Cancer of the Cervix, Uterus & Ovary
Cancers can hit the uterus and the ovaries. Uterine cancer is of two types: cervical and eudiometrical.
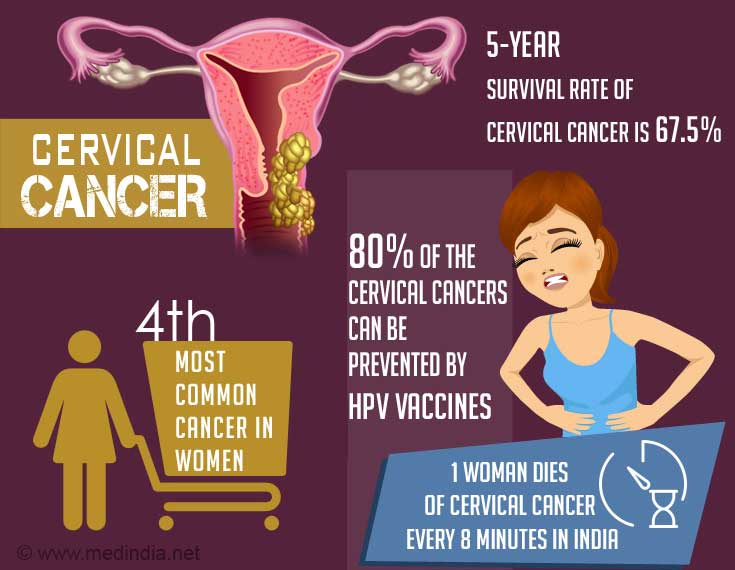
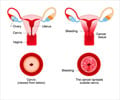
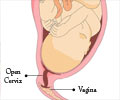
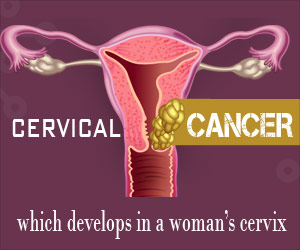
Cervical cancer
Occurs in the cervix, the canal between the vagina and the uterus. This is the most common cancer among Indian women.
You are more likely to be affected if you:
- Have had sexual encounters at an early age
- Have multiple sexual partners
- Have poor genital hygiene
Watch out for:
- Blood in vaginal discharge
- Unusual bleeding between periods
- Unusual bleeding after intercourse
Help at hand:
The cervix can be removed through surgery, if the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body. Radiotherapy is useful in the second and third stages.
Precautions:
The Pap test detects signs of cervical cancer early on. Have a Pap test every year if you are:
- Over 18
- Sexually active
Endometrial Cancer
Occurs within the uterus. Usually occurs among older women and is influenced by genetic predisposition to the disease.
You are more likely to be affected if you:
- Are over 40
- Are overweight
- Take hormones
- Are infertile
- Do not ovulate
Watch out for:
- Blood in vaginal discharge
- Abnormal bleeding - bleeding other than menstrual flow
Help at hand:
If only the uterus has been affected, a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) helps. If the cancer has spread, the surgery must be followed up with radiotherapy. Chemotherapy is used in advanced conditions.
Ovarian cancer
Occurs in the ovaries, which produces the ova or eggs. This type of cancer is common among older women.
Watch out for:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Loss of weight
- Back ache
- Occasional breathlessness
Help at hand:
The vast majority of women diagnosed with first and second stage ovarian cancer survive with proper treatment. If the cancer is caught in the first stage, cure is possible through surgery. This is supplemented with radiation for second-stage cancers. Chemotherapy is used only in the final stages.