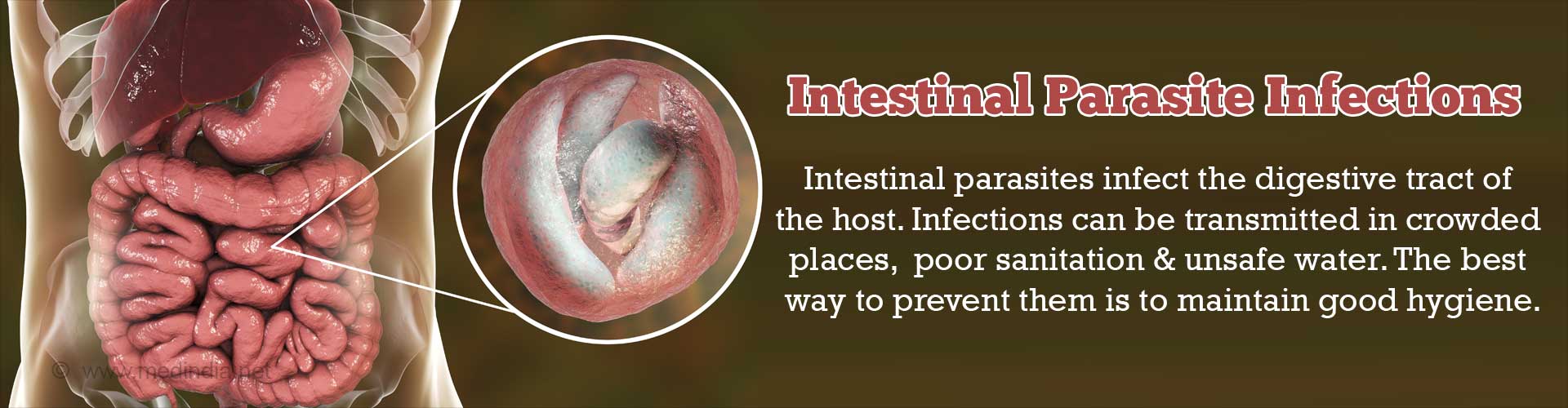
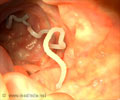
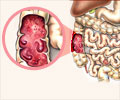
Indian J Med Microbiol
Diagnostic performance of mini parasep® solvent-free foecal parasite concentrator for the diagnosis of intestinal parasitic infections.
Mewara A, Khurana S, Gupta S, Munda VS, Singh S, Sehgal R
Various stool concentration techniques have been used to increase the microscopic detection of parasites. We assessed the enclosed, single-vial, Mini ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
PLoS ONE
An ELISA based on soluble egg antigens for the serodiagnosis of animal schistosomiasis turkestanica.
Ji R, Shen Y, Shi B, Li H, Tang W, Xia C, Lu K, Lamu D, Hong Y, Sun X, Liu J, Zhang L, Zhu C
The existing diagnostic techniques for detecting schistosomiasis turkestanica, such as aetiological assays, identify infection by parasitic worms via ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
Parasite Epidemiol Control
Prevalence and associated risk factors of intestinal helminthic infections in children from Lorestan province, Western Iran.
Mahmoudvand H, Badparva E, Khalaf AK, Niazi M, Khatami M, Nazer MR
Intestinal helminthic infections are among the most important global socioeconomic and health problems. This study aimed to estimate the frequency of ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
BMC Public Health
Epidemiology of intestinal parasitic infections in preschool and school-aged Ethiopian children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Chelkeba L, Mekonnen Z, Alemu Y, Emana D
Numerous studies have been carried out on assessing the prevalence of intestinal parasites infections (IPIs) amongpreschool and school-age children in ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
Vet. Parasitol.
Set up of an in vitro model to study early host-parasite interactions between newly excysted juveniles of Fasciola hepatica and host intestinal cells using a quantitative proteomics approach.
González-Miguel J, Becerro-Recio D, Sotillo J, Simón F, Siles-Lucas M
Fasciola hepatica is the causative agent of fasciolosis, a parasitic zoonosis of global distribution causing significant economic losses in animal pro ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
Indian J Med Microbiol
Diagnostic performance of mini parasep® solvent-free foecal parasite concentrator for the diagnosis of intestinal parasitic infections.
Mewara A, Khurana S, Gupta S, Munda VS, Singh S, Sehgal R
Various stool concentration techniques have been used to increase the microscopic detection of parasites. We assessed the enclosed, single-vial, Mini ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
PLoS ONE
An ELISA based on soluble egg antigens for the serodiagnosis of animal schistosomiasis turkestanica.
Ji R, Shen Y, Shi B, Li H, Tang W, Xia C, Lu K, Lamu D, Hong Y, Sun X, Liu J, Zhang L, Zhu C
The existing diagnostic techniques for detecting schistosomiasis turkestanica, such as aetiological assays, identify infection by parasitic worms via ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
Parasite Epidemiol Control
Prevalence and associated risk factors of intestinal helminthic infections in children from Lorestan province, Western Iran.
Mahmoudvand H, Badparva E, Khalaf AK, Niazi M, Khatami M, Nazer MR
Intestinal helminthic infections are among the most important global socioeconomic and health problems. This study aimed to estimate the frequency of ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
BMC Public Health
Epidemiology of intestinal parasitic infections in preschool and school-aged Ethiopian children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Chelkeba L, Mekonnen Z, Alemu Y, Emana D
Numerous studies have been carried out on assessing the prevalence of intestinal parasites infections (IPIs) amongpreschool and school-age children in ...
Read More
Source: PubMed
Vet. Parasitol.
Set up of an in vitro model to study early host-parasite interactions between newly excysted juveniles of Fasciola hepatica and host intestinal cells using a quantitative proteomics approach.
González-Miguel J, Becerro-Recio D, Sotillo J, Simón F, Siles-Lucas M
Fasciola hepatica is the causative agent of fasciolosis, a parasitic zoonosis of global distribution causing significant economic losses in animal pro ...
Read More
Source: PubMed