- Arthropod-borne Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat - By Susan E. & Shaw, Michael J. Day
- Vector-borne diseases - (http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthtopics/climate_change/health_effects/pages/vector_borne_diseases.aspx)
About
Vector-borne diseases are infectious diseases or illness transmitted through insects. Maintenance of good hygiene, pest control and vaccination are very important to prevent the spread of these infectious diseases.
Vector-borne diseases are infectious diseases or illness transmitted through insects such as mosquitoes, sandflies, ticks, fleas, lice, bugs and flies. Vectors can be classified as biological vectors or mechanical vectors. Biological vectors like mosquitoes and bedbugs carry the pathogen within their bodies and transmit them to the new host by biting. Mechanical vectors like flies pick up infectious agents outside their bodies and transmit them via physical contact. This article covers some diseases spread by biological vectors.

Vector-borne diseases are prevalent all over the world, especially in low socioeconomic regions. Most of the diseases are contagious. It is necessary to control the disease transmitting vectors, which have a negative impact on physical and mental well-being of the patient and the economy of the country. Maintenance of good hygiene, pest control and vaccination are very important to prevent the spread of these infectious diseases.
Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquitoes are prevalent worldwide from the Tropics to the Arctic region. Anopheles, Aedes and Culex are the main genera that bring about the transmission of various epidemic and endemic diseases. The list of major diseases that are transmitted by the mosquitoes is listed below:
Malaria:
- Malaria is one of the life-threatening parasitic diseases. It is caused by the protozoan, Plasmodium. The genus includes four species P.vivax, P.falciparum, P.malarie and P.ovale.
- The causative organism is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito.

- Symptoms of malaria include chills, fever, headache, malaise and myalgia. Symptoms may develop as early as 7 to 14 days after initial infestation. Falciparum malaria can result in seizures, mental confusion, kidney failure, and lung disease, which may require emergency treatment.
- Malaria is diagnosed based on physical examination, signs and symptoms experienced by patient, and blood tests. Polymerase chain reaction test is also used to detect malaria parasite.
- Malaria is treated with antimalarial drugs. The drug regimen is optimized based on the species of malaria parasite, concomitant medication and underlying condition of the patient.
West Nile Fever:
- West Nile Fever (WNF) is caused by West Nile virus. It mainly infects birds and is transmitted to human beings through the bite of an infected Culex mosquito.
- It is more prevalent in Africa, Middle East and West Asia.
- WNF is usually asymptomatic, but the patient may develop mild symptoms like headache, fever, skin rash, body aches and swollen lymph glands. The patient may develop meningitis or encephalitis resulting in severe symptoms like high fever, neck stiffness, tremor, coma, muscle weakness, convulsions and paralysis.

- WNF has no specific treatment or vaccine to prevent it. Treatment for chronic illness includes hospitalization, respiratory support, intravenous infusions and prevention of secondary infections.
Dengue:
- Dengue fever is the disease transmitted through infected Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- The disease symptoms develop after 5-6 days of being bitten by infected mosquito. Symptoms include severe headache, abrupt onset of fever, muscle and joint pains, skin rash similar to measles, nausea and vomiting.

- Dengue hemorrhagic fever and shock syndrome are severe forms of the disease which are characterized by frequent vomiting with or without blood, severe abdominal pain, bleeding from nose, mouth and gums, skin rashes, dryness of mouth and weak pulse. These conditions require hospitalization.
- Treatment is symptomatic as no specific drug or vaccine is available for dengue.
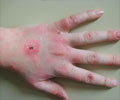
Filariasis:
- Filariasis is caused by the parasite Wuchereria bancrofti that is transmitted by the infected mosquitoes of species Culex quinquefasciatus and Mansonia annulifera/M.uniformis. The parasite moves inside the body to reach the lymphatic system.
- The disease causes swelling of legs with thickening of skin and underlying tissues and skin rash. W.bancrofti may also affect legs, ear lobes, arms, vulva, breasts and scrotum.
- Finger prick test is used to diagnose microfilariae in the blood to identify filariasis. Treatment involves the administration of anti-filarial medications.

Japanese Encephalitis:
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is a disease is transmitted by Culex mosquito.
- It primarily affects birds and animals and accidentally affects humans.
- JE causes encephalitis and meningitis. Symptoms include severe headache, fever, stupor, tremors, disorientation, coma, loss of coordination and other meningeal signs.
- Diagnosis is based on various blood tests. Treatment is symptomatic.
Chikungunya:
- Chikungunya is caused by Alpha virus spread by the bite of the infected Aedes mosquito. The disease is prevalent in Africa, South East Asia and India.
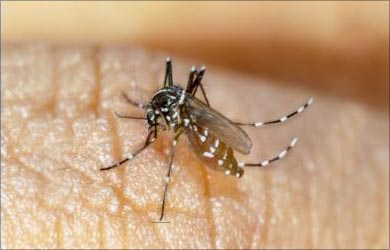
- Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, skin rash, nausea and vomiting. The patient shows a contorted posture with severe joint pain.
- Treatment is symptomatic.
Bug-Borne Diseases:
Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease or American Trypanosomiasis is a disease spread by triatomine bugs. These bugs transmit the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, thecausative agent of Chagas disease.
- Symptoms of Chagas disease include malaise, fever, swelling of eyes and swollen lymph nodes. The patient may suffer from heart disease.
- Diagnosis is based on patient history, physical examination, and blood tests to detect the presence of parasite T.cruzi. Once diagnosed, additional tests like ECG, abdominal x-ray and upper endoscopy are conducted.
- Treatment includes antiparasitic drugs to kill the parasite T.cruzi, and symptomatic treatment to manage the signs and symptoms of the disease. Medication is more effective during the early stages of the disease.
Sand-fly Borne Diseases:
Kala-Azar or Leishmaniasis:
- Leishmaniasis or Kala-Azar or Black Fever or African Trypanosomiasis is a disease caused by protozoa Leishmania. Infected sand fly or tse-tse fly (Phlebotomus aregentipes) acts like an intermediate host to transmit the disease.
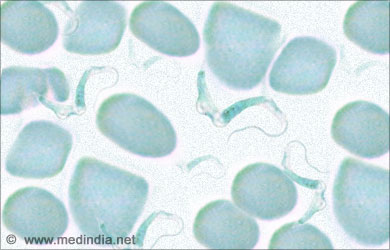
- Symptoms include recurrent fever, loss of appetite, anemia, dryness and discoloration of skin, and enlargement of spleen and liver.
- The disease is identified through physical examination, and serological tests. Treatment includes antileishmanial drugs and antibiotics.
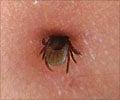
Tick-Borne Diseases:
Ticks are blood-feeding ectoparasites that transmit viral, bacterial and protozoan pathogens. Some of the tick-borne diseases are listed below:
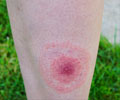
Lyme Disease:
- Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Infected Ixodes scapularis ticks acts as vectors in transmission of the disease.
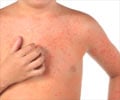
- Symptoms associated with the disease are dizziness, body and joint pains, and a distinct circular red rash (erythema migrans).
- The disease can be diagnosed on physical examination and blood tests.
- It is treated with antibiotics.
Relapsing Fever is also caused by a species of Borrelia bacteria which is transmitted by ticks and lice.
Babesiosis:
- The parasite Babesii microti causes babesiosis. It is transmitted by the bite of infected deer tick or Ixodes scapularis.
- Symptoms include headache, muscle pain, fever with chills, fatigue, sweating, nausea, vomiting and weakness.
- Diagnosis is based on physical examination and blood tests.
- Treatment includes antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever:
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is an infection caused by Rickettsia ricketsii. It is transmitted by the bite of infected American dog tick and Rocky mountain wood tick.
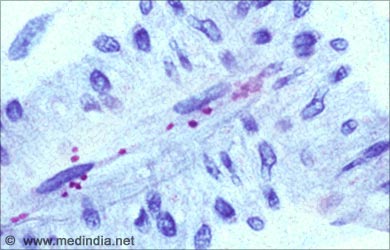
- Symptoms include moderate to high fever with chills, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, severe muscle pain, headache, weakness, and non-itchy red-spotted rash on wrist, forearms and ankles.
- The disease is diagnosed through physical examination and blood tests.
- Treatment includes antibiotics for a minimum for the three days after the fever subsides.
Tularemia:
- The bacterium Francisella tularensis is the causative organism for the disease Tularemia. Ticks, flies and other bugs mainly transmit the disease to small mammals like rabbits, rodents etc. Humans are infected through the bite of infected ticks, contaminated food and by handling infected animals. The disease is mostly prevalent in Northern America, Europe and Asia.
- Symptoms include chills, sudden fever, muscle pain, stiffness of joints, diarrhea, and dry cough. The patient may also develop mouth ulcers, sore throat, swollen and painful lymph glands. Some patients develop pneumonia.
- Diagnosis is based on physical examination and blood test. The disease is treated with antibiotics.
Other Important Insect-borne diseases are:
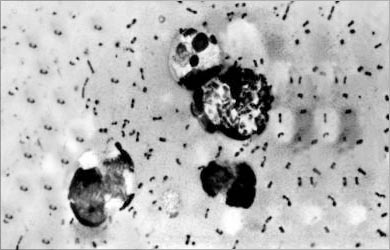
- Plague: Caused by enterobacterium Yersinia pestis. It is transmitted from rodents to humans through the bite of infected fleas.
- Rift Valley Fever (RFT): RVF is caused by Phlebovirus which is transmitted by infected mosquitoes of Culex and Aedes species.
- Yellow fever: Yellow Fever is caused by Flavivirus and is transmitted by infected mosquitoes of genus Aedes.
- Epidemic Typhus: Is caused by Rickettsia virus and is transmitted by head lice (Pediculus humanus).
- Ross River Virus: This disease is caused by Alpha virus which is endemic to Australia and transmitted by mosquitoes.
General Measures to Avoid Insect-borne / Bug-Borne Diseases:
Insects play a major role in transmission of many diseases, which are sometimes life-threatening and affect public health and economy. Hence, it is necessary to take preventive measures to avoid such diseases, especially in areas where these insects are prevalent.
- Avoid insect bites by wearing long sleeved clothing and long pants.
- Use insect repellents like DEET.
- Adopt regular pest control measures.

- Avoid traveling to places with high prevalence of disease. If you have to travel, it is advisable to get vaccinated when possible, sleep in screened areas or air-conditioned rooms, or use bed nets.

- Always wash and cook any food that could be contaminated with insect feces to avoid risk of infection.