- Cardiopulmonary bypass - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/cardiopulmonary_bypass)
- Stoney WS. Evolution of Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Circulation. 2009;119:2844-2853
- Passaroni AC. Cardiopulmonary bypass: development of John Gibbon''s heart-lung machine. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg 2015;30(2):235-45
- Machin D, Alsager G. Principles of cardiopulmonary bypass. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain 2006; Volume 6 Number 5
What is Cardiopulmonary Bypass?
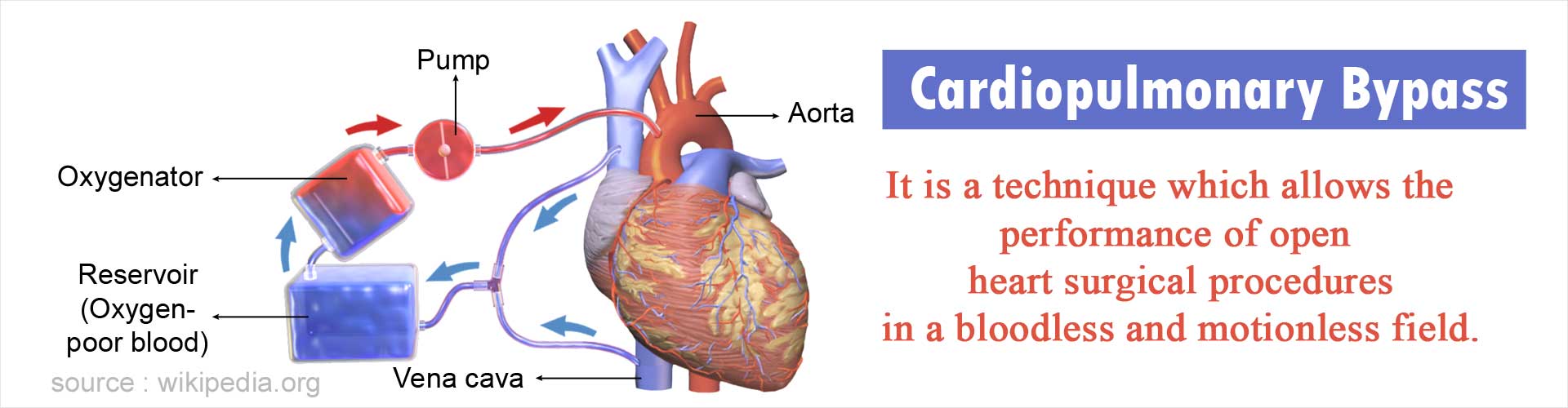
The cardiopulmonary bypass machine is a device which is used in open heart surgeries to support the body when the heart is stopped. It functions like both the heart and the lung; it oxygenates the blood and pumps the blood to the body during surgeries on the heart. It is also referred to as the heart-lung machine or the pump.
The device was used successfully for the first time during an open heart procedure by Dr. John Gibbon in 1953.
The device receives the deoxygenated blood from the body through cannulations and tubes connected to veins, oxygenates it and pumps back the oxygenated blood to the body. The cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has 2 main components, the pump and the oxygenator. The components are interlinked through silicone or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubes.
1. Pumps: The blood is delivered from the CPB machine to the body through pumps.
- Roller pumps: In roller pumps, the PVC tubing is compressed by rollers. Rolling helps to propel the blood through the tubes.
- Centrifugal pumps: In centrifugal pumps, the blood flow depends on the centrifugal force. It works better than roller pumps.
2. Oxygenator: The oxygenator oxygenates the blood received from the body as well as removes some carbon dioxide. There are various types of oxygenators that have evolved. Disc and bubble oxygenators that were used earlier have fallen out in favor of the safer membrane oxygenators.
- Disc oxygenator: Here the blood is exposed to the oxygen-rich atmosphere.
- Bubble oxygenator: The blood is oxygenated by bubbling the oxygen into the blood.
- Membrane oxygenator: The oxygenation of blood takes place through a membrane. Bubble oxygenators cause more damage and produce more microbubbles in the blood; microbubbles can lead to air embolism. They have hence been replaced by membrane oxygenators.
3. Cannula: There are many cannulae inserted into arteries and veins to aid in collecting and supplying the blood to the heart.
- Venous cannulation sites are the vena cavae, femoral vein and right atrium.
- Arterial cannulation sites are proximal aorta (distal to cross clamp), femoral artery, axillary artery, distal aorta and apex of the heart.
- The cardioplegia cannula delivers cardioplegia solution to stop the beating of the heart during the heart surgery. It is inserted at the proximal aorta (distal to cross clamp), coronary sinus or coronary ostia. Cardioplegia is necessary to protect the myocardium, the muscle of the heart.
When is Cardiopulmonary Bypass Used?
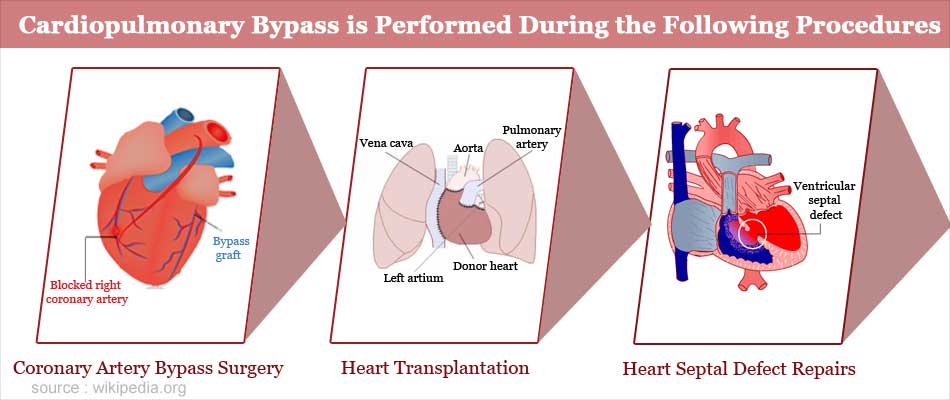
The following are a few procedures during which CPB is used.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery, which is a surgical procedure for patients with severe coronary heart disease that causes a block in the blood supply to the muscle of the heart
- Heart valve replacement or repair. The heart valves include the mitral valve, tricuspid valve, aortic valve and the pulmonary valve. The heart valves permit the passage of blood in a single direction
- Heart transplantation
- Lung transplantation
- Heart-lung transplantation
- Heart septal defect repairs like atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect and atrioventricular septal defect. The septa separate the chambers of the heart
- Large aneurysm repairs, for example, aortic aneurysm. An aneurysm is a dilated blood vessel with thin walls that can burst
- Pulmonary thrombectomy, which is a procedure that involves the removal of a thrombus from a pulmonary blood vessel
- Congenital heart defects like Tetralogy of Fallot and Transposition of great vessels
Cardiopulmonary Bypass and Hypothermia:
Cardiopulmonary bypass device can also be used to maintain hypothermia or low body temperature during cardiac surgeries. Hypothermia decreases the oxygen consumption by the heart, increases the protection and also the tolerance of vital organs like the brain for ischemia (reduced oxygen supply). The CPB can be used to bring the temperature to normal levels in patients with hypothermia.
What are the Risks & Complications of Cardiopulmonary Bypass?
The risks and complications associated with cardiopulmonary bypass procedure include the following:
- Hemolysis or breakdown of red blood cells
- Capillary leak syndrome, resulting in a leakage of fluid from the fine blood vessels called the capillaries
- Post-perfusion syndrome, which causes neurological symptoms like problems with attention, concentration and memory
- Air embolism, where air enters the blood stream and can cause a block in the circulation
- Formation of blood clots that can obstruct the circulation
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Systemic inflammatory response that can cause organ failure
- Bleeding
The consequences of the CPB can be reduced by the following means -
Pharmacological agents to reduce the effects on the inflammatory and fibrinolytic system include aprotinin, anti-fibrinolytic agents, corticosteroids, anti-oxidants, ACE-inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies and phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
Heparin is used to prevent clotting of blood, and protamine sulfate is used to reverse the anticoagulation.
Cell salvage devices may be used in order to remove the activated blood components and emboli from the blood suctioned at cardiotomy.