- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk482360/)
- All You Need to Know About Thiamine - (https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/natural/965.html)
- More Information on Thiamine - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002401.htm)
- About Thiamine - (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/)
- Vitamin B1 - An Overview - (https://www.nutri-facts.org/en_us/nutrients/vitamins/b1.html)
- Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Vitamin B1 - (https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/sci-com_scf_out93_en.pdf)
What is Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 is also known as thiamine and is an essential nutrient needed by the human body for the normal functioning of several organ systems. It was the first B vitamin discovered (out of eight B vitamins) and thus, was named vitamin B1.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Go to source)
All B vitamins help in converting food in the form of carbohydrates into glucose which is the source of energy in the body. This process is vital for a healthy metabolism.

Why is Vitamin B1 Important?
Vitamin B1 is important as it performs several roles in multiple different key processes in the body. It acts as a coenzyme and catalyzes the conversion of carbohydrates into sugar. It also helps in strengthening the immune system and in the functioning of the nervous system. The recommended daily allowance for vitamin B1 in adults is 1.2mg for males and 1.1 mg in females. Deficiency of thiamine results in a condition called beriberi.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
All You Need to Know About Thiamine
Go to source)
Functions of Vitamin B1
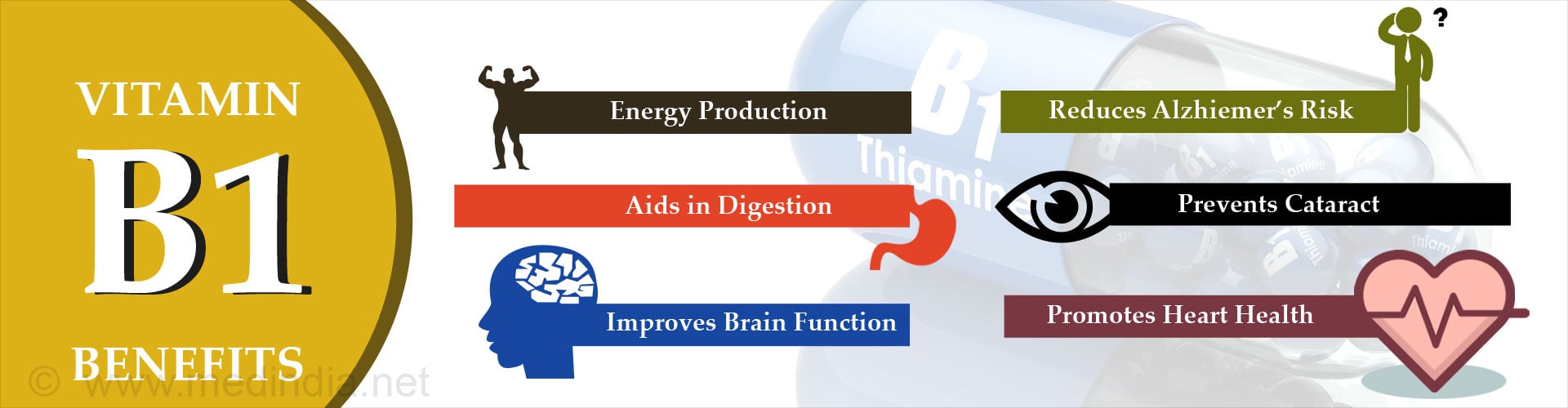
Thiamine is essential for the normal functioning of:
- The heart;
- Carbohydrate metabolism and energy production
- Nervous system development as well as functioning
- Vitamin B1 regulates the functioning of the nervous system, heart and brain. Its primary function is to efficiently produce energy for cell metabolism from food.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
More Information on Thiamine
Go to source) - It also maintains good eye sight and boosts immunity. This is one of the reasons why thiamine is used as a preventive treatment for cataract (eye disease that clouds vision). It is also prescribed to AIDS patients to partly compensate for the loss of immunity caused by the disease.
- Some people also believe that vitamin B1 is important to maintain mental health and promote a positive attitude. It may also reduce the likelihood of memory impairments and diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Thiamine also promotes healthy kidney functioning and slows down the onset and development of kidney disease in diabetes patients.
Vitamin B1 Sources
- Most people fulfill their needs for thiamine from their regular diet. The major vitamin B1 containing foods include meat products (pork, beef, poultry), legumes, whole grain products (cereals and unpolished rice), nuts, soybean, brown bread, yeast and peas. The technology these days has brought about an entire range of enhanced or thiamine fortified whole grain options like rice, wheat, and pasta.

- Artificial sources of thiamine include either vitamin B1 supplements or multivitamins. Thiamine supplements contain only thiamine while multivitamins (like Vitamin B complex) work like a combo pack and provide other vitamins too. Vitamin supplements are available in the form of tablets, lozenges and soft gels. In severe cases of thiamine deficiency, thiamine is administered intravenously or intramuscularly.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Thiamine
Go to source)
Vitamin B1 Benefits
Thiamine or vitamin B1 is used to treat symptoms caused by vitamin B1 deficiency. These include:
- Headache, weakness, irritability, depression and abdominal discomfort
- Reduced mental alertness due to excessive pyruvic acid in the blood
- Wernike-Korsakoff syndrome, which results in confusion and memory problems. It is common in alcoholic patients
- Beriberi: Beriberi is of two types – dry beriberi and wet beriberi. Dry beriberi mainly causes symptoms related to the nervous system like numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, mental changes and loss of memory while wet beriberi is associated with heart failure

Vitamin B1 Side Effects
Thiamine pills are relatively safe. Very few cases of allergic reactions have been reported. A daily dosage of 1.4mg is considered safe for expectant and new mothers.
Vitamin B1 Interaction with Foods
Certain food habits interfere with the absorption of thiamine and may lead to a deficiency. Drinking excess of caffeinated beverages like coffee and tea are an example of interference. A diet comprising of raw fish and shellfish may lead to vitamin B1 deficiency. Cooked seafood is safe to include in your diet as the heat destroys the chemicals that interfere with thiamine absorption in the body.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Vitamin B1 - An Overview
Go to source)
Health Tips
Vit B1 is a relatively safe supplement that can be used by one and all. Thiamine is required by the body to complete several functions and one should not ignore thiamine deficiency symptoms. One should consult a physician before starting supplement pills.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Vitamin B1
Go to source)