Glossary
Autosomal Recessive Disease-- An inherited disorder which is equally likely to occur in either sex. Wilson's disease is an autosomal recessive disease.Ceruloplasmin-- A simple protein found in the blood which binds itself to copper so that copper may be moved about the body by the circulatory system. Over 90% of Wilson's disease patients have abnormally low levels of blood ceruloplasmin.
Chelate-- A particular type of chemical reaction with a metal (such as copper). Many drugs used to treat Wilson's disease "chelate" copper into a form which patients bodies can eliminate.
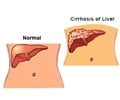
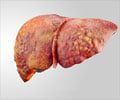
Cirrhosis-- a disease of the liver in which normal cells are replaced by scar tissue, which inhibits the organ's many functions.
Dysphagia-- Difficulty in swallowing. It is common for the swallowing reflex to be impaired in persons with Wilson's, things oftentimes "go down the wrong tube."
Dystonia-- Involuntary movements and prolonged muscle contraction. The type of dystonia caused by Wilson's disease causes patients to hold part of their body in an unnatural position.
Gastroenterology-- The diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive system
Gene-- A part of the DNA molecule which is responsible for the development of a certain characteristic.
Jaundice-- A yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes usually caused by diseases of the liver or bile ducts.
Kayser-Fleischer Rings-- Discoloration of the outer membrane of the iris caused by copper deposits. Although the ring is not present in all patients, it is never present in a person without Wilson's disease.
Liver biopsy-- A procedure, usually done while the patient is awake, in which a small piece of the liver is extracted with a special needle.
Penicillamine-- Perhaps the most commonly used drug for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is a variant of penicillin and is also used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Its brand names are Cuprimine and Depen.
Renal-- Relating to the kidney. Wilson's disease patients can sometimes cause the kidney to not function correctly.
Trientine-- A copper chelator sometimes used in the treatment of Wilson's.
Zinc acetate-- A drug used in maintenance therapy for Wilson's disease that works by blocking absorption of copper in the digestive system, therefore preventing further copper accumulation. A person must first be "decoppered" by a chelating agent.