectomy is carried out to remove the affected testicle. An evaluation of the cancer cell type helps to decide on the mode of treatment.
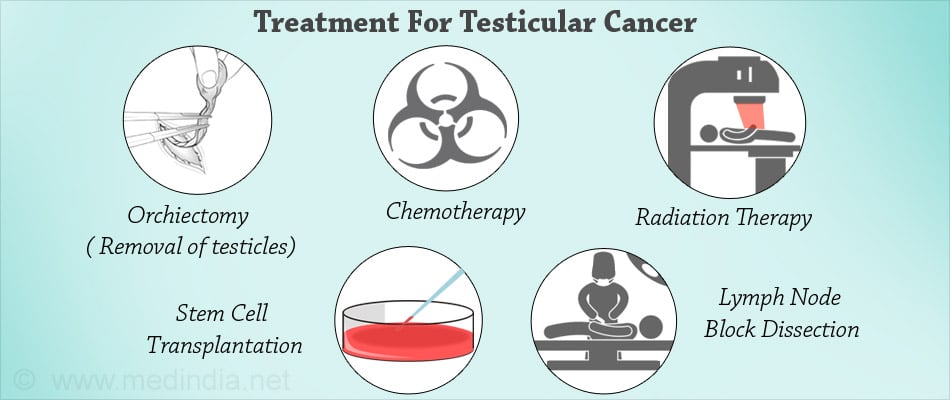
The phenomenal cure rate of testicular cancer in recent times has been attributed to improvement in adjuvant therapy which is given to patients after the surgery. This treatment may involve chemotherapy, radiotherapy or watchful surveillance. The latter includes regular checkups, scans and consultation with the doctor.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy drugs are administered to treat testicular tumors or to prevent their spread. The drugs are usually administered intravenously. The procedure requires hospitalization and rest.
Most chemotherapy regimens are given in cycles and are based on using 3 drugs including cis-platin. Some of the popular chemotherapy drugs and their side effects are described below:
- Cisplatin: Using platimum based drugs, such as cis-platin, has revolutionized the cure of testicular cancer, while improving the chances of survival. Side effects may include nausea, vomitting, renal impairment, neuropathy (charecterizd by tingling and numbness of hands) and changes in hearing and taste.
- Bleomycin is a type of antibiotic that is toxic to cells.It binds to the DNA of malignant cells and prevents division. Side effects include fatigue, skin reactions, loss of apetite/ hair/fertility and sore lips/mouth. Some people treated with bleomycin suffer from a general feeling of sickness, pulmonary fibrosis and myelosuppression.
- Etoposide: This drug too like the others mentioned are used to treat different cancers. It functions by blocking the enzyme topoisomerase 2, which is required for cell division. It may be given as a capsule or may be administered intravenously.
Radiotherapy:
It is carried out to destroy the malignant cells that may exist post-surgery. Radiation is most often employed to treat malignancy that has spread beyond the testes to the lymph nodes behind the abdomen.
Some of the common side-effects of the treatment include:
- Changes in the skin, such as redness or soreness
- Tiredness
- Diarrhea
The type of adjuvant therapy that a person deserves is determined by the histology of the tumor cells and the stage of the disease.
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND)is carried out in the case of stage I non-seminomas. But this method is loosing its popularity due to the money and expertise required to carry it out. Lymph node surgery may also follow chemotherapy in the advanced stages of the initial cancer or in the case of large nonseminomas.
The treatment of testicular cancer depends entirely on the type of tumor. Seminomas are radiosensitive so they are treated by subjecting them to radiation. But non- Seminomas are radio-resistant, hence surgery is more suited to treat this form of tumor. Advanced form of testicular cancer always responds well to chemotherapy.
There may be side-effects from treatment but they are usually short-term.
Young men who have not finished their families are normally advised to get their sperm stored and cryo-preserved as the treatment can make the person sterile.