- Rosenow EC Ill, Myers JL, Swensen SJ, Pisani RJ. Drug-induced Pulmonary Disease. An Update. Chest 1992; 102 (1): 239-50.
- Cooper JAD, Jr, Zitnik RJ, Matthay RA. Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Disease. Annual Review of Medicine 1988;39:395-404.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.002143
- Ozkan M, Dweik RA, Ahmad M. Drug-induced lung disease. Cleveland Journal of Medicine 2001; 68 (9): 782-95.
- Seferian A, Chaumais MC, Savale L, Günther S, Tubert-Bitter P, Humbert M, Montani D. Drugs induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Presse Med. 2013;42(9 Pt 2):e303-10. doi - (10.1016/j.lpm.2013.07.005.)
- Cooper JA Jr, Matthay RA. Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Dis Mon. 1987 Feb;33(2):61-120.
- Daba MH, El-Tahir KE, Al-Arifi MN, Gubara OA. Drug-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Saudi Med J. 2004;25(6):700-6.
- West LM. Drug-induced respiratory disease. The Chronic Ill. 2005. Respiratory supplement: 10-12. - (10.1016/j.lpm.2013.07.005.)
- About Drug-induced Pulmonary fibrosis - (https://www.blf.org.uk/support-for-you/pulmonary-fibrosis/drug-induced-pulmonary-fibrosis)
- Information About Drug-induced pulmonary disease - (https://www.scripps.org/articles/1987-drug-induced-pulmonary-disease)
- Overview of Drug-induced pulmonary disease - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000104.htm)
- What is Drug-induced pulmonary disease? - (https://www.utmedicalcenter.org/your-health/encyclopedia/disease/000104/)
- Drug-induced lung disease - (https://radiopaedia.org/articles/drug-induced-lung-disease-1)
What are Drug-induced Pulmonary Diseases?
A number of medications are known to cause undesirable reactions and lead to changes in the lungs or alter respiratory function. These reactions are known as drug-induced pulmonary diseases. They could include pneumonitis, pulmonary edema, fibrosis, and even lung failure. At times, effective medicaments have to be withdrawn due to serious or lethal adverse effects.
What is the Mechanism for Drug-Induced Pulmonary Disease?
The mechanisms of drug-induced respiratory diseases vary with different drugs. Broadly, the mechanisms could be:
Direct toxicity:
Some drugs have a direct toxic effect on the lungs. This adverse effect depends on:
- The dose of the drug: The adverse effect is usually worse with a higher dose
- Age of the patient: The toxic effects may be more serious in very young or elderly individuals.
- Reduced kidney or liver function: Due to reduced liver or kidney function, the drug level in the blood can increase and result in toxicity.
Direct toxic effects usually take time before they manifest clinically.
Hypersensitivity reactions:
These are allergic reactions that can occur at any dose.
Pulmonary hemorrhage:
A bleed on the lungs usually occurs with the use of anticoagulants or drug-induced thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet counts).
Inflammatory reactions:
Inflammatory reactions can cause reversible or irreversible damage to the lungs.
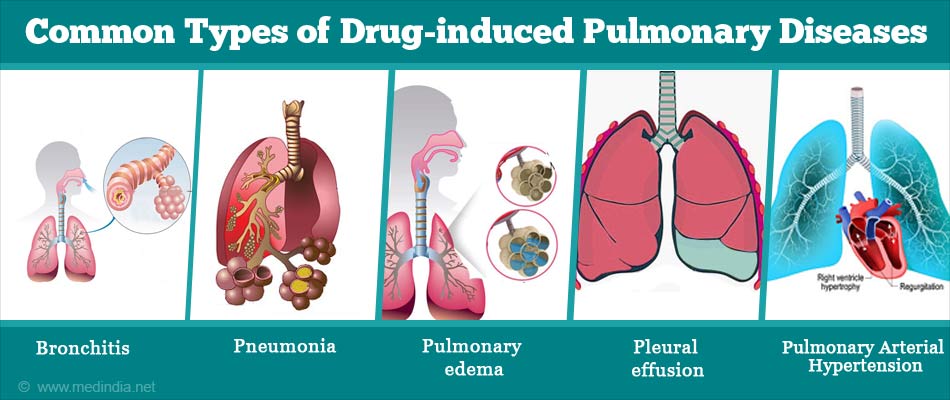
Which are the Common Types of Drug-induced Pulmonary Diseases?
The different types of lung or pulmonary diseases caused by drugs are:
- Allergic reactions like asthma or pneumonitis
- Lymph node swelling
- Alveolar haemorrhage, i.e. bleeding into lung sacs
- Bronchitis, i.e., inflammation of the airways
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary edema, i.e., fluid accumulation in the lungs
- Pleural effusion i.e., fluid accumulation around the lungs
- Pulmonary fibrosis i.e., formation of scar tissue in the lungs
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Lung failure
Which Drugs are Associated with Drug-induced Pulmonary Diseases?
Different categories of drugs and diagnostic agents cause a variety of lung diseases. There are more than 150 drugs which are known to cause these diseases. Some of these are listed below along with some of the diseases they can cause:
Chemotherapy agents
- Bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, carmustine can cause lung fibrosis
- Mitomycin C can cause pulmonary toxicity
- Methotrexate can cause nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
Immunomodulating agents
- Sirolimus can cause pulmonary toxicity
- Penicillamine, sulfasalazine can cause a systemic lupus (SLE) -like reaction that can affect the lungs
- Leflunomide can cause interstitial lung disease
Antibiotics
- Nitrofurantoin can cause lung fibrosis
Cardiovascular medications
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are associated with cough
- Amiodarone can cause lung fibrosis
- Beta-blockers can worsen asthma
- Bleeding into the lungs caused by warfarin and fibrinolytic drugs
Anticonvulsants
- Phenytoin can cause eosinophilic pneumonia
Painkillers
- Salicylates like aspirin and non-steroidal painkillers can cause bronchospasm or asthma
Others
- Amphetamine and fenfluramine can cause pulmonary hypertension (fenfluramine is banned in several countries)
- Bromocriptine can cause pulmonary edema and lung fibrosis
What are the Symptoms of Drug-induced Pulmonary diseases?
Symptoms that may be associated with drug-induced lung diseases may include the following:
- Cough
- Blood in the sputum
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Fever
- Chest pain

What Diagnostics Tests are Recommended to Detect Drug-induced Pulmonary Diseases?
It has always been a challenge for pulmonologists to diagnose drug-induced pulmonary disease. The medications can cause reactions in varied forms, which makes it difficult for pulmonologists to identify the drug or its reaction.
Patients with drug-induced lung diseases will give a history of drug intake before the reaction. Sometimes, the doctor will have to specifically ask for such a history. Tests that could detect changes in the lungs include the following:
- Imaging tests like chest x-ray and chest CT scan
- Lung function tests
- Bronchoscopy
- Blood tests to rule out SLE-like reactions as a cause of the lung disease
- Lung Biopsy, in rare cases
How are Drug-induced Pulmonary Diseases Treated?
- If possible, the physician must identify the drug which has induced the lung reaction and discontinue its use immediately.
- At times, the use of corticosteroid helps in reducing the inflammation in the pulmonary diseases.
- In cases of persistent bronchospasm, inhaled beta-2 agonists like salbutamol could help.
- The patient must wear a medical alert bracelet to indicate to others the possibility of a drug reaction occurring if the particular drug is administered, especially in an emergency situation.