- Nutrition and Hydration Requirements In Children and Adults - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562207/)
- Nutritional Requirements throughout the Life Cycle - (https://nutritionguide.pcrm.org/nutritionguide/view/Nutrition_Guide_for_Clinicians/1342043/all/Nutritional_Requirements_throughout_the_Life_Cycle)
About
Nutrition is critical for health and development at every stage of life. Each age group has specific caloric and nutrient requirements to support growth, development, and overall well-being(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Nutrition and Hydration Requirements In Children and Adults
Go to source).
From childhood growth spurts to the challenges of aging, the right nutrients play a vital role in maintaining physical and mental health. Ensuring a balanced intake of vitamins, minerals, and other key nutrients is the foundation for strong bones, sharp minds, and overall well-being, helping everyone thrive at every age. Without proper nutrition, the body struggles to function optimally, which can lead to deficiencies, weakened immunity, and long-term health complications.
Did You Know?
Nutrient needs change as you age, requiring adjustments in diet for optimal health. #nutritionmatters #healthyliving
Nutrients for All Age Group
Nutritional needs from infancy to senior years, including key data on caloric intake and essential nutrients are(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Nutritional Requirements throughout the Life Cycle
Go to source):
Infants (0-12 Months)
Caloric Needs:
- Infants require approximately 100 kcal/kg/day. For example, a 4-kg infant needs around 400 kcal/day, while a 6-kg infant needs about 490 kcal/day.
- Caloric needs increase during growth spurts.
Nutritional Focus:
Breast Milk or Formula: Essential for the first six months. Provides the necessary nutrients and antibodies.
Introduction of Solids: Begin around six months with iron-rich cereals and pureed fruits and vegetables.
Key Nutrients:
Protein: Supports growth and development.
Iron: Important for cognitive development and preventing anemia.
Calcium and Vitamin D:Crucial for bone development.
Toddlers (1-3 Years)
Caloric Needs: Daily Intake of 1000 to 1400 kcal, depending on activity level.
Nutritional Focus:
Balanced Diet: Incorporate a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy.
Hydration: Offer water regularly, limiting juice to avoid excess sugar.
Key Nutrients:
Calcium and Vitamin D: For strong bones.
Iron: For continued growth and energy.
Protein: Necessary for muscle development.
Fiber: Helps with digestion.
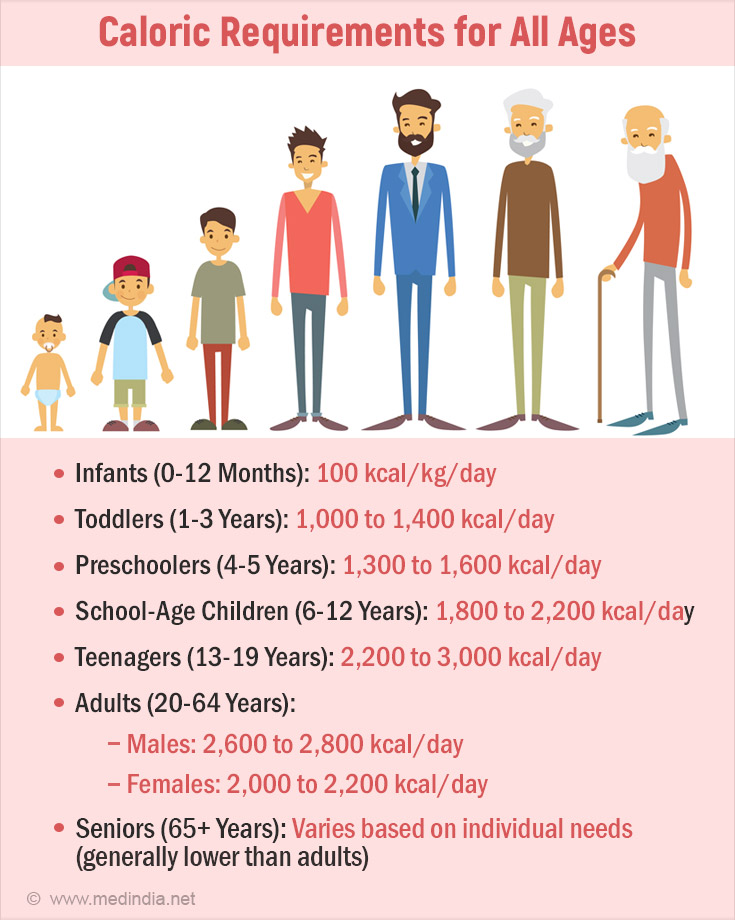
Preschoolers (4-5 Years)
Caloric Needs: Caloric requirements increase with age. For example, children 4-5 years old need about 1300 to 1600 kcal/day.
Nutritional Focus:
Variety and Balance: Encourage diverse foods and healthy eating habits.
Involvement: Include children in meal planning to foster healthy habits.
Key Nutrients:
Vitamins A and C: Support immune function and vision.
Iron and Zinc: Important for cognitive development and immune health.
Complex Carbohydrates: Provide energy and sustain blood sugar levels.
School-Age Children (6-12 Years)
Caloric Needs: 1800 to 2200 kcal/day, depending on age, sex, and activity level.
Nutritional Focus:
Balanced Diet: Ensure a mix of proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy.
Energy Needs: Increase during periods of growth and physical activity.
Key Nutrients:
Calcium and Vitamin D: For bone health.
B Vitamins: Aid in energy metabolism and brain function.
Iron: Prevents fatigue and supports growth.
Teenagers (13-19 Years)
Caloric Needs: 2200 to 3000 kcal/day, depending on sex and activity level.
Nutritional Focus:
Growth Spurts: Increased caloric and nutrient needs to support rapid growth and hormonal changes.
Balanced Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Key Nutrients:
Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for bone density during growth spurts.
Iron: Especially important for menstruating females.
Protein: Supports muscle growth and overall development.
Adults (20-64 Years)
Caloric Needs: 2600-2800 kcal/day for males and 2000-2200 kcal/day for females, varying with activity level and physical condition.
Nutritional Focus:
- Balance caloric intake with physical activity to maintain a healthy weight.
- Focus on preventing chronic diseases through a balanced diet.
Key Nutrients:
Fiber: Aids in digestion and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Antioxidants: Protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important for maintaining bone health.
Seniors (65+ Years)
Caloric Needs: Caloric needs decrease due to reduced metabolic rate and physical activity. Specific caloric needs vary by individual.
Nutritional Focus:
Nutrient Density: Prioritize nutrient-rich foods due to lower caloric needs.
Hydration: Ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
Key Nutrients:
Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential to prevent osteoporosis and maintain bone health.
Vitamin B12: Recommended from supplements or fortified foods due to decreased absorption with age.
Fiber: Helps with digestion and prevents constipation.
Protein: Important to maintain muscle mass and strength.
General Dietary Recommendations
Carbohydrates:
- Daily Intake: 50-55% of total calories should come from carbohydrates.
- Types: Prefer complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index over simple sugars. Limit simple sugars to 5-10% of total caloric intake.
- Sources: Include legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Proteins:
- Daily Intake: Approximately 20% of total calories should come from protein sources.
- Recommendations: 6 g/kg body weight for adults. Essential amino acids must be included in the diet.
- Sources: Include meat, eggs, and legumes. Plant-based proteins can reduce the risk of certain diseases.
Fats:
- Daily Intake: 25-30% of total calories should come from fats. Saturated fats should be limited to less than 10% of total calories.
- Types: Include essential fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6. Limit cholesterol intake to less than 300 mg/day.
- Sources: Opt for unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and avocados.
Dietary Fiber:
- Daily Intake: 38 g/day for men and 25 g/day for women aged 19-50 years. For children, the goal is age+5 grams.
- Benefits: Improves digestive health, reduces risk of cardiovascular disease, and helps with cholesterol levels.
Minerals and Trace Elements:
- Calcium: 1000 mg/day for adults.
- Iron: 18 mg/day for women and 8 mg/day for men.
- Other Trace Elements: Copper, zinc, and selenium are also important. Limit salt intake to fewer than 6 grams per day.
Vitamins:
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision and immune function (RDA: 700-900 μg/day).
- Vitamin C: Important for collagen synthesis and immune function (RDA: 90 mg/day).
- Vitamin D: Helps with calcium absorption (RDA: 600 IU/day).
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant (RDA: 33 IU/day).
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting (RDA: 120 μg/day).
Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining health and preventing disease across all stages of life. Understanding and meeting these needs can help ensure overall well-being and quality of life.