Glossary
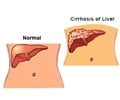
Cirrhosis - A type ofchronic, progressive liver disease.Fibrosis - The growth offibrous tissue.
Hepatitis - An infection or inflammation of theliver.
Obesity - Over weight.
Diabetes - A condition in which the body cannot properly store or use glucose (sugar), the body's main source of energy.
Blood pressure - The pressure of the blood on the walls of the arteries, dependent on the energy of the heart action, the elasticity of the walls of the arteries, and the volume and viscosity (resistance) of the blood.
Endoscopy - The use of a thin, lighted tube (called an endoscope) to examine the inside of the body.
Ultrasound - A test that bounces sound waves off tissues and internal organs and changes the echoes into pictures (sonograms).
CT - This is a X- ray procedure enhanced by computer the results are three dimensioned scan through a body part showing bone and body tissue.
MRI - A painless method using magnetic fields for taking pictures of internal organs
Malaise - The vague feeling of illness or discomfort.
Fatigue - Feeling Weak.
Edema - The vague feeling of illness or discomfort.
Ascites - Fluid collection.
Bruising - A bruise or "contusion" is an traumatic injury of the soft tissues which results in breakage of the local capillaries and leakage of red blood cells. In the skin it can be seen as a reddish-purple discoloration which does not blanch when pressed upon. When it fades it becomes green and brown as the body metabolizes the blood cells in the skin. It is best treated with local application of a cold pack immediately after injury.