Blood Donor Screening
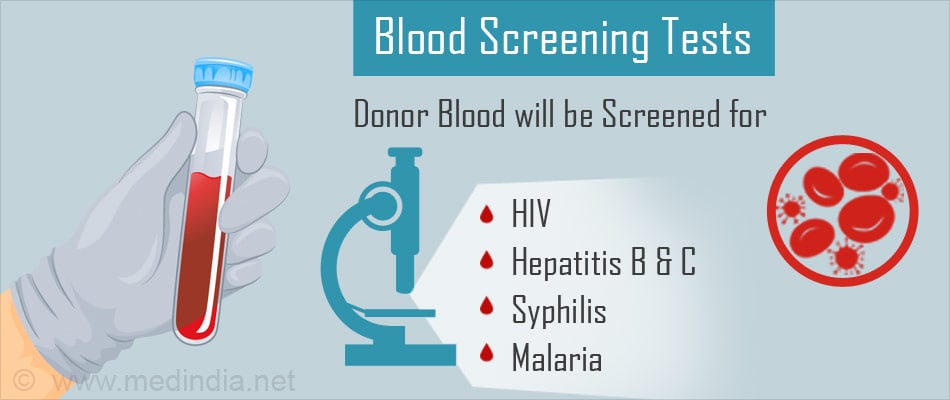
The primary tests recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) are four in number. They are -
- Surface Antigen (HbsAg) for Hepatitis B
- Antibody to Hepatitis C
- HIV antibodies (for subtypes 1 and 2)

- Serology test for Syphilis
In 2006, a WHO survey revealed that in 56 of 124 countries where the survey was carried out these basic tests were not done. Besides these core tests recommended by the WHO a variety of other tests are also carried out depending on the local need. Some of these include tests for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (v CJD), West Nile Virus, cytomegalovirus and the HIV nucleic acid test (p24 antigen) that may help to detect a recently infected donor. The cytomegalovirus has negligible effect on a healthy recipient but may prove to be harmful on immuno-compromised patients, infants or pregnant women.
It is also mandatry that blood donors should be free of fever a fortnight prior to donating blood. They should also be free of diseases such as Malaria and Filaria.
Cross matching is also carried out before transfusions. Here the plasma of the recipient is tested for antibodies against the antigens on the red blood cells of the donor blood. If agglutination takes place, the blood is not compatible and transfusion cannot take place. If there is no agglutination the blood can be transfused.
In case of emergency, however, ABO and Rh compatible blood is used for transfusion, which may be non cross - matched.