What is Carotid Endarterectomy?
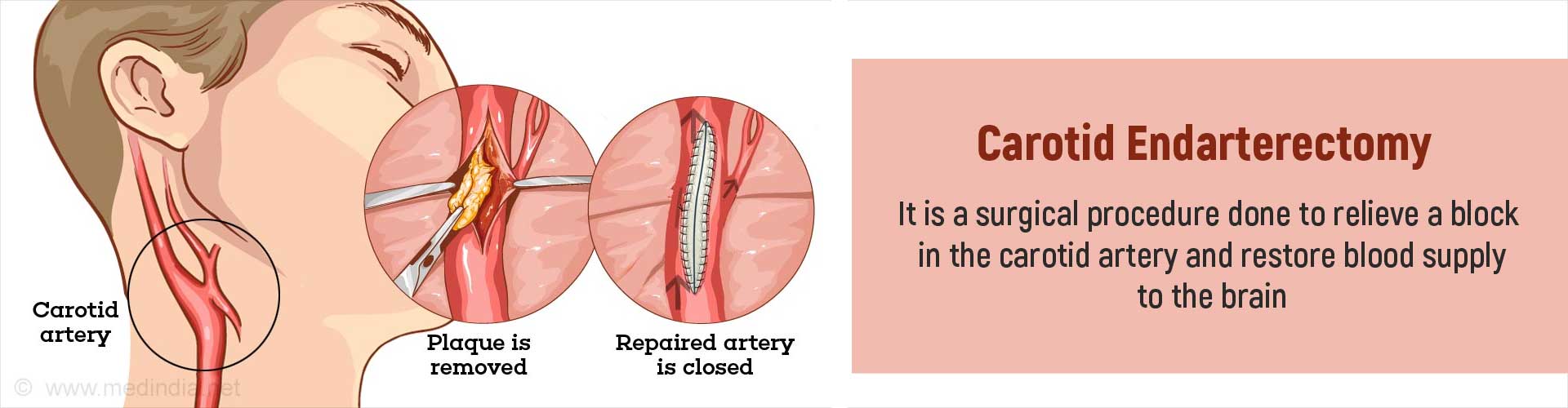
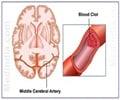
Carotid endarterectomy is a vascular surgical procedure where a block in the common or internal carotid artery is relieved to restore blood supply to the brain.
The common carotid arteries are important arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the head and neck region. The right common carotid artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk, while the left common carotid artery arises from the arch of the aorta. Each common carotid artery divides into external and internal carotid arteries. While the external carotid branch supplies blood to the face, scalp and neck, the internal carotid supplies oxygenated blood to the brain.
An obstruction in a carotid artery occurs in a similar way as that in other arteries of the body. Excess cholesterol deposits under the artery lead to the formation of an accumulation called plaque, and a condition called atherosclerosis. As the plaque grows in size, its surface can rupture, resulting in the formation of a clot, which can obstruct blood flow through the artery. The clot can get dislodged and travel in the bloodstream blocking a small artery along the flow of the blood. Since the brain requires a continuous supply of oxygen, if a complete block is not immediately relieved, the part of the brain will die resulting in a stroke.
During carotid endarterectomy, the surgeon will open up the carotid artery, remove the block, and then close it.
Which Patients Need a Carotid Endarterectomy / What are the Indications of Carotid Endarterectomy?
Carotid endarterectomy is done to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke, especially in those who may have had transient ischemic attacks (TIA) (symptoms of a temporary stroke that do not last for more than 24 hours) in the past. Patients who have a block of 50% or more in their carotid artery are advised carotid endarterectomy. It is particularly useful in individuals with a block of between 70 to 90%. Since the procedure itself carries a risk of stroke, the procedure should be carried out only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
What are the Tests Recommended Before Carotid Endarterectomy?
If you have experienced a TIA or any other symptom that suggests reduced blood flow to the brain, your doctor will carry out a careful neurological examination. With the stethoscope placed in the carotid artery, your doctor may be able to hear a whistling sound called a bruit which indicates a narrowed area through which the blood flows. Other confirmatory tests that the doctor may recommend to make a diagnosis include -
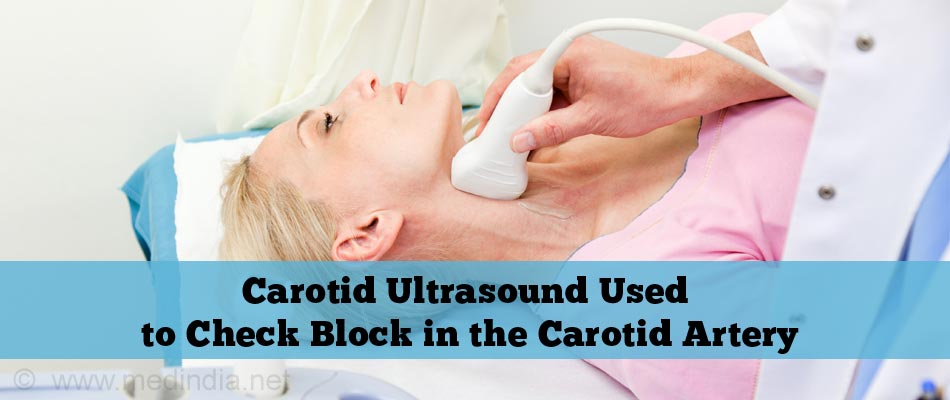
- Carotid ultrasound: A carotid ultrasound is used to check for a block in the carotid artery. A gel is applied on the neck, the ultrasound probe is placed on the carotid artery and the images are observed on a screen. The procedure is completely safe and painless and gets done in a few minutes. It does not expose you to any radiation. The Doppler ultrasound, a special technique that can detect blood flow through the carotid artery, is often carried out along with the standard carotid ultrasound. You do not need any preparation before the procedure, though you may want to wear an open necked shirt and avoid wearing any jewelry around your neck.
- Carotid angiography: A carotid angiography is done only if the block is not clear on a carotid ultrasound. A dye is injected into a vein and its passage through the carotid arteries is studied using x-rays. The picture may also be obtained with magnetic resonance imaging (magnetic resonance angiography), or a CT scan (CT angiography)
Once it is confirmed that you need to undergo a carotid endarterectomy, you will also have to undergo some routine tests which are required before any elective surgery (which is more planned). These tests include the following:
- Blood tests like hemoglobin levels, blood group, and liver and kidney function tests
- Urine tests
- ECG to study the electrical activity of the heart
- Chest x-ray
In older group of patients, a detailed assessment of the heart maybe required
How is Carotid Endarterectomy Performed?
Type of Anesthesia - Carotid endarterectomy is done under general anesthesia. You will be asleep during the procedure and will not be aware of what is going on. It can also be done under local anesthesia, where an injection is administered in the neck to numb the area. You will also be given a sedative to help you relax during the procedure
Pre-operative Check-up - Routine tests as indicated above are ordered a few days before the surgery. Admission is required a day or two before the surgery. Medications to prevent blood clots may be prescribed before the procedure.
Fasting before surgery - Overnight fasting is required and occasionally intravenous fluids maybe required to keep you well hydrated. Sedation is sometimes required for good overnight sleep before the surgery.
Shift from the ward or room to the waiting area in the operating room - An hour or two before the surgery, you will be shifted to the operating room waiting area on a trolley.
Once the surgical room is ready, you will be shifted to the operating room.
Shift to the Operating room - The ambiance in the operating room can sometimes be very daunting and a small amount of sedation can help overcome your anxiety. From the trolley, you will be shifted on to the operating table.
Anesthesia before surgery - The anesthetist will inject drugs through an intravenous line and make you inhale some gases through a mask that will put you in deep sleep for anesthesia. Once you are in deep sleep, a tube will be inserted into your mouth and windpipe to administer the anesthesia gases to overcome pain and keep you comfortable.
What Happens During the Surgery?
Before the surgery, you will be administered heparin to prevent your blood from clotting and your heart function will be closely monitored. During the surgery, with your head turned to one side, the surgeon will make a small cut in the neck over the common carotid artery and its bifurcation into the internal and external branches. The carotid sheath that surrounds the carotid artery will be opened and the artery exposed taking care not to damage any nearby nerves. The surgeon will make a small cut over the artery and carefully dissect out the block. Following this, the carotid artery will be closed with sutures or through the application of a patch. Once it is confirmed that the bleeding has stopped, the skin incision will be closed with sutures.
Another procedure similar to carotid endarterectomy called carotid angioplasty is also sometimes used to remove blocks from the carotid artery, especially when the endarterectomy procedure may not be considered as safe. In this procedure, a tube with a deflated balloon is introduced into a blood vessel and is guided to the blocked part of the carotid artery, where it is inflated. This process opens up the artery. A stent is usually placed in this part to keep the artery open.
What Happens After the Carotid Endarterectomy Procedure?
Waking up from Anesthesia - Once the surgery is over, if you have received general anesthesia, you will wake up and the tube down the wind pipe will be removed. You will be asked to open your eyes before the tube is removed. You will be sedated and the voice of the anesthetist may be faint. Once the tube is out, you may have cough and sometimes nausea.
There may be a tube going into the stomach called a nasogastric or Ryle’s tube to keep it empty. There will also be an intravenous line. You will remain on oxygen. Once fully awake, you will be shifted on the trolley and taken to the recovery room.
Recovery After Carotid Endarterectomy
Recovery room - In the recovery room, a nurse will monitor your vital parameters such as pulse and blood pressure and observe you for an hour or two before shifting you to the intensive care unit, from where you will be shifted to the ward once you are stable. Your blood pressure will need to be particularly monitored since it fluctuates following the surgery.
Post-operative recovery - You will remain in the hospital for a day or two following the procedure. You may prefer soft foods since the discomfort in the neck may make it difficult to swallow.
Follow-ups - You will have to visit the hospital for follow-ups as recommended by your doctor. You will be prescribed medications like aspirin and anti-cholesterol, anti-hypertensive and anti-diabetes medication to prevent the formation of future plaques.
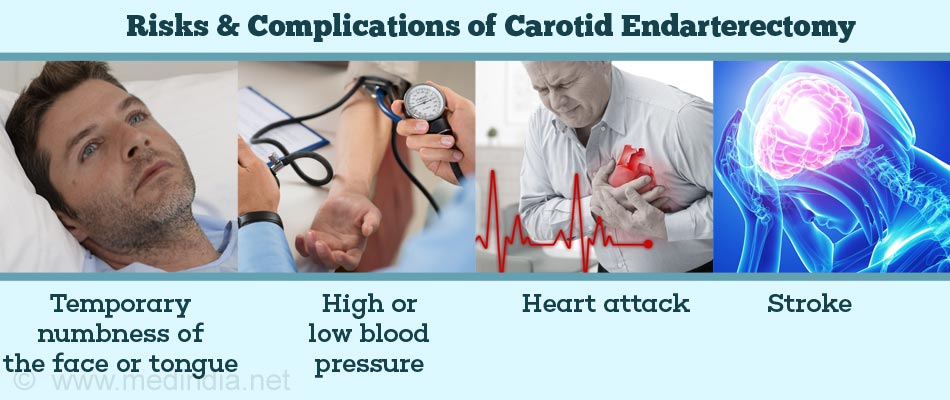
What are the Risks & Complications of Carotid Endarterectomy?
Possible complications of carotid endarterectomy include the following:
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Temporary numbness of the face or tongue
- Bleeding
- Infection
- High or low blood pressure
- Heart attack
- Seizure
- Stroke. However, a successful surgery significantly reduces the risk of stroke due to the block, which justifies performing the surgery
- Restenosis may occur if adequate precautions are not taken to prevent it after the operation