- 3D/4D ultrasound - (http://www.femicare.org/en/3d-4d-ultrasound)
- 3D ultrasound - (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3d_ultrasound)
- The benefits of 3D-4D fetal echocardiography - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3150085/)
What is 3D and 4D Ultrasound during Pregnancy?
3-Dimensional ultrasound and 4-Dimensional ultrasound are obstetric ultrasound procedures that provide clearer insights into the developing fetus than the traditional sonography. 3D and 4D ultrasounds are optional and are not included in the standard prenatal tests. The doctors prescribe 3D and 4D ultrasound scans if the parents are interested. This type of ultrasonography is prescribed if the doctor suspects any birth defects like cleft palate or other structural birth anomalies.
3D and 4D ultrasounds use sound waves to create an image of the baby in the womb, like the traditional ultrasound procedures. However, the difference between 3D and 4D ultrasound is that while the 3D ultrasound pictures are three-dimensional still images of the baby, 4D images show real-time movements like facial features, limbs and body in detail and sometimes, the baby’s expressions. The images of the 4D scan line up in such a way that they look like a video.
The sound waves during 3D and 4D ultrasonography are directed at various angles, unlike the 2D ultrasound, where the sounds are directed at a single angle. The advanced software creates images from the sound waves that are reflected off from various surfaces. This technique, called “surface rendering”, is used in the 3D and 4D ultrasound procedures. Except for the dimension of the motion, the procedures of 3D and 4D ultrasounds are similar.
When can a 3D or 4D ultrasound be performed?
The best time to get a 3D and 4D ultrasound scan is during the 26 weeks to 30 weeks of pregnancy. At 26 weeks of pregnancy, the baby has very little fat under the skin and the bones are clearly visible. However, the face may not be visible at 30 weeks as it goes deep down in the pelvis. The visibility of the face also depends on the direction the baby is facing, inside the womb. Limbs and extremities can be seen very clearly during this stage of pregnancy.
Since viewing the 3D images and 4D images of the baby is more about bonding with the baby rather than diagnosing problems, this kind of sonogram is not generally covered in the insurance. Also, the special transducers and software required for 3D and 4D ultrasounds are expensive, these procedures are done at exclusive or private clinics.
Most of the hospitals do not go for sex determination of the fetus until 20th week of pregnancy. One might want to go for 3D and 4D ultrasound for determining the gender. While the chances of sex determination of the fetus are only 50% during 15 weeks, it rises to almost 99% at 16 weeks.
Preparing for 3D and 4D Ultrasound
Unlike the regular sonogram procedure, the woman ready to undergo a 3D ultrasound is not advised to have a full bladder before their 3D ultrasound appointment. She is advised to take regular amounts of water for one or two weeks prior to the appointment. This is to ensure an adequate amount of amniotic fluid around the fetus and also ensures the clarity of the fluid.
The woman may be asked to expose her belly for the placement of the probe, otherwise, there is no undressing required.
Advantages of 3D/4D Ultrasound during Pregnancy and Prenatal Check up
Most of the time 3D and 4D ultrasound prenatal scan is done for the purpose of viewing the baby in the womb. Such sonogram images make a wonderful collection of keepsake photos. Sometimes, the medical professionals use ultrasound scans as a medical diagnostic tool.
A 3D ultrasound and 4D ultrasound give a great deal of precise information about various internal organs or pathological structures. Better visualization of various structures like fetal skeleton is possible with these techniques. Sufficient information about the condition of the fetal heart is obtained from the 3D ultrasound images, to find out any structural or valve defects. Superficial fetal anomalies like cleft lip, neural tube defects, tumours etc are better visible in 3D ultrasound scans than 2D scans.
The following information about the growing fetus can be accessed with 3D and 4D scans.
During Prenatal check up:
- Developmental anomalies
- Bone shape abnormalities like club feet, cleft palate, spina bifida, dwarfism, fusion of bones
- Dysplasia
- Location of the placenta and evaluation of placenta previa
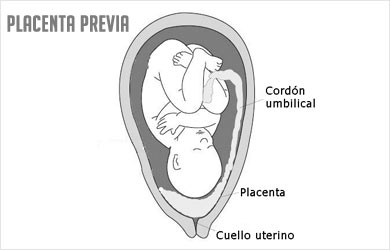
- 3D placental insertion and inferior segment analysis
- For fetal biopsy: Umbilical cord sampling puncture is easily viewable, Kidney dilatation, Uropathy and amniocentesis
- Fetal health: Abnormal gestures of fetus, sleep-wake patterns of the fetus
- Movements of the fetus: Deglutition (swallowing), respiratory movements, fetal digestive peristaltic motion, movements of eyelids, limbs and mouth
- Fetal neuro-myopathy diseases, muscle reactions and tonicity (tightness of muscles)
Fetal cardiac function:
- Fetal cardiac activity and abnormality: correlation between valves, chambers and vessels, volume of heart cavities, communication between atrial and ventricular communication, assessment of valvular function.
- Efficient and accurate information of fetal heart function
- Visualization of 2-3 planes, enabling spatial orientation of the fetal heart
- Volume calculation of cavities of the heart
- Correlation between valves, chambers and vessels
- Outflow of blood from left ventricle and right ventricle, opening and closing of valves are better viewed
- Communication between atrial and ventricular chambers
- Diagnosis of fetal heart defects like in utero
Gynecological uses of 3D and 4D ultrasound
- Endometrial hyperplasia can be better viewed and exact equivalent volume measurement can be done
- Equivalent hysterosonography realization
- Location and measurement of ovarian and endometrial tumours
- Exact volume measurement of cysts, polyps, myoma or fibroma
- Tumour monitoring after chemotherapy with 4D scans and also using contrast media
- Contrast media also used for evaluating fallopian tubes
- Positioning of Intra-uterine devices

Clinical Uses 3D and 4D ultrasonography apart from Obstetric ultrasound
Apart from its use in prenatal assessment, 3D and 4D ultrasonography have been used in detecting problems and evaluating post-operative and post-chemotherapy progress in patients.
In Children:
- Measurements of the neonatal brain, symmetry and volume
Ophthalmology
- Volume measurement of normal structures of the eye
- Tumour findings
- Foreign particle detection within vitreous humor
- Retinal detachment evaluation
Breast
- Breast tumour evaluation, diagnosis and pre and post chemotherapy evaluation
- Contrast media use on breast tumours
- Compression and retraction patterns of tumours viewed in 3D and 4D ultrasound
Urology
- Exact seed implantation can be done in Brachi therapy
- Accurate 4D biopsy
- Accurate volume measurement of prostate and bladder, growth and tumours in these locations
- Checking the position of urinary catheter
- Exact assessment of the post-micturitional residue
Musculoskeletal
- Musculoskeletal biopsy guidance
- Examination and measurements of rotator-cuff, meniscus positioning (knee), hip measurement
- Bone microsplit evaluation
- Evaluation of partial tendon separation
- Fetal bone shape abnormalities
- Evaluation of arthritis
- Post-operative assessment of bone screw placement
Internal Medicine
- Accurate 4D biopsy of liver and kidney
- Evaluation of acute abdominal syndrome and identifying appendix torsion, ileum sigmoidal fistula, Crohn’s disease, endometriosis, recto-sigmoidal fistula, rectitis, oroctitis
- Parenchyma or tumour volume assessment
- Colic polyps and tumour identification and monitoring while treatment
- Contrast media use in kidney or liver tumour
- Colonoscopy, cystoscopy






