- Pruritus in Female Patients - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/541867)
What is Vaginal Itching?
Itching around the vaginal and vulvar regions are common symptoms that affect women of all age groups. In some cases, the cause is local like a local infection. In other cases, conditions that cause itching in other parts of the body may also be associated with vaginal itching.
Diagnosis of vaginal or vulvar itching is made based on the history and physical examination of the patient. Culture of vaginal swab may be obtained if an infection is suspected. A biopsy of an itchy lesion may help in diagnosis of the cause and to rule out cancer.

If there is no definite underlying cause, vaginal itching usually subsides with adequate hygiene of the private parts. Though women may feel that vaginal douching will improve the cleanliness, it is actually untrue. Vaginal douching removes all the protective bacteria from the vagina, making it easier for disease-causing organisms to attack.
What are the Causes, Diagnoses and Treatments for Vaginal Itching?
Some of the conditions that could cause vaginal or vulvar itching include:
Infections: The normal vagina in women is acidic in nature due to the presence of lactobacilli. These have a protective effect on the vagina and prevent the growth of disease causing organisms. Itching may be due to:
- Fungal infection: Candidiasis is a fungal infection which results in a thick, curdy white vaginal discharge with itching. The vagina and vulva appear red and inflamed. It is commonly seen in women in the reproductive age group and during antibiotic use, which may kill the lactobacillus. Conditions that reduce immunity like diabetes, use of corticosteroids and HIV may also result in candidal infection. Diagnosis is confirmed through laboratory testing of vaginal swab. Treatment is with anti-fungal medications. Ringworm infection is another fungal infection that can affect the vulvar skin and result in itching. The lesions are characteristic with the edges being more prominent. Ringworm is also treated with antifungal drugs.
- Parasitic infection: Vaginal infection with a protozoan called can result in itching, burning, redness, difficulty in passing urine and vaginal discharge. Treatment is with medications, Metronidazole or tinidazole. Other parasites like scabies and pubic lice may also cause vulva itching. These can be detected on physical examination.
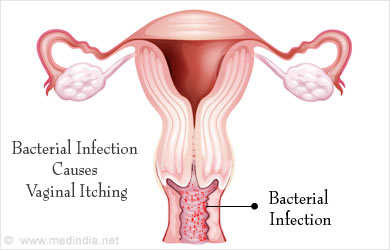
- Bacterial infection: Bacterial infection of the vagina may also result in itching. The infection often causes a thick and foul-smelling discharge, which may be yellowish to greenish in color. Many bacterial infections are transmitted sexually. The infections are diagnosed based on history, physical examination and sometimes culture of the organisms. More serious infections like gonorrhea and chlamydia should be ruled out.
- Worm infestation: Infestation with pinworms can also cause irritation and redness of the vulvar and vaginal region. It is common in young girls. It is treated with deworming.
Atopic and contact dermatitis: Allergy or irritation from the use of certain soaps, use of sanitary pads, lubricants etc. which come in contact with the vagina may cause a skin reaction, which causes itching. Urinary and fecal incontinence, and poor hygiene can also result in itching. The skin in the vulvar region may be reddened or thickened. Some pain may be present if the woman develops superficial skin cuts. It is necessary to obtain a list of products that come in contact with the region.
Atrophic vulvitis: Atrophic vulvitis is a condition where the skin of the vulva thins out in postmenopausal women. It occurs due to lack of estrogen at this age. Women may complain of itching or burning feeling in the vulva. The vulva is also susceptible to repeated infections, which can worsen the burning. Local estrogen is applied to the affected skin to treat the condition.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy causes increase in vaginal discharge, which could be one of the reasons for vaginal itch during pregnancy.
Other skin lesions that affect other parts of the body can also affect the vulva and sometimes the vagina and cause itching. These include:
- Lichen simplex chronicus, which results from repeated itching due to other conditions like lichen sclerosus. Nerve-related conditions like diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia that cause itching may also cause lichen simplex chronicus. The skin appears thicker and darker than normal.
- Lichen sclerosus, where an eight shaped white plaque is formed around the vulva and anus. Besides itching, soreness and burning may also be present. Diagnosis is through physical examination.
- Lichen planus, which is similar in presentation to lichen sclerosis. However, it has more extensive involvement, and can affect the vagina in addition to the vulva. Therefore, it can result in pain during sex. It may appear as erosions, small boils or whitish thickened skin.
- Psoriasis, which appears as a red raised patch near the vulva or the anal region. The patient presents with itching, burning and pain. It usually does not affect the vagina. Psoriatic lesions may be present in other parts of the body as well.
Vulvar cancer: In rare cases, cancer of the vulvar region may be associated with itching. The patient may also complain of some bleeding and pain in the region. A swelling or an ulcer may be noted on examination. A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis.
Systemic illness: Conditions like liver or kidney disease that result in generalized itching can also result in itching of the vulvar and vaginal region. These are detected using blood tests.