Surgery for Hernia
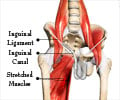
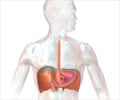
All Hernias usually need to be surgically repaired to prevent complications such as irreducibility and strangulation.
The treatment of every hernia is individualized and it depends on whether it is reducible or irreducible or possibly strangulated.
Treatment of Reducible Hernias
- All reducible hernias should be surgically repaired to avoid the possibility of future intestinal strangulation.
- If pre-existing medical conditions make surgery unsafe, then the doctor may not repair the hernia but will watch it closely. He may recommend an abdominal ‘truss’ or a support belt temporarily for support.
Treatment of Irreducible Hernias
- All acutely irreducible hernias need emergency surgery because of the risk of strangulation.
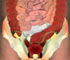
- If during surgery the bowel is found to be gangrenous (dead), due to loss of blood supply then resection of that segment of intestine is performed
Treatment of Strangulated Hernias
- All strangulated hernias need emergency surgery.
- A strangulated or necrotic hernia necessitates bowel resection.
- Extensive resection of the bowel may require temporary colostomy, where a part of the colon is connected to the anterior abdominal wall, leaving the patient with an opening on the abdomen called a stoma.
Types of Surgical Procedures
- Abdominal open repair surgery- done by making small incisions over the herniated area.
- Laparoscopic surgery- is less invasive procedure through keyhole punctures.
The surgery takes about an hour and can be performed on an outpatient basis, which means the patient can go home the same day of the procedure. The surgeon will determine the best method of repair depending on the individual situation.
Depending on the location and size of the hernia the different techniques employed are:
Herniotomy and closure of sac is the treatment of choice for Small Reducible Hernia in children. The surgeon returns the contents of the hernial sac to the abdominal cavity and closes the opening. This procedure is commonly performed laparoscopically as an outpatient procedure.
Another effective surgical procedure is herniorraphy or Hernioplasty, which reinforces the weakened area with sutures, fascia, or a mesh (sheet) made of synthetic material (usually called Prolene mesh) wire. This is the treatment of choice for Large Reducible Hernias.
A Strangulated or necrotic hernia necessitates Bowel Resection. Rarely, an extensive resection may require temporary colostomy. In either case, resection lengthens postoperative recovery and requires an antibiotic, parenteral fluid, and electrolyte replacement.