- What is Tonsillitis? - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544342/)
- Acute tonsillitis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22338587/)
- Chronic tonsillitis and biofilms: a brief overview of treatment modalities - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6134941/)
- Peritonsillar Abscess - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519520/)
- Tonsillitis and sore throat in children - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4273168/)
- Follicular Or Croupous Tonsillitis - (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/445260)
- Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9745311/)
- The analysis of risk factors associated with tonsillitis in district Mardan, Pakistan - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32799268/)
- Overview of Tonsillitis - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tonsillitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378479)
- Understanding Recurrent Tonsillitis - (https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/understanding-recurrent-tonsillitis)
- Tonsillitis - (https://medlineplus.gov/tonsillitis.html)
- Tonsillitis and sore throat in children - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4273168/)
- Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536942/)
- Coblation versus other surgical techniques for tonsillectomy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6483696/)
- Tonsillectomy - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003013.htm)
- Tonsillitis: Overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK401249/)
- About Tonsillitis - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21146-tonsillitis)
About
Tonsillitis refers to acute inflammation of the tonsils.
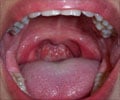
The tonsils (mostly referring to the palatine tonsils) are two small lymphoid organs that lie on either side of the back of the throat that one can see when the mouth is opened.
The adenoids are found behind the nose and high up in the throat(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Tonsillitis?
Go to source). The adenoids are situated behind the nose and quite high up the throat. Adenoids unlike tonsils require special instruments to be viewed. Lingual tonsils are also situated at the back of the throat.
Tonsillitis occurs primarily in children and sometimes in adults. Tonsillitis in adults is mostly due to viral infections, but it could also be caused by a bacterial infection such as strep throat. Some of the signs and symptoms of tonsillitis include fever, swollen tonsils, sore throat, difficulty or pain while swallowing and tender lymph nodes on the sides of the neck(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Tonsillitis?
Go to source). It can be classified as acute, recurrent, or chronic tonsillitis.
The infections that cause tonsillitis are contagious and can be transmitted through the air or contaminated objects. Both the tonsils and adenoids act as the body’s first line of defense (by producing antibodies) to protect the throat against disease germs that enter via the nose and mouth. Incidentally, this also makes these lymph nodes particularly vulnerable to infection and inflammation.
What are the Types of Tonsillitis?
- Acute Tonsillitis or acute sore throat is caused either by a virus or bacteria(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Acute tonsillitis
Go to source). - Recurring Tonsillitis: Occurs when there are up to seven culture-proven episodes of tonsillitis or throat infections in one year, five in two consecutive years or three each in three consecutive years. In such cases, the cessation of the antibiotic leads to another bout of the bacterial infection within a few weeks, thus causing it to recur again(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Chronic tonsillitis and biofilms: a brief overview of treatment modalities
Go to source). - Chronic Tonsillitis: Occurs when recurring tonsillitis infections cause chronic sore throat, Bad breath and persistent tender cervical nodes(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Chronic tonsillitis and biofilms: a brief overview of treatment modalities
Go to source). - Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA) or Quinsy: Peritonsillar Abscess is a bacterial infection that develops lateral to the tonsillar region when an acute tonsillitis infection has been left untreated. An abscess or a swollen area with pus forms in this peritonsillar region. The pathogens are typically Staphylococci, Streptococci, Haemophilus and Fusobacterium necrophorum. No virus is involved. Severe throat pain,
fever , drooling, foul breath, difficulty opening the mouth, and altered voice quality are the symptoms(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Peritonsillar Abscess
Go to source). - Tonsil or Tonsillar Hyperplasia or Tonsillar Hypertrophy: Abnormal enlargement of the palatal tonsils with cardinal symptoms including snoring, difficulty in swallowing and (rarely) difficulty in speaking(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillitis and sore throat in children
Go to source). - Follicular Tonsillitis: Follicular tonsillitis usually begins with a temperature of 102 to 104 degrees, accompanied by chills and rigors, a full bounding pulse, throbbing headache, aching of the bones of the extremities and loss of appetite. The tonsillar symptoms do not become prominent until six to twelve hours later(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Follicular Or Croupous Tonsillitis
Go to source).
What are the Causes of Tonsillitis?
The most common cause of tonsillitis is either a bacterial or a viral infection(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Tonsillitis?
Go to source).
- It can spread from person to person by coughing and sneezing.
- Adults who have some form of immunodeficiency (for e.g. HIV-infected patients) are also susceptible to tonsillitis.
- Taking antibiotics which destroys the normal flora of organisms in the mouth and uncontrolled diabetes are other causes of tonsillitis.
- Adenovirus, rhinovirus, influenza, coronavirus, and respiratory syncytial virus are the most common viruses that cause acute tonsillitis. Less common viruses are the herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus, and HIV.
- Most bacterial tonsillitis (strep throat) is caused by Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS)(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections
Go to source).

What are the Risk Factors of Tonsillitis?
Age - Children above the age of 2 are more likely to get tonsillitis. Bacterial tonsillitis is more common in children between 5 and 15 years of age. Tonsillitis is rare in adults.
Exposure - Daycare and school going children are more exposed to tonsillitis due to close contact with other children and exposure to viral and bacterial infections(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
The analysis of risk factors associated with tonsillitis in district Mardan, Pakistan
Go to source).
What are the Symptoms of Tonsillitis?
Common symptoms of an acute tonsillitis are(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Tonsillitis?
Go to source):
- Sore throat - Pain in the throat
- Tender, red, swollen tonsils or lymph glands in the neck or jaw with white spots or pus
- Difficulty swallowing and hence difficulty in ingesting
- High to moderate rise in body temperature / fever >38.3°C measured rectally
- In case of sepsis on the tonsils, there may be fever with chills.
- Blisters or painful ulcerated areas on the throat
- Cough
- Headache
- Lethargy and malaise (discomfort)
Tonsillitis symptoms in adults(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Overview of Tonsillitis
Go to source):
- Red, swollen tonsils.
- White or yellow coating or patches on the tonsils.
- Sore throat.
- Difficult or painful swallowing.
- Enlarged, tender glands (lymph nodes) in the neck.
- A scratchy, muffled or throaty voice.
Infected tonsils and adenoids block the normal breathing of a person and the drainage of the sinuses. This obstructed air passage can cause:
- Sleep disorders like apnea
- Snoring in children
- Pain in the ear and neck
- Bad breath
What are the Complications from Tonsillitis?
Recurring Tonsillitis leads to inflammed or swollen tonsils. In the long run it could cause(10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Understanding Recurrent Tonsillitis
Go to source) -
- Obstructive sleep apnea (disrupted breathing)
- Tonsillar cellulitis or infection of the surrounding tissues
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Difficulty in breathing
Tonsillitis caused by group A streptococcus or another strain of streptococcal bacteria when left untreated poses risk of rare disorders such as(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
What is Tonsillitis?
Go to source):
Rheumatic fever, an inflammatory disorder that affects the heart, joints, skin and brain. It affects children between the age of 5 and 15 and usually develops 2 weeks after untreated or partially treated strep throat or scarlet fever.
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, develops 1 or 2 weeks after an untreated throat infection. It causes inflammation of the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli or the filtering units of the kidneys. This results in impaired filtration and inadequate removal of waste and excess fluids from blood.
How is Tonsillitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical symptoms.
Initial diagnosis is done by a physical inspection of the mouth, throat, ears and nose using a lighted instrument.
In case of infection, the tonsils will be enlarged, usually red with white spots on them. Some cases of strep throat might reveal a rash. Gentle examination of the neck and jaw will reveal swollen, tender glands.
A throat swab or a culture of the tonsils is taken to identify bacterial infection. In particular, the diagnosis of GABHS tonsillitis is confirmed by obtaining cultures from both tonsillar surfaces and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
A Complete Blood Cell count (CBC) can also be taken to check whether the infection is caused by a bacteria or a virus(11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillitis
Go to source).
How is Tonsillitis Treated?
Tonsillitis treatment is given based on whether it is caused by a virus or bacteria.
- Viral tonsillitis : A tonsillitis caused by a virus can usually be managed without the use of antibiotics. The body will recover normally in 7 - 10 days.
- Bacterial tonsillitis requires a course of antibiotic treatment(12✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillitis and sore throat in children
Go to source).
Antibiotics to treat Tonsillitis
Among the beta-lactam antibiotics,
For children under 12 years of age and for chronic recurrent tonsillitis,
An alternative to the long-term penicillin therapy is the short-term therapy with azithromycin (20 mg/kg) for three days or clarithromycin and cephalosporin for five days. However it has not been evaluated whether the short-term therapies are effective in preventing the late complications of Rheumatic fever and
Hospitalization may be required in severe cases if the fever does not subside within the stipulated number of days. A continuous intravenous supply of fluids and antibiotics will help retain fluids and control pain.
Surgery is an option to treat the following:
- Frequently recurring tonsillitis that causes complications like Obstructive sleep apnea, or difficulty in breathing or swallowing
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Bacterial tonsillitis that does not respond to antibiotic treatment or
- Peritonsillar abscess formed around the tonsils
Tonsillectomy is performed using a scalpel under a general anesthetic and the tonsils are removed from the wall of the throat, and the blood vessels attached to them are tied off. It is also known as a "total" or "extra-capsular" tonsillectomy(13✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
Go to source).
One surgical method is the Cold Dissection method that uses a raspatory or a course file and the scissors to dissect the infected tonsils from the tonsil bed. The blood vessels feeding the tonsils are pinched off and then selectively ligated or coagulated with bipolar forceps. Bleeding is stopped by pressing a dry swab into the tonsil bed for about 1 minute.
Coblation advanced technology: This method involves the use radiofrequency energy and saline to create a plasma field that effectively dissociates the molecular bonds of the target tissues(14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Coblation versus other surgical techniques for tonsillectomy
Go to source).
Tonsillectomy is an outpatient procedure, unless complications arise during surgery. Recovery period is usually 7 to 14 days. Drawbacks are post operative pain and bleeding. Surgical procedures that reduce the bleeding are continuously evaluated.
Of late, surgeons have reverted to a safer procedure Tonsillotomy or the partial removal of the tonsils. Only the portion bulging into the throat or medial portions of the tonsils are removed in this procedure(15✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillectomy
Go to source).
This procedure has a lower hemorrhage rate, shorter procedure time, and more rapid recovery to a pain-free state. A long-term follow-up done indicated that partial removal of the tonsils is as effective as total tonsillectomy for the long-term management of children suffering from
In the case of peritonsillar abscess (PTA), an alternate option to tonsillectomy is to drain it either by a needle and syringe or by incision - cutting it with a scalpel and allowing the pus to drain(16✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tonsillitis: Overview
Go to source).
How do you Prevent Tonsillitis?
- Keep a safe distance from tonsillitis patients and avoid sharing utensils and drinking glasses with them
Wash hands frequently (especially before eating) using a mild soap- Cover your mouth with a tissue or the hand when you Cough or sneeze, and teach your children to do the same. Wash hands after coughing or sneezing.
- Keep your child at home if they are sick.
- Tonsillitis can also be treated with homeopathic medicine.

Home Remedies for Tonsillitis
These guidelines are for tonsillitis caused by viruses (where antibiotics are not prescribed) and bacteria (to provide extra comfort and to reduce pain).
- Take plenty of rest.
- Gargle with warm salt water (1 teaspoon in a glass of water) if throat is paining.
- Consume adequate warm fluids to soothe the throat and prevent
dehydration . - Use a cool-mist vaporizer or humidifier in the room for
easy breathing . - Use a pain killer like
paracetamol / acetaminophen and / or ibuprofen if throat pain persists. - Using lozenge can keep the mouth and throat moist and more comfortable.
- Keep clear of household irritants like
cigarette smoke and cleaning products.