- An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6028052/)
- Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Cotransporter - (https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/sodium-glucose- cotransporter-2-sglt2-inhibitors)
- Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors - (https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/sodium-glucose-cotransporter-2-sglt2-inhibitors)
- Diabetes facts & figures - (https://idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html#:~:text=The%20IDF%20Diabetes%20Atlas%20Tenth,and%20783%20million%20by%202045.)
- Diabetes facts & figures - (https://idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html#:~:text=The%20IDF%20Diabetes%20Atlas%20Tenth,and%20783%20million%20by %202045.)
- Type 2 diabetes - (https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/type-2-diabetes.html)
- Diabetes Mellitus Treatment - (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128036785001089)
- SGLT2 Inhibitors (Gliflozins) - (https://www.diabetes.co.uk/diabetes-medication/sglt2-inhibitors.html)
- Discovery of Novel N-Glycoside and Non-Glycoside hSGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - (https://www.scirp.org/Slz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=2571297)
- Empagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evidence to date - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26586935/)
- SGLT2 inhibitors: New medicines for addressing unmet needs in type 2 diabetes - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4221776/)
- Efficacy and safety of sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24320621/)
- Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Potential Complication of Treatment With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26078479/)
- Cardiometabolic Effects of a New Class of Antidiabetic Agents - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25754876/)
Introduction
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors provide a beneficial choice of treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus/T2DM). It can be used as an alternative for those who are reluctant to start on injectable insulin and have cardiovascular risks. However, further research is warranted to verify their long-term outcomes(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source).
What are SGLT2 (Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) Inhibitors?
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a newer class of oral anti-hyperglycemic agents, FDA-approved for the treatment of diabetes mellitus(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source). They are generally prescribed for treatment along with diet and exercise(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Cotransporter
Go to source).
Also called gliflozins or flozins, the other classes of SGLT2 inhibitors are canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin — available both as single-ingredient products and in combination(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Cotransporter
Go to source).
Rising Global Burden of Diabetes
The global prevalence of diabetes has been rising across the world with nearly 537 million adults (20-79 years old) living with diabetes in 2021. The figures are expected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045 as per IDF Diabetes Atlas Tenth edition 2021(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diabetes facts & figures
Go to source).
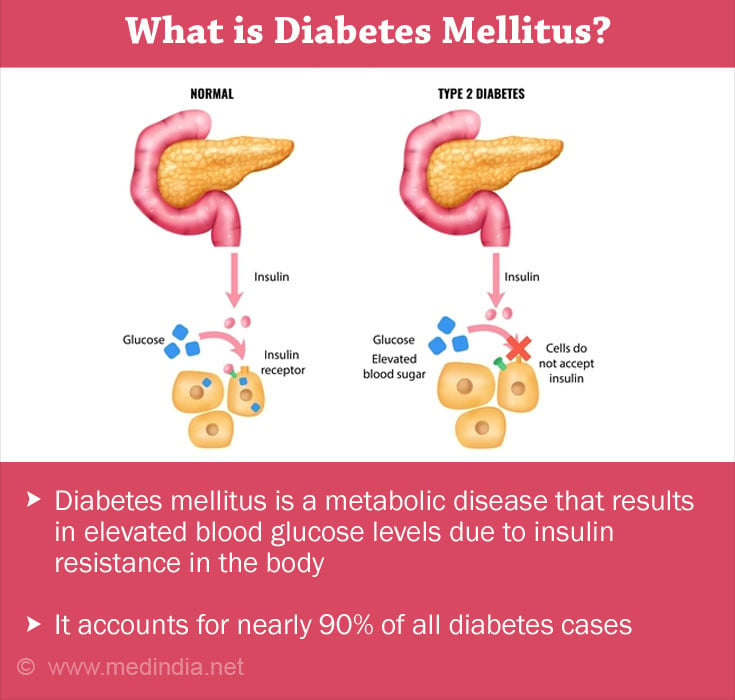
Amongst this, type 2 diabetes accounts for nearly 90% of all diabetes cases, wherein, the body forms insulin resistance — failure to respond to insulin(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Type 2 diabetes
Go to source). It is henceforth crucial to restoring the impaired glucose metabolism in T2DM with a varied approach along with lifestyle modification.
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Diabetes Treatment
SGLT2 inhibitors have been approved for T2DM treatment since 2013and generally taken once a day with or without food(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
SGLT2 Inhibitors (Gliflozins)
Go to source).
The discovery of SGLT2 inhibitors started with the already existing knowledge of 'dihydrochalcone phlorizin' - a natural product that is found in a number of fruit trees. This product has been used for physiology research for over 150 years. The main action of the molecule is to excrete glucose in the urine (renal glycosuria) and also block intestinal glucose absorption through inhibition of the sodium-glucose symporters located in the proximal renal tubule and mucosa of the small intestine(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Discovery of Novel N-Glycoside and Non-Glycoside hSGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source).
Overall SGLT2 inhibitors help in improving carbohydrate metabolism among diabetics thereby becoming an ideal target in the management of T2DM(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Empagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evidence to date
Go to source).
Apart from targeting the increased glucose levels in the blood, SGLT2 inhibitors have other important benefits in diabetics - such as weight, better blood pressure control and hence the heart health(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source). However, the similar efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors has not been elucidated among type 1 diabetics(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Cotransporter
Go to source).
How do SGLT2 Inhibitors Work?
Kidneys contribute significantly to glucose homeostasis as they facilitate glucose uptake (from blood), reabsorption, and gluconeogenesis (synthesis of new glucose molecules from non-carbohydrate sources)(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diabetes Mellitus Treatment
Go to source).
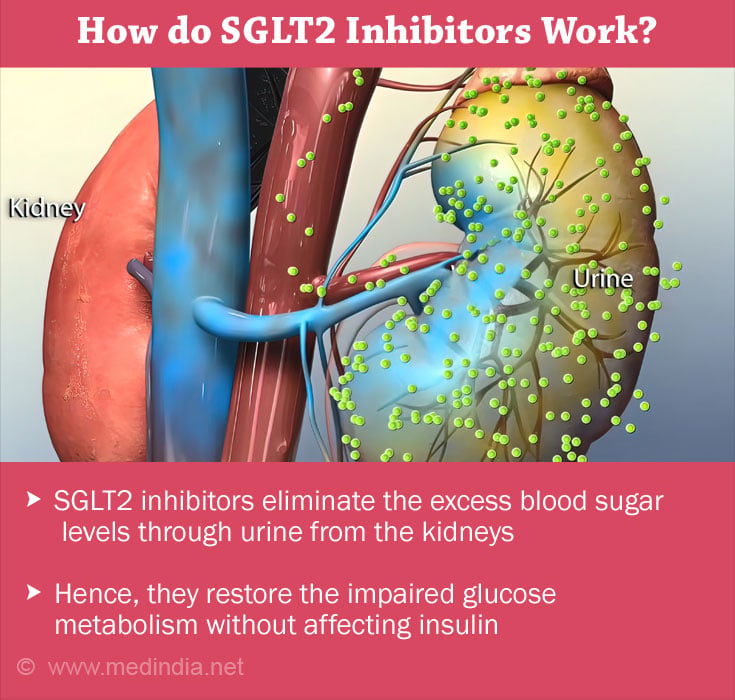
SGLT2 are proteins that are expressed in the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidneys and are responsible for over 90% of glucose reabsorption from the kidneys(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diabetes Mellitus Treatment
Go to source). The SGLT2 inhibitors work by lowering the blood sugar levels via their excretion from the kidneys and preventing their reabsorption in the kidneys(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors Cotransporter
Go to source).
SGLT2 inhibitor is also shown to decrease the renal glucose threshold by 55% (renal glucose threshold is generally increased in T2DM; normal — 180 mg/dL)(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
SGLT2 Inhibitors (Gliflozins)
Go to source, 9✔ ✔Trusted Source
SGLT2 inhibitors: New medicines for addressing unmet needs in type 2 diabetes
Go to source). As SGLT proteins function independently of insulin, they aid in the reduction of excess blood glucose levels via urine without altering the insulin release(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source).
What are the Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors
- SGLT2 inhibitors are found tohave similar bioequivalence when compared to other oral anti-hyperglycemic drugs with added metabolic benefits(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
An Update on SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Go to source).

- Aid in weight loss — key approach to diabetes management
- Reducethe increased blood pressure among hypertensive patients
- Reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE)
What are the Side Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Genital infections were found to be the most common adverse side effect of SGLT2 inhibitors(10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Efficacy and safety of sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Go to source). - Other side effects include mycotic infections in the genital area, and urinary tract infections(11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Potential Complication of Treatment With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition
Go to source). - Volume depletion in the body can lead to increased thirstand orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure that occurs on standing after sitting or lying down) are other side effects of these drugs as they induce osmotic diuresis (increased urination) in diabetic patients(12✔ ✔Trusted Source
Cardiometabolic Effects of a New Class of Antidiabetic Agents
Go to source).
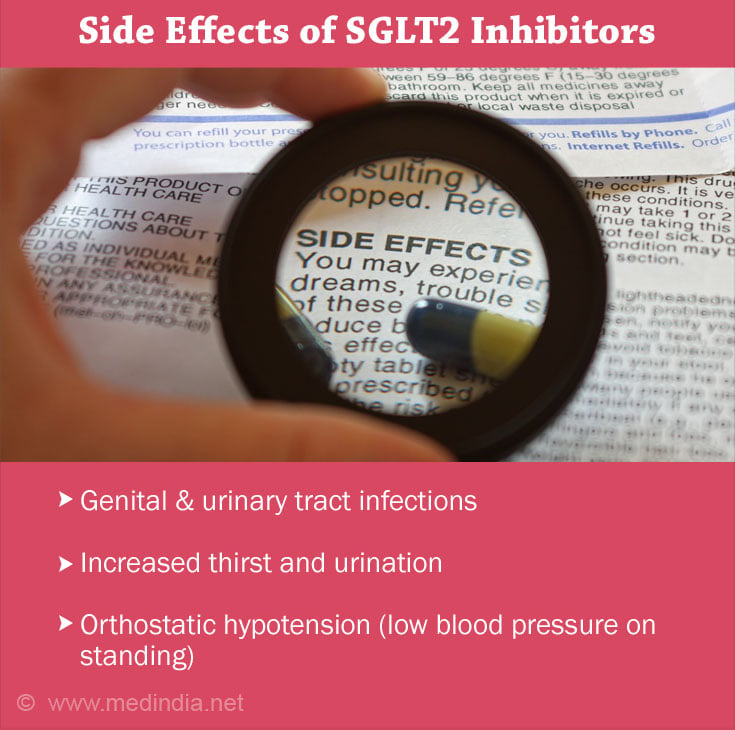
SGLT2 inhibitors may induce other possible side effects apart from those mentioned above. It is important to consult your physician immediately if you notice any unusual complaints when taking the drug.
With significant developments in the management of T2DM over the past year, it is important to weigh both the safety and risk of these drugs before prescribing them to the patients.






