Intersex - True Picture
There is a disturbing trend within the human species to regard variants among them with curiosity, amusement, suspicion and a generous dose of contempt. For the differently- wired, it is an endless struggle to have to prove to the world that they too are the handy work of the same natural force that moulded the rest of the race and not some freak phenomena.
Intersex is a group of individuals in whom there exists a discrepancy between the external genitalia and internal gonads (testes and ovary). The UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights define them as - "do not fit the typical definitions for male or female bodies".
Such variations may involve ambiguity with the genitalia with combinations of chromosomal genetic type and sexual phenotype other than the normal XY-male and XX-female chromosomal pattern. In the past these people were referred to as ‘hermaphrodites’ and the condition as hermophroditism. Taking into account the insensitivity and inaccuracy of this ancient term, these conditions are now referred to as ‘Disorders of Sex Development’ or DSD.
Inter-sex and Sports - Honour and Shame
All hell broke loose for Semenya, the South African athlete who won the 800 m event but was publically shamed in 2009 because here femininity was not convincing enough. Laboratory tests revealed that she was more a ‘male’ than a female and her clinical tests proved that she had internal testes and that the uterus was non-existent. She was also being accused of having benefited from her ‘maleness’. Her sexual possibilities were publicly discussed and she was subjected to severe mental agony.
Another case is that of Shanthi Soundararajan, a talented athlete from Tamil Nadu, India. Till 2006, everything was going well for her and the world seemed at her feet after she won an international event. But then again for her all hell broke loose, when it was revealed that she genotypically differed from the typical female and that there was more maleness in her than the rest of the species.
Shanthi was subjected to public scrutiny with the media going overboard, discussing sordid details, and speculating about her ‘true’ gender. As the final act of ignominy she was stripped of her medal which she had earlier received with great fanfare. It came as little surprise that Shanthi attemped suicide.
Both the talented athletes, Semenya and Shanthi, are inter-sex individuals.
Anatomy of Reproductive System
In human beings, the process of sexual reproduction involves the sperm impregnating the egg and the fusion of the two specialized cells called germ cells cell results in a single cell called zygote. The zygote multiplies rapidly to eventually give shape to the foetus. Errors in the fusion or development of the foetus can result in some of the sexual anomalies that lead to intersex.
The male reproductive system of a man consists of a pair of testes, ducts, accessory glands and a penis. The functions of the male reproductive system are:
- Production of sperms.
- Transmission of sperms to the female.
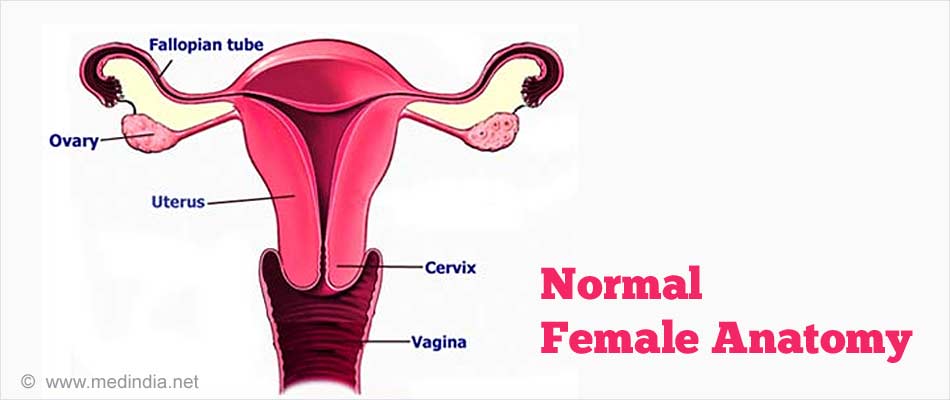
The female reproductive system consists of two ovaries (produce ova and female hormones), Fallopian tubes, uterus (muscular organ which supports the fetus during it’s 40 week gestation period before birth), vagina and external genitalia.
The functions of the female reproductive system are:
- Production of ovum eggs.
- Receiving the sperms.
- Providing suitable environment for fusion (fertilization) of the egg and the sperm.
- Child birth.
- Nourishment of the baby with breast milk until it can take a mixed diet.
Intersex Types – Not Quite a Boy or a Girl
Intersex can be classified into four categories the details of which are discussed below.
a) 46 XX Intersex.
A person with this condition has the genotype of a female 46, XX. External genitalia will appear like that of a male. The labia of the female external genitalia gets fused and the clitoris is enlarged to look like a penis giving the appearance of male genitalia.
It must be noted that the person usually has a normal uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. Some of the causes include:
Overexposure of a female fetus to excess male hormones while still in the mother’s womb. This may even be due to tumors producing male hormones in the mother.
Aromatase deficiency- Aromatase is an enzyme that normally converts male hormones to female hormones. Excessive aromatase activity leads to the overproduction of female hormone estrogen while its deficiency can result in 46, XX intersex, where enough estrogen is not produced. This is not noticeable until puberty when these XX girls begin to display male characteristics.
b) 46, XY Intersex
The 46, XY person has the genotype of a male but the external genitalia may resemble that of a female or it may be ambiguous or incompletely formed. Testes when present may be normal or malformed. In some cases it may be absent. The condition used to be called ‘male pseudohermaphroditism’. It is also referred to 46, XY with undervirilization and it occurs due to the following possible causes:
- Testosterone formation is a multi-step process that requires the functioning of different enzymes. Dysfunction of these enzymes can result in its inadequate production and results in the formation of 46, XY intersex.
- In some cases of 46, XY intersex, normal internal testes may be present that ensures adequate testosterone production. However deficiency in the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase impairs the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone a step necessary for proper maleness to manifest.
- Malformation syndromes such as Smith Lemli –Opitz and Campomelic dysplasia also have 46 XY karyotype with female or ambiguous genitalia. These occur due to mutations in the autosomal genes DHCR7 (which codes for 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase) or it could be due to deletions in the autosomal gene SOX-9
- In some cases of 46XY there is a loss of SRY genes located on the Y chromosomes. These SRY genes are responsible for the development of the male attributes.
- Sometimes, in a 46 XY individual, a duplication of the dosage sensitive region (DSS) on the short arm of the X (Xp) results in female external genitalia.
- Mutation in the gene DAX 1 is also associated with XY females
- Swyer syndrome is a type of hypogonadism. Here the functional gonads,the ovaries, are absent but the person resembles a normal female and has a karyotype 46, XY.
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome(AIS) is the most common cause of 46, XY intersex. A person with
AIS individuals produce adequate amounts of testosterone but they lack the receptors that sensitize the body to the male hormone androgen. As a result the person’s body cannot detect the androgens and, therefore, is unable to develop as male. These individuals grow as females and it really comes as a surprise to many of them when the abnormality is detected or when they find out that they are infertile.
c) True Gonadal Intersex.
A person is said to be true gonadal intersex when both testicular and ovarian tissues are present. These tissues may be found separately or they may be present as a single ovo-testis. The genotype may denote 46 XX, 46 XY or both. The external genitalia may appear to be male or female or it may be ambiguous. The underlying cause of this condition, once referred to as “true hermaphroditism”, is yet unknown.
d) Complex Intersex Disorders
These intersex disorders are characterized by the impaired sexual development and involves conditions such as Turners syndrome (45,XO), Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) and super females (47,XXX). These individuals are not classically intersex but display deficiencies in their overall sexual development.