- Eye & Vision Problems - (http://www.aoa.org/patients-and-public/eye-and-vision-problems)
- Types of Visual Problems and Anxiety - (http://www.calmclinic.com/anxiety/symptoms/visual-problems)
About
Common conditions that give rise to vision problems are refractory errors, corneal ulcer, cataract, glaucoma, and conditions affecting the retina.

The human eye is one of the five sense organs that enables us to see the surrounding world. The components of the eye include:
- The white part of the eye is called Sclera.
- Pigmented circular part of the eye in the center of the eye that determines its color is called Iris
- The transparent dome over the iris is called Cornea.
- The circular opening in the center of the iris that lets the light in is called Pupil.
- The transparent layer of tissue lining the inner surface of the eyelids and the front part of the eye except cornea is called Conjunctiva.
- A lens is located just behind the iris and pupil, which helps to focus light on the specialized light-sensing tissue called Retina.
- The Optic nerve that carries the impulses from the retina to the brain.
Eyes play a vital role in our daily activities. Any abnormality in the eye disturbs the normal vision. While some vision problems are genetically inherited, others may arise as a result of lifestyle habits, aging, other disease conditions, medications or physical injury. It is necessary to know the symptoms of various eye conditions that would help in prompt diagnosis and correction to lead a comfortable life.
Causes of Vision Problems
Vision problems are caused by several conditions. These include:
Refractive Errors: Refractive errors are the most frequent eye problems caused due to a problem in the focusing of light by the eye. The patient commonly complains of headache, eye ache and blurring of vision. Some of the common refractive disorders are:
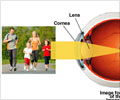
- Myopia or Near sightedness: In this condition, an individual is able to see near objects clearly, but the far away objects appear blurred. The patient, often a school-going child, may complain of frequent headaches. It can be diagnosed by periodic eye testing by an ophthalmologist.
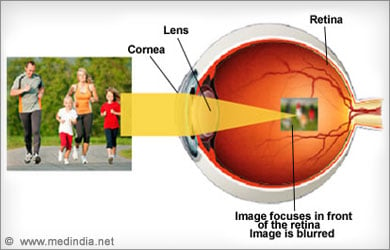
- Hypermetropia or Farsightedness: Hypermetropia is a condition where an individual is able to view faraway objects clearly, but nearer objects appear blurred. Common symptoms include headaches and eye strain after close work. Diagnosis is made after a detailed eye examination.
- Astigmatism: Astigmatism is caused either due to irregularity in the surface of the cornea or lens. This results in blurred vision.
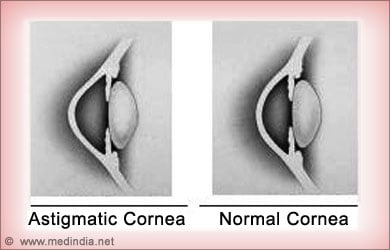
Age-related Eye Problems: As the years go by, eyesight becomes weak and the person could have problems with seeing. Common age-related eye problems include:
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): The macula is the part of the retina on which the light falls. This region converts the light into electrical impulses that are carried by the optic nerve. AMD causes blurred vision and distortion of objects. The central field of vision is mainly affected. Cigarette smoking, hypertension and high cholesterol levels could increase the risk of developing this condition.
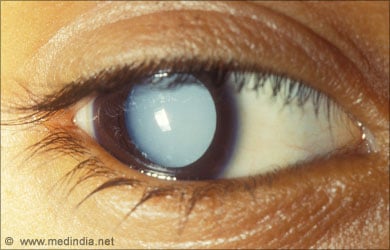
- Cataract: Cataract is one of the most common causes of vision impairment in elderly people. This condition is characterized by fogging of the lens and results in blurred vision, glare, and inability to view clearly even with glasses.
- Presbyopia: Presbyopia is a condition that commonly affects people in their forties. It occurs due to loss of flexibility of the lens, which makes it difficult to focus on objects at different distances. Common symptoms of presbyopia include tendency to hold reading material at a distance, blurred vision, headaches and eyestrain.
Infections and Inflammation: Superficial infections of the eye like conjunctivitis (infection of the conjunctiva) and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) usually do not affect vision, though they cause considerable discomfort. Deeper inflammation like uveitis can cause some blurring.
- Uveitis: Uveitis is an inflammatory condition of uvea of an eye, affecting the middle pigmented layer of an eye. It may occur due to autoimmune disorders, infections, eye injury and certain cancers. Symptoms include redness of eye, severe eye pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity and dark floating spots in the field of vision.
Increase in Intraocular Pressure:
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a condition where the eye fluid pressure increases. If left untreated, it can damage the optic nerve resulting in vision loss and blindness. In some cases, the patient does not suffer any symptoms initially. In these cases, peripheral vision is lost first, followed by central vision. In a condition called angle-closure glaucoma, the patient has severe symptoms like redness of the eye with severe pain. This condition requires immediate attention.
Eye Problems due to other Disease Conditions:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes can affect the eyes in several ways. It predisposes a person to developing cataract. In addition, it can also affect the light-sensitive retina, resulting in a condition called diabetic retinopathy. The patient complains of blurred vision and presence of floaters in the field of vision. The central field of vision may also be affected.
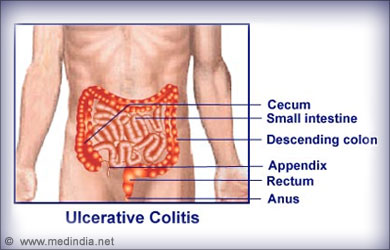
- Autoimmune Disorders: Various autoimmune disorders like Graves’ disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn''s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, lupus, multiple sclerosis and Behcet disease are associated with eye problems. Thus, patients with these diseases should undergo regular eye check-ups to diagnose any problem early.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions that affect the brain can affect vision. A stroke affecting the part of the brain associated with vision can result in blindness. Migraine headache may be preceded by visual changes with the appearance of flashing lights, wavy lines or spots before the eyes. The symptoms of the underlying condition are usually obvious in these cases.
- Vitamin A Deficiency: Vitamin A deficiency affects vision and causes night blindness as the first symptom. In this condition, the patient cannot see clearly in dim light. If the deficiency is not corrected, the condition could progress to dryness of the eye and eventually lead to blindness.
Other Eye Problems that can Affect Vision Include:
- Amblyopia: Amblyopia or lazy eye is a condition where the vision in one eye is reduced due to some condition affecting only that eye like myopia or hypermetropia, or squint eyes. Therefore, the brain tends to use only one eye to see.

- Color Blindness: Color blindness is a condition where the patient cannot differentiate colors, usually between green and red. The condition is usually inherited and therefore a family history may be present. Diseases affecting the retina and optic nerve may also cause color blindness.
- Retinal detachment: Retinal detachment is a condition where a part of the retina separates from its attachment to the eyeball. The patient may complain of floaters or flashes of light before the eyes. There could also be darkening of peripheral vision. The condition may follow trauma to the eye, and is relatively more common in people with severe hypertension or uncontrolled diabetes.
- Optic Neuritis: Optic neuritis is a condition where the optic nerve is inflamed. It commonly affects patients with autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, though other conditions like infections or certain medications can also cause optic neuritis. The patient complains of vision loss which may be temporary or permanent, pain which worsens with movement of the eyes, flashing of lights and loss of color vision.
Trauma: Trauma to the eye can affect vision. For example, burn injury or a sharp object can cause a corneal ulcer. A severe injury can cause a detached retina.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect vision. Sildenafil, or Viagra as it is more commonly known, can affect color vision resulting in a blue tinge on objects. Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine can cause retinal toxicity. Ethambutol, an anti-tuberculosis drug, can cause blurring of vision and red-green color blindness. Thus, a history of medication intake should be obtained from a patient complaining of vision problems.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which doctor should I visit in case I suffer from Vision problems?
You should visit an ophthalmologist in case you suffer from visual problems. An optometrist can help to diagnose refractory errors.
2. How is a Refractive errors Treated?
Refractive errors are treated by diagnosing the degree of correction and correcting it with suitable spectacles or contact lenses. In older individuals, the refractive errors can be corrected by laser surgery if the patient is fit for the procedure and desires it.