- Medication Induced Neuropathy - (https://neuropathyjournal.org/medication-induced-neuropathy/)
- Living with Autonomic Neuropathy - (http://neuropathyjournal.org/living-with-autonomic-neuropathy/)
- Drug-induced peripheral neuropathies - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1598252/)
- Prevention and management of drug-induced peripheral neuropathy - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1653573)
What is Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is a disorder in which the peripheral nervous system gets damaged.
The peripheral nervous system is responsible for sending messages from the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) to the rest of the body. A blood-nerve barrier protects the peripheral nerves. In some patients, genetic and metabolic factors could cause peripheral nerve toxicity which affects the peripheral nervous system.
Neuropathy leads to a loss of sensation or movement in parts of the body.
Peripheral nerve disorder is also known as peripheral neuritis or peripheral neuropathy.
Some commonly used therapeutic medications can cause adverse effects that could include neuropathy. This is known as drug-induced neuropathy. These medications cause nerve damage which may be reversible when the drug is discontinued; or in extreme cases, the nerve damage can be permanent.
Peripheral neuropathy is known as mononeuropathy when only one nerve is affected. In most cases, many nerves are involved; in that case, it is called polyneuropathy.
Some common symptoms can be numbness or tingling, muscle weakness or paresthesia (pricking sensation).
Peripheral neuropathy can be a slowly progressing condition and at times can be severe and debilitating. If diagnosed at an early stage, the progress of peripheral neuropathy can be controlled.
What are the Causes of Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
Some medications can be toxic to the nerves and drug-induced neuropathy is caused by such medications. For example, many chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment are highly toxic and can kill neurons. Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common adverse effect of many commonly used cancer treatments.
What are the Drugs that are Known to Cause Neuropathy?
Some categories of drugs are known to cause neuropathy:
Antimicrobials
- Isoniazid
- Ethambutol
- Nitrofurantoin
- Metronidazole
- Chloroquine
Antineoplastic agents
- Vinca alkaloids (vincristine)
- Paclitaxel
- Cisplatin
- Docetaxel
Blood pressure or Cardiovascular drugs
- Perhexiline
- Hydralazine
- Amiodarone – a blood pressure medication
Hypnotics and psychotropics
- Methaqualone
- Thalidomide
Drugs for Autoimmune disease
- Infliximab
- Leflunomide
Anticonvulsants
- Phenytoin
- Carbamazepine
- Phenobarbital
Drugs to treat HIV/AIDS
- Didanosine
- Emtricitabine
- Tenofovir
Antirheumatics
- Indomethacin
- Gold
Others
- Disulfiram - used to treat alcoholism
- Dapsone - to treat leprosy and severe dermatological conditions
- Allopurinol - to treat gout
- Thalidomide - to treat multiple myeloma and leprosy
- Statins - to lower cholesterol
- Colchicine - used to treat gout

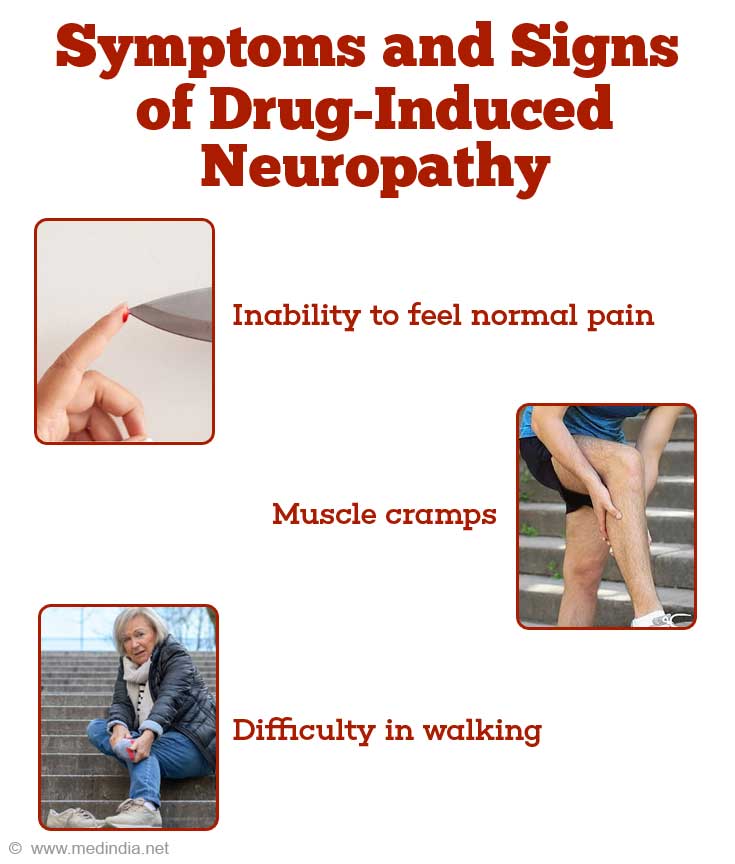
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
There are three known types of peripheral neuropathy, and the symptoms associated with each vary depending on the type:
- Sensory neuropathy - In this type, the sensation is affected due to damage to sensory fibers. Common symptoms include pricking and tingling sensation, numbness particularly in the feet, and loss of balance.
- Autonomic neuropathy - Affects the functioning of internal organs. This type results in damage to autonomic nerves which are typically responsible for involuntary movements in the body. These include breathing, heartbeat, bladder function, digestion, swallowing, bowel control, and sexual functions.
- Motor neuropathy - In this type, motor nerves in the muscles get affected, and the patient is unable to move muscles as they become weak or experience muscular atrophy. Common symptoms include muscle weakness or paralysis, muscle cramps and foot drop.
The common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- numbness in the feet and hands, accompanied by tingling or shooting pain
- difficulty in walking or losing balance while walking
- weakness of limbs
- poor gripping power of hands
- burning sensation
- muscle cramps
- a feeling of wearing gloves or stockings, even when not wearing them
- inability to feel normal pain
- incontinence
- breathing difficulties
- excessive sweating
- excessive sensitivity to touch
- non-cardiac tachycardia
- problems in sexual performance
How do you Diagnose Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy cannot be diagnosed with a single test.
A thorough investigation of the patient’s medical history is required to understand the symptoms and the likely cause of symptoms.
The physician may advise general blood tests to check diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, liver or kidney dysfunction, metabolic disorders and signs of an abnormal immune system.
More specialized neurological examinations could be conducted to check muscle strength and efficiency of nerve conduction; some of these include Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve conduction velocity test (NCV).
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can help understand muscle quality and identify the cause of neuropathy in tumors or herniated discs.
Genetic tests may be suggested to understand the presence of inherited neuropathies.
A skin biopsy may be suggested to diagnose any fiber damage.
Spinal tap (lumbar puncture) test can be conducted to detect infections, tumors or autoimmune disorders like multiple sclerosis.
What are the Treatment Options for Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
Drug-induced neuropathy though uncomfortable and debilitating, is not life-threatening. Symptoms usually go away when the toxic drugs are changed or discontinued or if the dosage is reduced according to the doctor’s advice.
Treatment however is based on the severity of symptoms and may include the following:
- Reducing the dose of the causative drug that induces neuropathy
- Substituting a less toxic medication
- Pain caused due to neuropathy can be treated with two types of medications - anti-depressants and anti-seizure medications; they can be used individually or in combination. At times, the side effects of these medications can be worse than the neuropathy symptoms. Hence, it is important for the physician to evaluate the course of medication for each patient
- Morphine, an opiate pain reliever may need to be prescribed to control severe pain
- The healthcare provider may advise use of special shoes or footwear

What are the Risk Factors and Complications of Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
The high-risk factors for drug-induced neuropathy include the use of medications to treat the following conditions:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Alcohol abuse
- Vitamin deficiency
- Infections such as shingles, hepatitis C, Epstein-Barr virus
- Kidney, liver or thyroid disorders
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
Complications could include:
- Inability to work because of permanent loss of sensation
- Burns and skin trauma - as the person may not feel temperature changes or pain on parts of the body which have become numb
- Infections - Loss of sensation in a particular area of the body can lead to infections, as the area can get injured without the person knowledge
- Loss of movement or being susceptible to falls - due to lack of balance
How do you Prevent Drug-Induced Neuropathy?
Patients who consume drugs known to be neurotoxic must regularly undergo neurological examination and functioning of the motor and sensory nerve conduction.
In general, patients who are under therapeutic treatment and who experience symptoms like pain, muscle cramps, and paresthesia during treatment must undergo neurological testing and motor-sensory nerve conduction.
Drugs must be cautiously used in patients with a risk of developing neuropathy, for example, in patients suffering from renal or hepatic failure, diabetes mellitus or malnutrition.
One must exercise regularly to overcome the occurrence of neuropathy.
The diet should be nutritious and should include fruits and vegetables, ginger and a right quantity of water. Foods containing gluten, refined grains, sugar and saturated fats must be avoided.