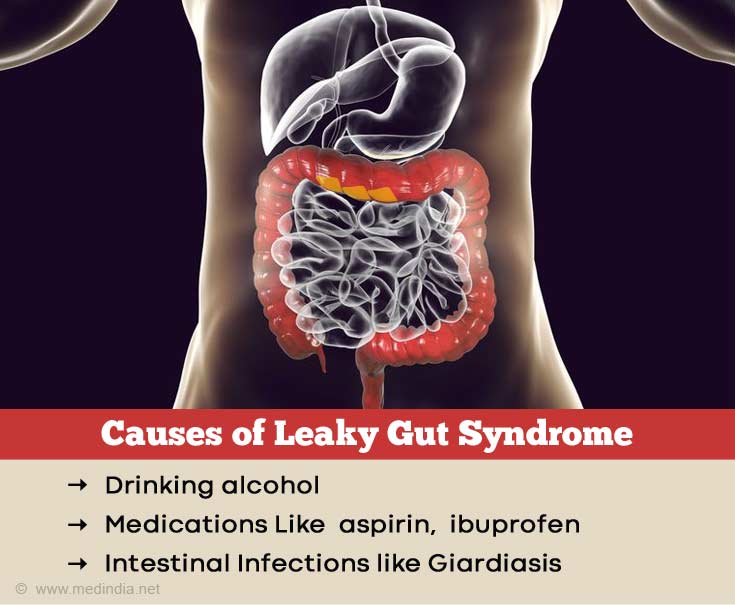
What are the Causes of Leaky Gut Syndrome?
The exact cause of LGS is unknown. It has been suggested that microorganisms, toxins and other substances can pass into the bloodstream due to a leaky gut. As a result, the immune system attacks these foreign substances and due to this immunological reaction the various symptoms of LGS manifest.
Therefore, some possible causes that have been suspected include the following:
- Intestinal Hyperpermeability: This occurs due to loosening of the tight junctions that are present on the mucosal lining of the gut.
- Alcohol: High amounts of alcohol consumption can cause inflammation of the gut, which can lead to a leaky gut.
- Medications: Painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, indomethacin, diclofenac, and others can cause irritation of the gut lining. These drugs can damage the tight junctions, causing leakage of substances through these gaps into the bloodstream.
- Poor Diet: A high-fat diet may weaken the intestinal lining. Both a poor diet and certain medications may cause inflammation of the colon or intestine.
- Intestinal Infections: These include salmonellosis, giardiasis, amebiasis, and norovirus infection. Sepsis can also damage the gut lining.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Examples include Crohn’s disease and celiac disease. Gluten must be avoided in the case of celiac disease.
- Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapy medications as well as radiotherapy of the abdomen, can damage the mucosal lining of the gut.
- Complicated Gut Surgery: Complicated gastrointestinal (GI) surgery can potentially damage the intestinal lining, leading to a leaky gut.