Risk factors for Erectile Dysfunction
Some underlying diseases, psychological factors, hormonal disturbances, alcoholism and cigarette smoking increase the risk of erectile dysfunction.
According to the National Institutes of Health, erectile dysfunction is also a symptom in many disorders and diseases. Direct risk factors for erectile dysfunction may include the following-
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Prostate problems
- Depression
- Alcohol ingestion
- Lack of sexual knowledge
- Poor sexual techniques
- Inadequate interpersonal relationships
- High levels of blood cholesterol
- Smoking, which accentuates the effects of other risk factors such as vascular disease or hypertension
- Hypogonadism in association with a number of endocrinological conditions
- Vascular disease and vascular surgery
- Low levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
- Drugs
- Neurogenic Disorders
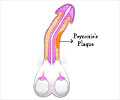
- Peyronie's Disease (distortion or curvature of the penis)
- Priapism (painful and prolonged erection)
- Many chronic diseases, especially renal failure and dialysis
Age appears to be a strong indirect risk factor in that it is associated with increased likelihood of direct risk factors, some of which are listed above. It is estimated that nearly 5% men become impotent by the age of 40-years, and 15-25% by the age of 65-years.