What are the Different Types of Lung Biopsy Procedures?
Lung biopsy can be performed by various methods, which are described below:
Bronchoscopic biopsy-
- Bronchoscopic biopsy is used for collecting abnormal lung tissues present near the breathing tubes (bronchi).
- A flexible bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth or nose to reach the lungs from where the lung tissue sample is collected.
- It is a non-invasive procedure compared to open lung biopsy and usually takes between 30 and 60 minutes.
- After the procedure, the patient may develop a sore throat and hoarseness. This can be treated with salt water gargling. The patient may feel a bitter taste and difficulty in swallowing due to the anesthesia. Some patients may develop fever, which usually subsides within 24 hours.
Needle biopsy procedure-
- Needle biopsy procedure is used to obtain abnormal lung tissues which are located close to the chest wall.
- The patient is given a sedative about an hour before the biopsy in order to relax the patient.
- The biopsy site is marked with small metal markers. The skin is then cleansed with an antiseptic solution and a local anesthetic is injected over the incision site to numb the area.
- Before inserting the needle into the lung, a small superficial incision is made on the biopsy site; the patient is then asked to take a deep breath and hold it till the needle is inserted into the lung under ultrasound or fluoroscopy guidance. During the insertion of the needle, one may experience a sharp pain or burning sensation for a few seconds.
- After collection of the required biopsy material, the needle is removed and pressure is applied at the biopsy site. Bleeding is avoided by applying a bandage over the puncture site.
- Needle lung biopsy procedure may take about 30 to 60 minutes.
- Patients are advised to rest at home for a day or two before resuming regular activities, and to avoid strenuous activities for a week after the biopsy.
- Lung collapse may occur because of air that leaks in through the hole made by the biopsy needle. In such conditions, a tube is inserted in the chest to remove the air.
CT-guided needle lung biopsy-
- CT-guided needle lung biopsy involves monitoring of the biopsy procedure by a computerized tomography (CT) scan of the chest.
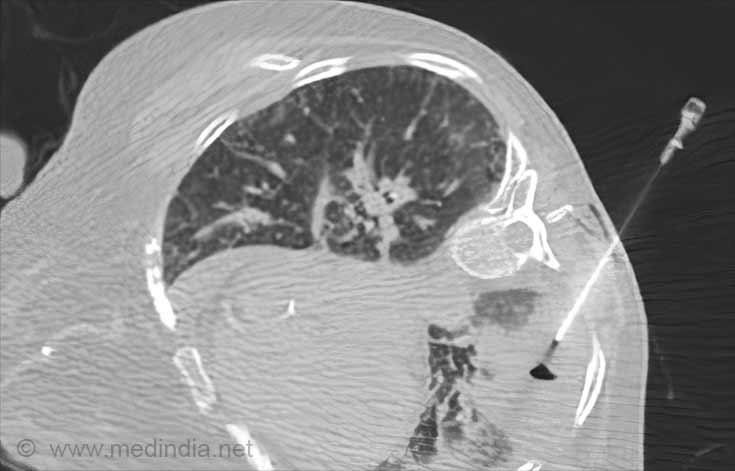
- The patient is not supposed to drink or eat for 8 hours prior to the procedure.
- The procedure is done as an outpatient procedure by giving a local anesthesia. The patient can be discharged within 4 to 5 hours after the procedure and does not require any hospitalization.
- Rarely, patients may develop lung collapse after the procedure. Therefore, a chest x-ray is taken 3 to 4 hours after the biopsy procedure.
Open biopsy-
- Open biopsy is done as an outpatient procedure.
- The biopsy involves removing part or all of the lump or area of interest. If the entire lump is removed, this method may also be called a lumpectomy.
- A breast ultrasound, MRI, or mammogram may be used to find the growth if the surgeon cannot easily feel the lump or cyst. A needle or wire is placed in the area during the imaging test to help the surgeon find the growth.
Mediastinoscopy with biopsy-
- A mediastinoscope is inserted in the space in the chest between the lungs (mediastinum), and tissue is collected from any unusual growth or lymph nodes.
- The patient is given general anesthesia before the procedure. An endotracheal tube is placed in the nose or mouth to help the patient breathe.
- A small incision is taken in the neck. The mediastinoscope is inserted through this incision and gently passed into the mid-part of the chest.
- Tissue samples of the growth or lymph nodes are taken and the scope is then removed. The incision is closed with sutures.
- A chest x-ray is usually taken at the end of the procedure.
- The procedure usually takes 60 - 90 minutes.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)-
- VATS is a recently developed surgery that enables doctors to view the inside of the chest cavity after making only very small incisions.
- It allows surgeons to remove masses close to the outside edges of the lung.
- It is also useful for diagnosing certain pneumonia infections or tumors of the chest wall, and treating repeatedly collapsing lungs.






I need to have a lung biopsy. I'm scared. any reassuring comments out therre
Can valley fever caught in Arizona lead to lung cancer