Blood Pressure Range
High blood pressure is also known as hypertension. It is measured in mm Hg (millimetres of mercury).
Blood pressure is always given as two numbers- systolic pressure (when the heart beats) and diastolic pressure (when the heart relaxes). When the measurements are written down, both are written one above or before the other with the systolic being the first number. It is measured using an instrument called the spygnomanometer. It can also be measured digitally.
It is very difficult to correctly define normal blood pressure as the blood pressure range can vary widely. A single blood pressure monitor reading is not reliable. Blood pressure monitor readings must be taken at different times of the day to determine average blood pressure over a period.
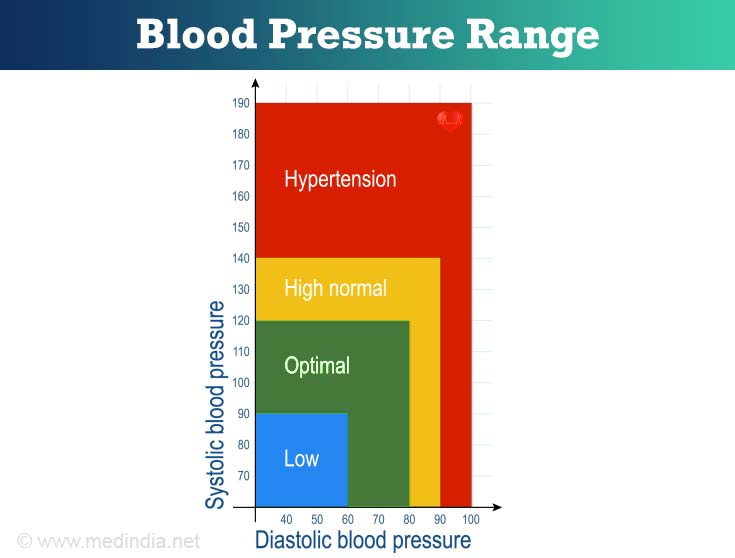
High Blood Pressure Range
| Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) | Stages of High Blood Pressure |
| 210 | 120 | Stage 4 |
| 180 | 110 | Stage 3 |
| 160 | 100 | Stage 2 |
| 140 | 90 | Stage 1 |
Normal Blood Pressure Range
| Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) | Pressure Range |
| 130 | 85 | High Normal Blood Pressure |
| 120 | 80 | Normal Blood Pressure |
| 110 | 75 | Low Normal Blood Pressure |
Low Blood Pressure Range
| Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) | Pressure Range |
| 90 | 60 | Borderline Low blood Pressure |
| 60 | 40 | Too Low Blood Pressure |
| 50 | 33 | Dangerously Low Blood Pressure |
Note:
- When systolic and diastolic pressure falls into different categories, the higher category should be used to classify the blood pressure level example 160/80 mm Hg would be considered as Stage 2 High Blood Pressure.
- A blood pressure of 130/80 mmHg would be considered as high blood pressure for people with diabetes or chronic kidney disease.